SETTLING TRADE DISPUTES THROUGH ‘LITIGOTIATION’
Relevance: GS 2 – Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Why in the News?
- The dispute between India and the U.S. was filed over a decade ago.
- It involves import restrictions imposed by India on U.S. poultry products due to concerns about avian influenza (bird flu).
- The resolution of this long-standing Indo-U.S. poultry dispute was achieved through a strategic approach combining litigation and negotiation, referred to as ‘litigotiation’.
Diplomatic Resolution of Trade Disputes
- International diplomacy often involves careful handling of sensitive issues.
- Major trade and commerce differences are sometimes set aside to focus on overall bilateral relations.
- Resolving trade frictions requires bold diplomatic efforts to benefit industries on both sides.
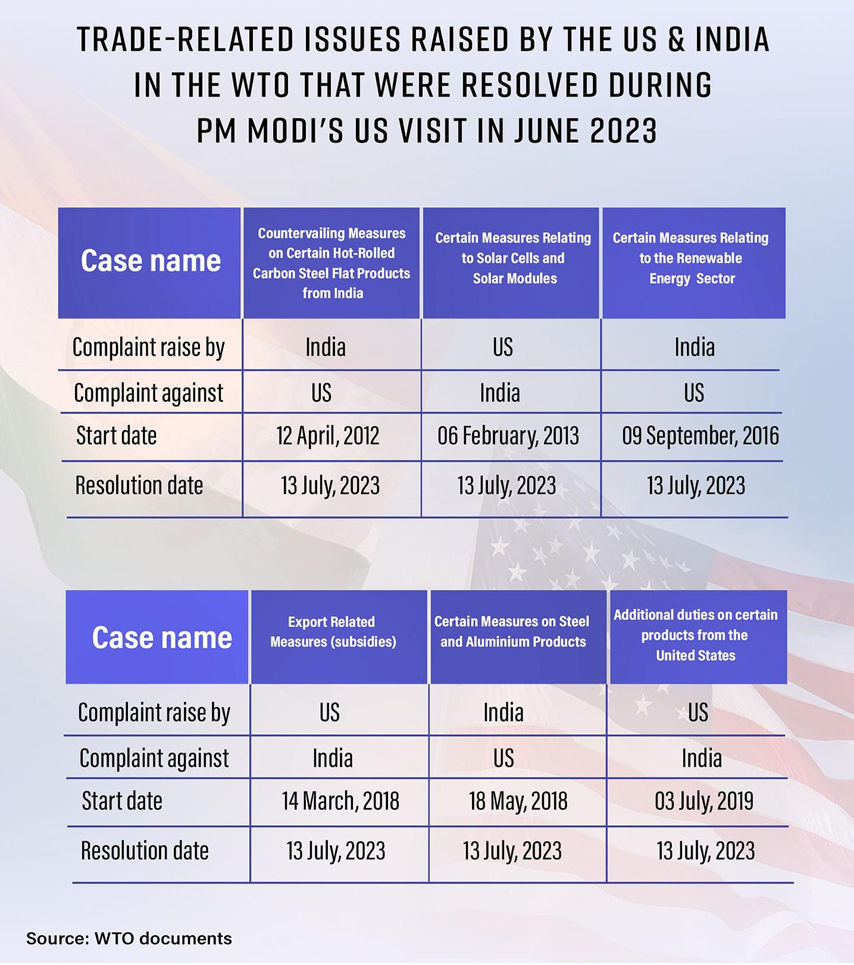
- India and the U.S. managed to resolve seven longstanding trade disputes at the World Trade Organization (WTO) within a year.
- In late March, the last lingering trade dispute on poultry products was settled.
- Both countries notified the WTO of their mutually agreed solution and withdrew their respective pending cases.
- The settlement of the poultry dispute followed six other WTO dispute resolutions after Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s U.S. visit.
Background of the Dispute
- The dispute was filed over a decade ago, making it the oldest of the seven disputes between India and the U.S.
- It concerns India’s import restrictions on U.S. poultry products due to avian influenza (bird flu) fears.
- The U.S. initiated the dispute in 2012, challenging the import restrictions as unjustified.
- Nature of the Dispute
- The issue involved sanitary and phytosanitary (SPS) measures related to animal and human health and safety.
- It was one of the first instances of a developing WTO member’s SPS measures being brought before a WTO panel.
- The U.S. argued that India deviated from international standards set by the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE) without scientific justification, violating WTO’s SPS Agreement.
WTO Rulings and Developments
- Both the WTO panel and the Appellate Body ruled in favor of the U.S.
- India was given a year to modify or withdraw its inconsistent measures.
- The U.S. alleged non-compliance by India and filed a retaliation claim at the WTO.
- India responded with a counter-dispute to prove its revised measures were in line with WTO rules.
- Attempts at Resolution
- Over the past decade, both disputes were kept in abeyance as India and the U.S. sought a mutual settlement.
- The resolution efforts were aimed at reconciling differences and conforming to WTO rules.
- Resolution and Trade-off
- Fresh impetus and persistent efforts from both sides led to India avoiding a $450 million annual claim.
- India agreed to reduce tariffs on select products such as cranberries, blueberries, frozen turkey, and premium frozen duck meat for luxury hotels.
- This trade-off balances interests considering the long pendency of the dispute.
Negotiation Challenges
- The complexity of resolving this dispute is evident as it wasn’t settled along with six other disputes by mid-2023.
- Negotiators faced a challenging task, reflecting the intricate nature of the issues involved.
- Resolving all seven disputes showcases a remarkable success in international trade dispute settlement.
- It demonstrates that major trading partners can resolve sensitive trade matters through diplomatic channels despite domestic challenges.
- This resolution, coupled with India’s participation in theS.-led Indo-Pacific Economic Framework, strengthens the India-U.S. partnership.
Economic Significance and Diplomatic Breakthrough
- The dispute is not the most economically significant for India compared to other WTO disputes, like those involving Indian foreign trade policy schemes (special economic zones and export-oriented unit schemes).
- Its resolution marks a significant diplomatic achievement.
- Commonality of Bilateral Solutions: Settling disputes through bilateral solutions is common at the WTO.
- Example: S. and EU resolved disputes over Boeing and Airbus subsidies through diplomacy after multiple WTO challenges.
- WTO rules favor amicable dispute resolution, with litigation as a last resort.
- Significance of the Settlement Package
- The package’s significance lies in the number of disputes settled and the complexity of their subjects, including subsidies, countervailing duties, and SPS measures.
- Without a functional Appellate Body (defunct since 2019), resolving long-standing trade conflicts requires innovative solutions.
- Emphasizes the importance of bilateral diplomatic channels for resolving complex trade issues.
- Implications for International Trade
- The outcome shows that even with multilateral body paralysis, major trading partners can resolve differences through bilateral negotiations within the litigation framework.
- Encourages fostering a stable international trade environment where disputes are promptly addressed and not allowed to linger.
Way Forward to Address Multilateral Body Paralysis
- Strengthen Bilateral Negotiations: Encourage direct negotiations between countries to resolve disputes swiftly.
- Enhance Mediation and Arbitration: Develop robust mediation and arbitration mechanisms as alternatives to litigation.
- Revive the Appellate Body: Work towards restoring the functionality of the WTO Appellate Body.
- Promote Regional Trade Agreements: Utilize regional trade frameworks to manage and resolve trade disputes.
- Innovate Dispute Resolution: Introduce flexible and adaptive dispute resolution processes to handle complex issues.
- Strengthen Multilateral Collaboration: Foster greater cooperation among WTO members to enhance trust and collaboration in dispute settlement.
Alternative articles
https://universalinstitutions.com/world-trade-organization-wto/
Mains question
Discuss the significance of resolving long-standing trade disputes through bilateral negotiations in the absence of a functional WTO Appellate Body, and its implications for international trade stability. (250 words)