SpaceX Starship Test: Comprehensive Update on Successful Ninth Rocket Launch
SpaceX Starship Test: Comprehensive Update on Successful Ninth Rocket Launch
Here’s a comprehensive update on SpaceX’s successful ninth test flight (Flight 9) of the Starship Super Heavy rocket, marking another milestone in space exploration and bringing us closer to future moon landings and Mars missions. This latest achievement showcases the progress made by Starship Elon Musk and his team in advancing rocket performance and pushing the boundaries of space technology. From the days when pioneers like Robert Goddard first launched the first rocket, we’ve come a long way in our quest to explore the cosmos.
Key Highlights of the Ninth SpaceX Starship Test Flight (May 28, 2025 IST)
Launch Site & Timing
- Location: SpaceX’s Starbase facility in Texas, near Boca Chica Beach, South Texas.
- Time: Launched at 5:00 am IST (May 28, 2025) / 6:30 pm CDT (May 27, 2025).
- Objective: Validate in-flight systems, demonstrate controlled booster return, and push further into reusability testing for this future space shuttle.
Mission Milestones Achieved
- Successful Liftoff: Clean rocket launch and stage separation for the SpaceX Starship rocket launch, demonstrating improved rocket performance compared to previous flights. The launch team carefully monitored for any signs of potential starship explosion, a risk that was successfully mitigated.
- Controlled Booster Splashdown:
- The Super Heavy booster executed a successful and controlled descent into the Gulf of Mexico.
- SpaceX did not attempt the “chopstick” catch with robotic arms for this flight, instead opting for a safety-first water splashdown.
Starship Upper Stage:
- Reached suborbital trajectory, flying farthest yet among the recent tests.
- Conducted multiple engine burns and maneuvering trials to collect in-flight data.
- Flight images captured during this phase provided valuable insights into the spacecraft’s performance.
Key Reusability Tests:
- Several thermal protection and heat shield tiles tests.
- Navigation and attitude control assessments for future orbital missions and spacecraft reentry.
- Despite the success, SpaceX Elon Musk and his team remained vigilant for any potential flight anomalies or propellant leaks that could lead to spacecraft breakup, a risk that was successfully avoided during this mission.
Technological Significance
- Reusability Advancements: Every test improves SpaceX’s confidence in recovering and reusing both stages of the reusable rocket, reducing long-term launch costs. This builds upon the success of the Falcon rocket series.
- Moon & Mars Readiness: Crucial step toward making NASA Artemis missions and SpaceX’s Mars colonization vision a reality, advancing space exploration efforts. The Starship program aims to surpass the achievements of the Apollo mission in terms of lunar exploration capabilities.
- Validation of Upgrades: Enhanced Raptor engines, reinforced heat shield tiles, and stage control systems were tested under real conditions during this spacecraft testing. These improvements are essential for the rocket capsule’s performance in various space environments and preventing spacecraft breakup during critical phases.
🌖 Why This SpaceX Starship Test Matters
Unlike past flights where both stages were lost due to malfunctions or reentry issues, this flight marks major progress in controlled recovery and flight duration. It shows that Starship is nearing operational capability for orbital missions and eventual crewed flights. This is essential for NASA’s Artemis III, which will use a version of Starship as a lunar lander for future moon landing missions.
The success of Flight 9 demonstrates significant advancements since the first rocket launched by SpaceX, showcasing the rapid progress in rocket technology and reusability. It’s a far cry from the early days when pioneers like Robert Goddard first asked “who launched the first rocket?” and paved the way for modern space exploration.
🔭 What’s Next for Starship
- Full orbital flight test with Starship reentry over the Indian Ocean.
- Upcoming tests may reintroduce launch tower booster recovery via robotic arms.
- Integration with fuel depot technologies, necessary for long-distance interplanetary missions.
- Increasing launch cadence to accelerate development and testing phases.
- Potential collaboration with the Federal Aviation Administration to streamline future launch approvals.
- Exploring synergies between Starship and Starlink satellites for advanced payload deployment capabilities.
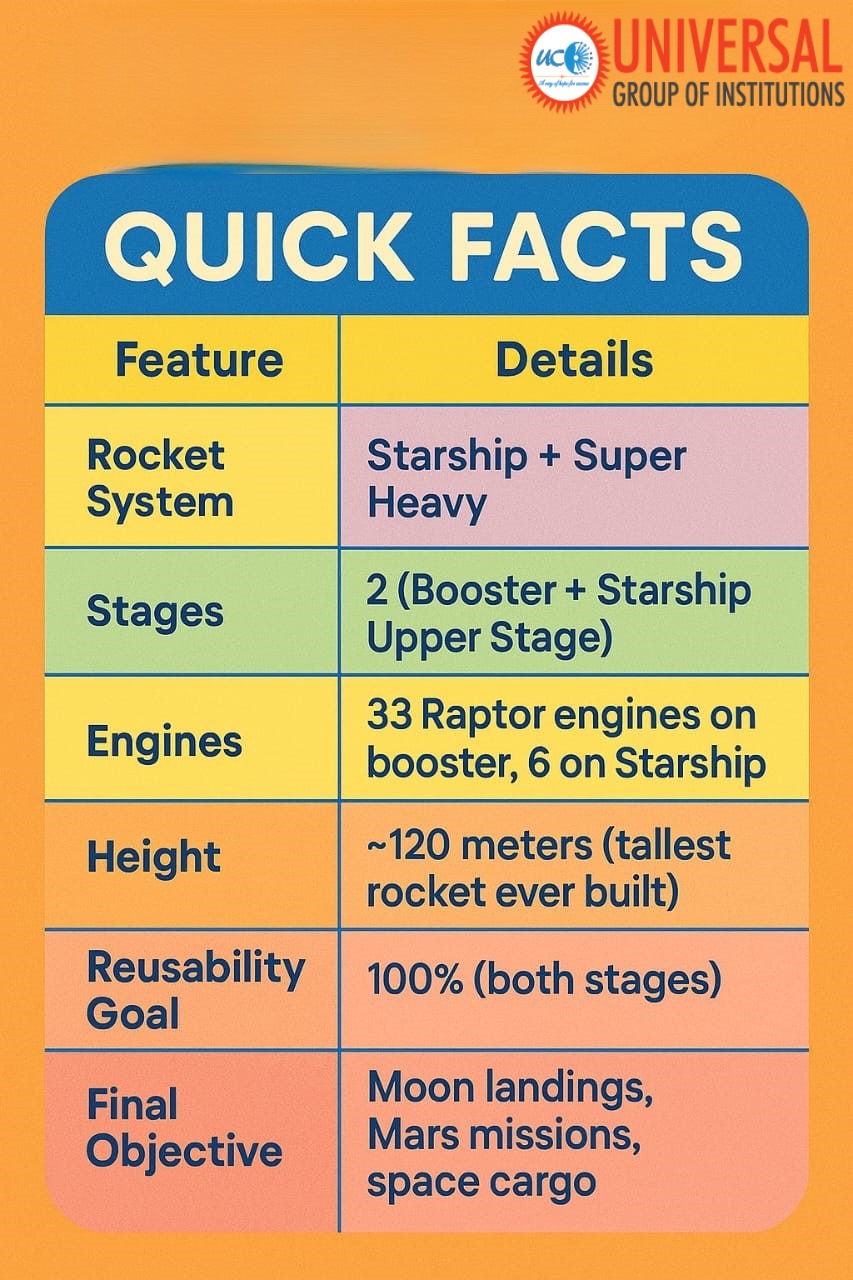
📌 Quick Facts
- Feature
- Details
- Rocket System
- Starship + Super Heavy
- Stages
- 2 (Booster + Starship Upper Stage)
- Engines
- 33 Raptor engines on booster, 6 on Starship
- Starship Height
- ~120 meters (tallest rocket ever built)
- Reusability Goal
- 100% (both stages)
- Final Objective
- Moon landings, Mars missions, space cargo
This successful SpaceX launch today, overseen by Starship Elon Musk, represents a significant leap forward in the development of the Starship program. As SpaceX continues to refine this reusable rocket system, it’s clear that the future of space exploration is becoming increasingly accessible and sustainable. The company’s ability to overcome challenges such as propellant leaks and flight anomalies demonstrates the resilience and innovation driving the space industry forward. With each successful test, we move further from the days of asking “who launched the first rocket?” to planning interplanetary missions, all while carefully managing risks like potential starship explosions and ensuring the integrity of spacecraft during critical phases of flight.