Space Startups
News
- In the final nine months of the current fiscal year, space sector startups in the nation have drawn over 1,000 crore rupees in private investment, according to Union Minister Jitendra Singh.
- According to him, India’s space economy will grow significantly by 2040 from its current modest level of 8 billion dollars. He stated that the Indian space economy is expected to reach 100 billion dollars by 2040, according to the Arthur D. Little Report.
- As per him, ISRO has launched over 430 foreign satellites to date, generating over 290 million euros from European satellite launches and over 170 million dollars from American satellite launches.
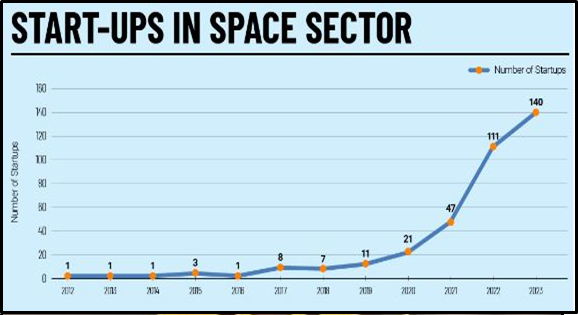
- As a result of changes brought about and the opening of the industry to public-private participation, the number of space startups in India is growing quickly. In just four years, the number of space startups has increased from zero to over 1,180.
Private Involvement in the Indian Space Program:
- Skyroot Aerospace: A Hyderabad-based startup that launched Vikram S (Mission Prarambh), India’s first privately built rocket, on December 11, 2021.
- Agnikul Cosmos: A startup company based in Chennai is creating Agnibaan, a tiny satellite launch vehicle that can send payloads up to 100 kg into low-Earth orbit.
- Pixxel: A Bengaluru-based startup is developing a constellation of high-resolution earth observation satellites that will enable real-time data collection and analysis for a range of uses, including disaster relief, forestry, urban planning, and agriculture.
- Bellatrix Aerospace: is a Bengaluru-based startup that is creating cutting-edge propulsion technologies for launch vehicles and satellites, including green propellants, electric thrusters, and orbital transfer vehicles.
Arthur D. Little Report
Indian Space Policy of 2023:
- Goal: To promote and formalize the involvement of the private sector in India’s space industry, with the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) principally responsible for advanced space technology research and development.
- The private sector’s entry: It will be legal for private businesses to construct launch vehicles, rockets, and satellites as well as to gather and distribute data.
- In order to support their space-related operations, it encourages private companies to invest in building new infrastructure for the space sector and make small-charge facilities use of ISRO facilities.
Importance of Private Sector Engagement in the Indian Space Industry:
- Innovation: By creating new technologies, goods, and services that can meet the wide range of changing customer needs, they contribute more creativity and innovation to the space industry.
- Commercialization: By establishing new markets and chances for income generation and profit-making, they can increase the commercialization and monetization of India’s space assets and services.
- Economic and social Development: By offering space-based services and solutions to a range of industries, including agriculture, health care, and education, they can support the nation’s social and economic development.
- Competition: By providing customers with more options and choices at lower prices and better quality, they foster a healthy and competitive environment in the space sector.


 Arthur D. Little Report
Arthur D. Little Report

