SMALL MODULAR REACTORS: CHALLENGES AND PROSPECTS
Why in the news?
- The Indian government is partnering with the private sector to study and test small modular reactors (SMRs), aiming to enhance the country’s nuclear energy capabilities.
- Nuclear energy is considered a crucial component in the global energy mix, particularly as renewable technologies develop and fossil fuels remain affordable and prevalent.
source:slideshare
Challenges of SMRs
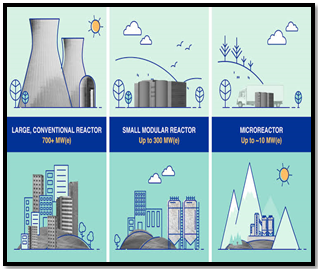
- SMRs (10 MWe to 300 MWe) aim for safety and commercial viability through modular designs and lower capital costs.
- They face external costs, including regulatory safeguards and frequent refueling, increasing proliferation resistance concerns.
Commercial Viability
- SMRs’ success in India depends on achieving commercial viability in stable market conditions and grid stability.
- SMR tariffs may not be lower due to fixed costs and safety expectations, leading to increased reactor capacities from 220 MW to 700 MW for economic feasibility.
| What are Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)?
About SMRs
Characteristics
Safety and Longevity
Associated Article: https://universalinstitutions.com/can-small-modular-nuclear-reactors-help-india-achieve-net-zero/ |