SAFEGUARDING INDIAN SEAFARERS
Syllabus:
- GS 3 :
Security challenges and their management in India.
Why in the News?
The article is in the news due to the rising safety concerns of Indian seafarers in the wake of recent attacks on commercial ships and the growing challenges they face in their work environment, prompting calls for international cooperation and better protections.
Source: RiskIntellegence
Rising Safety Concerns and International Efforts
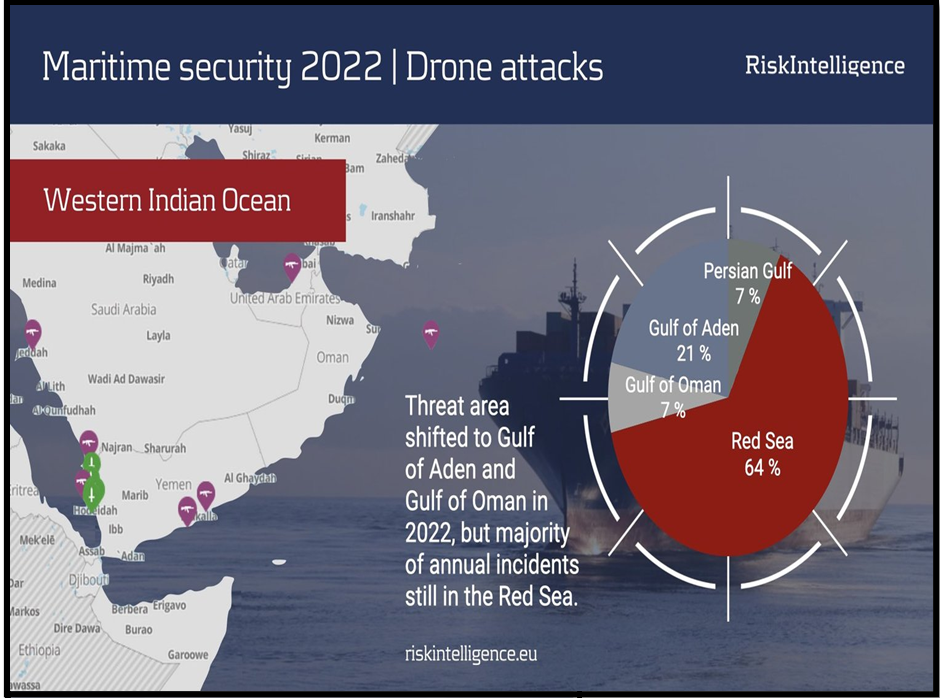
- Recent Attacks: Indian seafarers face significant risks due to attacks on commercial ships in regions such as the Red Sea and the Strait of Hormuz.
- Indian Submissions to IMO: India submitted papers to the International Maritime Organization (IMO) Legal Committee, addressing seafarers’ security, contract issues, and broader maritime security challenges.
- Advocating Cooperation: India emphasized the need for international collaboration to address maritime threats such as piracy, armed robbery, extremist attacks, and emerging risks like drone attacks.
- Maritime Security Focus: India advocates for a comprehensive approach to maritime security that includes both international cooperation and improved contractual conditions for seafarers.
- IMO’s Role: India recognizes the IMO’s efforts in combating maritime fraud and calls for further international cooperation to tackle various maritime challenges.
| Key Terms:
Red Sea The Red Sea is a vital waterway connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Indian Ocean through the Suez Canal. It serves as a major trade route, facilitating the movement of goods between Europe, Asia, and Africa. The region is also known for its unique biodiversity and marine life. Strait of Hormuz The Strait of Hormuz is a narrow waterway connecting the Persian Gulf to the Gulf of Oman and the Arabian Sea. It is one of the world’s most strategic chokepoints for oil transportation, with a significant portion of global oil exports passing through it. The region is often subject to geopolitical tensions. International Maritime Organization (IMO) The International Maritime Organization (IMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for regulating global shipping. Established in 1948, the IMO sets international standards for safety, security, and environmental performance in the maritime industry. It plays a key role in promoting cooperation and best practices among member states. |
Resurgence of Sea Piracy and India’s Response
- Pirate Attacks: Recent incidents off the coast of Somalia and other areas signal a resurgence of piracy, including hijackings and targeted attacks on vessels.
- Proactive Measures: India calls for increased vigilance and international cooperation to combat piracy and protect seafarers, following the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea.
- Impact on Seafarers: Unlawful recruitment practices and exploitation have been reported since 2020, affecting the well-being of Indian seafarers.
- Global Coordination: India urges international coordination to address the challenges faced by seafarers and ensure their rights under the Maritime Labour Convention, 2006.
- Broader Implications: Piracy and other maritime threats not only impact seafarers’ safety but also have broader consequences for international trade and global supply chains.
Indian Seafarers’ Global Role and Challenges
- Significant Workforce: India ranks third globally in terms of its seafaring workforce, representing 9.35% of the global seafaring population.
- Vulnerabilities Exposed: Recent incidents such as the seizure of MSC Aries and detention of MT Heroic Idun in Nigeria highlight Indian seafarers’ vulnerabilities.
- Lack of Legal Support: Surveys indicate that many Indian seafarers lack legal representation, feel unfairly treated, and are unaware of their rights.
- Financial Pressures: Indian seafarers often face financial burdens, including costly legal processes and lack of compensation for detention or other challenges.
- Need for Awareness: There is a need for increased awareness and education regarding seafarers’ rights and available support services.
Human Rights Initiatives and Escalating Piracy Concerns
- Initiatives Launched: The Indian government and the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) launched the ‘human rights at sea’ initiative to address seafarers’ challenges.
- Increasing Piracy: Recent data shows a more than 10% increase in serious piracy incidents over the last 10 months, posing a significant threat to seafarers’ safety.
- Comprehensive Solutions Needed: Addressing piracy requires comprehensive land-based solutions such as private guards on ships, as well as international cooperation.
- Protection Strategies: Strategies to protect seafarers include improving safety measures on board ships and enhancing security in high-risk areas.
- Human Rights Concerns: Seafarers are often subject to abuses, including being held in foreign jails, stranded in foreign waters, and subjected to illegal detentions.
Exploitation by Iranian Shipping Companies
- False Promises: Indian seafarers are often lured by Iranian shipping companies with promises of high salaries and opportunities in the Middle East.
- Exploitation Practices: Seafarers face exploitation such as overwork, inadequate food and living conditions, and being forced to transport illegal cargo.
- Lack of Legal Recourse: Seafarers often struggle to hold ship owners accountable for exploitation due to the use of foreign registrations to evade taxes and oversight.
- Complex Legal Challenges: Legal disputes involving Indian seafarers and foreign ship owners often present complex challenges that require international coordination.
- Repatriation Difficulties: In some cases, Indian seafarers face challenges in returning home due to lack of support and legal barriers.
Urgent Need for Support
- Career Commitment: Despite facing significant risks, many Indian seafarers remain committed to their careers at sea.
- Pandemic Resilience: Indian seafarers demonstrated resilience and professionalism during the COVID-19 pandemic, enhancing India’s standing in the global maritime market.
- Rising Security Concerns: Recent attacks on commercial ships have heightened safety concerns among Indian seafarers, with some considering quitting their jobs.
- Government Support Needed: There is an urgent need for increased government support to address seafarers’ concerns and ensure their safety and well-being.
- Improving Protections: Enhancing protections for seafarers, including better contracts and safety measures, is critical to maintaining a skilled and committed workforce in the maritime industry.
Way Forward
- Strengthen International Cooperation: Collaborate with international organizations, such as the IMO and other maritime nations, to tackle global maritime threats and enhance safety measures for seafarers.
- Improve Seafarer Education and Awareness: Conduct targeted awareness campaigns to educate seafarers about their rights and available support services, as well as best practices for safety at sea.
- Enhance Contractual Protections: Advocate for better contractual conditions for seafarers, including clear terms and provisions for safety, fair treatment, and legal support in case of disputes or challenges.
- Combat Unlawful Recruitment and Exploitation: Work with international partners to identify and address unlawful recruitment practices and exploitation, ensuring better oversight and protection for seafarers.
- Comprehensive Anti-Piracy Strategies: Implement comprehensive, multi-faceted approaches to combat piracy, including land-based solutions, increased security measures on ships, and enhanced coordination with regional authorities.
- Promote Technological Innovations: Invest in and promote advanced technologies, such as real-time tracking and communication systems, to improve the safety and security of seafarers on board.
- Support Seafarer Repatriation: Create efficient repatriation processes and provide assistance for seafarers stranded in foreign waters or facing legal challenges abroad.
- Government Support: Urge governments to prioritize seafarers’ welfare and safety by providing greater resources and support for protection measures, legal assistance, and repatriation.
- Human Rights Protections: Advocate for stronger human rights protections for seafarers, including mechanisms to address abuses and violations promptly and effectively.
- Community Engagement and Support: Foster community engagement and support networks for seafarers, both within their home countries and internationally, to enhance their overall well-being.
Conclusion
Indian seafarers play a vital role in global trade, but they face increasing dangers and challenges. Addressing their safety and well-being requires international cooperation, stronger protections, and government support to maintain a robust and skilled maritime workforce.
Source:The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
“Discuss the challenges faced by Indian seafarers in the current global maritime environment. What measures can be taken to improve their safety and well-being while ensuring a smooth functioning of the international shipping industry?”
Associated Article: