Start-Up India- 2.0
Relevance
- GS Paper 2 Important aspects of governance, transparency and accountability, e-governance, applications, models, successes, limitations, and potential;
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Tags: #startupIndia #scheme #currentaffairs #upsc.
Support from the government
Several factors and government initiatives have provided critical support and handholding to startups in India. These include:
- Government Schemes:
- National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing Innovations (NIDHI): Launched by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), this program nurtures knowledge-based and technology-driven innovations into successful startups.
- Promoting and Accelerating Young and Aspiring Innovators and Startups (PRAYAS): Provides financial support to startups.
- Enhancing Biotechnology: The Department of Biotechnology, through the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC), supports and nurtures biotechnology firms to foster innovation.
- Defense Sector: Launched by the Department of Defense Production, it aims to achieve self-reliance and promote innovation and technology development in the defense and aerospace sectors by engaging industries, research institutes, academia, and providing grants for R&D.
- Atal Innovation Mission: The mission has set up Atal Incubation Centres (AIC) to incubate startups in various sectors.
- Atal New India Challenge (ANIC): A program to aid startups with technology-based innovations that address sectoral challenges of national importance and societal relevance.
- Role of Forex Flow: Inflows of foreign exchange, especially from leading tech companies like Facebook, Google, and Microsoft, have demonstrated the potential of the Indian market and provided financial support to startups.
- Role of Technology: Startups leverage new-age technologies such as artificial intelligence, internet of things, data analytics, big data, robotics, etc., to bridge market gaps and drive innovation.
These initiatives and factors play a crucial role in supporting and nurturing the growth of startups in India.
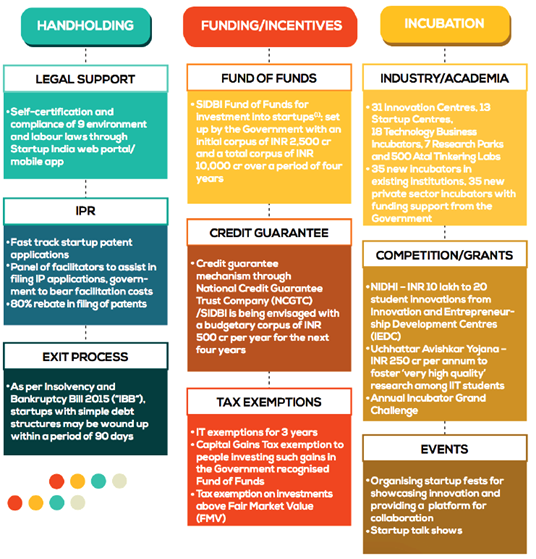
Initiatives under Startup India Schemes
Startup India Action Plan (2016)
- Unveiled on 16th January 2016.
- Comprises 19 action items in categories like simplification and handholding, funding support and incentives, and industry-academia partnership and incubation.
- Laid the foundation for government support, schemes, and incentives to nurture a vibrant startup ecosystem in India.
Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) Scheme
- Government established FFS with a corpus of Rs. 10,000 crore.
- DPIIT monitors the scheme, and SIDBI operates it.
- The total corpus will be provided over the 14th and 15th Finance Commission cycles based on scheme progress and fund availability.
- FFS provides capital for startups at various stages, reducing dependence on foreign capital and encouraging domestic venture capital funds.
Credit Guarantee Scheme for Startups (CGSS)
- Designed to provide credit guarantees for loans to DPIIT-recognized startups.
- Eligible lenders include Scheduled Commercial Banks, Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs), and Venture Debt Funds (VDFs) under SEBI registered Alternative Investment Funds.
- Aims to offer credit guarantees up to specified limits for loans extended by Member Institutions (MIs) to eligible DPIIT-recognized startups.
Regulatory Reforms (Since 2016)
- Over 50 regulatory reforms have been introduced by the Government.
- These reforms focus on enhancing the ease of doing business, simplifying capital raising, and reducing compliance burdens for startups.
Ease of Procurement
- Central Ministries/Departments are directed to relax conditions related to prior turnover and prior experience in public procurement for all DPIIT-recognized startups, provided they meet quality and technical specifications.
- The Government e-Marketplace (GeM) Startup Runway has been created as a dedicated platform for startups to directly sell products and services to the government.
Support for Intellectual Property Protection (SIPP)
- Startups receive expedited examination and disposal of patent applications.
- SIPP allows startups to file patent, design, and trademark applications through registered facilitators, with only statutory fees to be paid.
- Facilitators offer guidance on various intellectual property rights (IPRs) and international protection.
- The government covers facilitators’ fees for all patent, trademark, or design applications.
- Startups receive an 80% rebate on patent filing fees and a 50% rebate on trademark filing fees compared to other companies.
Self-Certification under Labor and Environmental Laws
- Startups are permitted to self-certify their compliance with 9 labor and 3 environmental laws for 3 to 5 years from the date of incorporation.
Income Tax Exemption for 3 Years
- Startups incorporated on or after April 1, 2016, can apply for a 3-year income tax exemption.
- Recognized startups granted an Inter-Ministerial Board Certificate are exempt from income tax for 3 consecutive years within the first 10 years since incorporation.
International Market Access to Indian Startups
- The initiative aims to connect the Indian startup ecosystem with global counterparts through government partnerships, international forums, and global events.
- Startup India has established connections with over 17 countries, offering soft-landing platforms for startups from partner nations and encouraging cross-collaboration.
Faster Exit for Startups
- The government has designated startups as ‘fast track firms,’ allowing them to wind up their operations within 90 days, as opposed to the 180 days required for other companies.
Startup India Hub
- The Startup India Online Hub, launched on June 19, 2017, is an online platform connecting various stakeholders in the entrepreneurial ecosystem, including startups, investors, funds, mentors, academic institutions, incubators, accelerators, corporates, and government bodies.
Exemption from Section 56(2)(viib) of the Income Tax Act (2019)
- DPIIT-recognized startups are eligible for exemption from the provisions of section 56(2)(viib) of the Income Tax Act.
Startup India Showcase
- A platform for showcasing the most promising startups in the country, representing cutting-edge sectors such as Fintech, Enterprise Tech, Social Impact, HealthTech, and EdTech.
- These startups have demonstrated exceptional innovation and have been nurtured and supported by ecosystem stakeholders.
National Startup Advisory Council
- Constituted in January 2020 to advise the government on building a strong ecosystem for innovation and startups, driving economic growth and employment.
- Comprises ex-officio members and non-official members representing various startup ecosystem stakeholders.
Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS)
- Designed to provide essential capital to startups during their early growth stages.
- Aims to support proof of concept, prototype development, product trials, market entry, and commercialization.
National Startup Awards (NSA)
- Recognizes and rewards outstanding startups and ecosystem enablers.
- Focuses on innovative products, scalable enterprises, and their potential to generate employment, create wealth, and demonstrate measurable social impact.
- Finalists receive handholding support across various tracks including Investor Connect, Mentorship, Corporate Connect, Government Connect, International Market Access, Regulatory Support, Startup Champions on Doordarshan, and Startup India Showcase.
States’ Startup Ranking Framework (SRF)
- An initiative to leverage competitive federalism for creating a thriving startup ecosystem.
- Aims to help states identify and adopt best practices, highlight policy interventions promoting startups, and foster competitiveness among states.
Startup Champions on Doordarshan
- A one-hour weekly program showcasing the stories of award-winning and nationally recognized startups.
- Telecasted in both Hindi and English on Doordarshan network channels.
Startup India Innovation Week
- An annual event organized around National Startup Day, 16th January.
- Brings together startups, entrepreneurs, investors, incubators, funding entities, policymakers, and other stakeholders to celebrate entrepreneurship and promote innovation.
Startup India Investor Connect Portal
- Developed under the Startup India Initiative in collaboration with SIDBI.
- Serves as an intermediary platform connecting startups and investors to mobilize capital.
- Aims to enable early-stage startups from any part of the country to showcase themselves to leading investors and venture capital funds.
- Over 1,900 startups and 82 Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs) are currently registered on the platform.
National Mentorship Portal (MAARG)
- Developed to provide accessible mentorship for startups across the country.
- Offers advisory, assistance, resilience, and growth support to startups.
ASCEND (Accelerating Startup Caliber & Entrepreneurial Drive)
- Conducts sensitization workshops on startups and entrepreneurship for all eight North Eastern States.
- Aims to enhance knowledge on entrepreneurship and create a robust startup ecosystem in these states.
Startup20 Engagement Group
- Established under India’s G20 Presidency to promote harmonization and collaboration among global economies.
- Acts as a voice for the global startup ecosystem, bringing together stakeholders from varied backgrounds.
- Aims to support startups by fostering synergies between startups, corporates, investors, innovation agencies, and other ecosystem stakeholders at an international level to create global synergies.
Mains Question
Analyze the key policy measures and challenges in sustaining a dynamic startup ecosystem.