Series of Earthquakes Rattle Myanmar in 2024
Series of Earthquakes Rattle Myanmar in 2024
Why in the News?
A 4.2-magnitude earthquake hit Myanmar, a day after a 4.5-magnitude tremor. These follow powerful quakes of 7.7 and 6.4 magnitude in March 2024, raising health concerns, including TB, HIV, and waterborne diseases, in affected areas.
Fresh Seismic Activity in Myanmar:
- A 4.2-magnitude earthquake struck Myanmar at a depth of 10 km, as per the National Center for Seismology.
- This follows a 4.5-magnitude quake a day earlier, signalling continued tectonic activity.
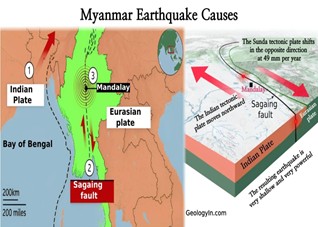
- The country lies in a seismically active zone, making it vulnerable to frequent tremors.
Devastating Quakes in March 2024
- On March 28, 2024, central Myanmar was jolted by major earthquakes measuring 7.7 and 6.4 on the Richter scale.
- These caused extensive damage, rendering many people homeless.
- Relief and rescue operations were launched, but recovery has been slow in some regions.
Rising Health Concerns Post-Disaster
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has flagged increasing risks of infectious diseases in quake-hit zones.
- Diseases like tuberculosis (TB), HIV, and waterborne infections pose significant threats due to poor sanitation and displacement.
- There is an urgent need for healthcare intervention and disease surveillance in affected areas.
Faults: Definition and Types |
| ● A fault is a fracture or zone of fractures in the Earth’s crust where blocks of rock move relative to each other due to tectonic stress. |
| ● Movement may be sudden (causing earthquakes) or gradual (creep). |
| ● Normal Fault: The hanging wall moves downward; occurs in extensional zones. |
| ● Reverse Fault (Thrust Fault): The hanging wall moves upward; found in compression zones like subduction areas (e.g., Japan). |
| ● Strike-slip Fault: Blocks slide horizontally past each other. |
| ○ Right-lateral: Far block moves to the right (e.g., San Andreas Fault). |
| ○ Left-lateral: Far block moves to the left. |