Role of ICT in Governance
Relevance
- GS Paper 2 Important Aspects of Governance, Transparency and Accountability, E-governance- applications, models, successes, limitations, and potential; Citizens Charters, Transparency & Accountability and institutional and other measures.
- Tags: #Governance #ICT #eGovernance #RoleOfICT #DigitalIndia #TransparencyAndAccountability #GS2.
What is Governance?
- The World Bank Defines Governance as “the manner in which the power is exercised in the administration and management of a country’s economic and social resources for growth and Development”.
- 10th Five Year Plan defines Governance as “Governance relates to the management of all such processes that in any society, define the environment which permits and enables individuals to raise their capability levels, on one hand, and provide opportunities to realize their potential and enlarge the set of available choices, – on the other”.
Need?
Good governance promotes transparency, accountability, rule of law, and the participation of stakeholders in decision-making. It is essential for maintaining order, ensuring fairness, and achieving desired outcomes in both public and private sectors.
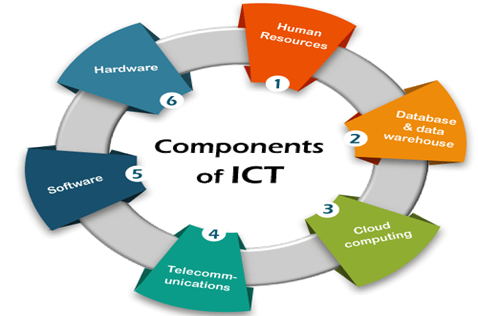
Information and communication Technology(ICT)
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) refers to a broad range of technologies and tools used to manage and exchange information electronically. This encompasses computers, software, networks, telecommunications systems, and other digital devices. ICT facilitates the creation, storage, processing, transmission, and retrieval of data and information.
Role of Information and Communication Technology
ICT plays a fundamental role in modern communication, data management, and overall technological infrastructure, enabling various sectors like business, education, healthcare, and more to operate efficiently and connect on a global scale.
Role Of Information and Communication Technology in Governance
- Information and Communication Technology (ICT) plays a pivotal role in modern governance by transforming how governments interact with citizens, deliver services, and manage operations.
- This transformation is underpinned by the digitalization of information and communication processes, enabling greater efficiency, transparency, and responsiveness.
There is a multi-faced role of ICT in Governance
Improved Service Delivery
- ICT enables government departments to offer services online, simplifying interactions for citizens.
- Various state and central government websites serve as portals for accessing services, from applying for licences to obtaining certificates.
- Example: Digi-Locker : Document Revival and Storage
- Filing Portal : Income tax Services
Enhanced Transparency
- ICT promotes transparency in governance by facilitating public access to government operations and data.
- Government websites, open data initiatives, and online portals provide channels for citizens to retrieve official documents, including reports and budgets.
- Open government data serves as a tool for holding authorities accountable, enabling citizens, researchers, and journalists to scrutinize government information.
Example: Right to Information (RTI) Act
Digital platforms for filing RTI applications and tracking responses enhance transparency in government functioning.
CM Helpline in Madhya Pradesh
It enables citizens to complain against any Official and hold him accountable.
E-Governance Initiatives
India has witnessed a proliferation of e-governance initiatives aimed at digitising and simplifying public services.
The National e-Governance Plan (NeGP) and its subsequent iterations are at the forefront of these efforts.
Example: Aadhaar – Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI)
It serves as a digital identity, streamlining access to government services and benefits. Aadhaar has been integrated into various public welfare schemes, ensuring efficient delivery.
Digital India
- ICT is the backbone of Digital India.
- Launched in 2015, the Digital India program is a flagship initiative focused on transforming India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy.
- It aims to provide digital infrastructure, enhance digital literacy, and deliver services electronically.
Example: Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY)
- PMJDY, under the Digital India umbrella, focuses on financial inclusion.
- ICT plays a critical role in managing accounts and facilitating transactions.
Mobile Governance
Given the widespread adoption of mobile phones, mobile governance initiatives have gained prominence. Mobile apps and SMS services provide a convenient means for citizens to engage with the government.
Example: Umang App
The Unified Mobile Application for New-Age Governance (Umang) is a multilingual mobile app that offers access to various central and state government services, from paying bills to booking railway tickets.
Digital Payments and Financial Inclusion
Using ICT , Digital payment platforms have expanded financial inclusion, enabling citizens to make transactions, access banking services, and receive government benefits electronically.
Example: BHIM (Bharat Interface for Money)
BHIM is a mobile app for making simple, quick, and secure digital payments. It facilitates peer-to-peer and merchant payments, promoting a cashless economy.
E-Education and E-Health
ICT supports education and healthcare initiatives. E-learning platforms and telemedicine services improve access to education and medical care, especially in remote and underserved areas.
Example: e-Sanjeevani:
The e-Sanjeevani platform provides telemedicine services, connecting patients with healthcare providers.
SWAYAM (Study Webs of Active Learning for Young Aspiring Minds)
SWAYAM is a government initiative that provides free, high-quality education through online courses. It offers a wide range of subjects and allows students to access educational resources remotely.
Electoral Processes
ICT has enhanced the electoral process, making it more accessible, efficient, and transparent. Electronic voting machines (EVMs) and online voter registration are notable advancements.
Example: Online Voter Registration
The Election Commission of India offers online voter registration, allowing eligible citizens to enroll as voters or update their details conveniently.
Public Safety and Emergency Response
ICT systems support public safety and emergency response. Systems like the Emergency Response Support System (ERSS) enable citizens to seek help during emergencies.
Example: ERSS “112” Helpline
The ERSS “112” helpline integrates police, fire, health, and other emergency services. Citizens can dial 112 in distress, and the system dispatches the appropriate response team.
Data Analytics and Decision-Making
ICT enables data-driven decision-making in governance. Big data analytics can identify trends, allocate resources efficiently, and design evidence-based policies.
Example: National Data Sharing and Accessibility Policy (NDSAP)
NDSAP promotes the sharing and use of government data for public good. Data analytics under NDSAP help improve decision-making in areas such as healthcare and urban planning.
Challenges ICT in Governance
- Bridging the Digital Gap: A top priority is to ensure that ICT benefits all citizens, irrespective of their socioeconomic status. Overcoming the digital divide remains a persistent challenge.
- Promoting Digital Competence: Fostering digital literacy is crucial, equipping citizens with the necessary skills to effectively use digital services and engage in digital governance.
- Cybersecurity Measures: Governments must make significant investments in cybersecurity to safeguard against cyberattacks, data breaches, and digital vulnerabilities.
- Privacy Dilemma: The increased data collection by governments raises concerns about privacy. Striking a balance between security and safeguarding privacy is a continuous challenge.
- Regulatory Framework Establishment: Governments need to put in place comprehensive legal and regulatory frameworks to govern digital operations and the management of data.
The role of ICT in governance is undeniably transformative, enhancing transparency, efficiency, and citizen participation. To harness its full potential, governments must address cybersecurity challenges, ensure data privacy, bridge the digital divide, promote digital literacy, and establish robust regulatory frameworks. Embracing these imperatives will empower ICT to assume a more central role in shaping the future of efficient and all-encompassing governance.
| Mains Question
“Discuss the transformative role of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in governance. Highlight the challenges governments face to ensure effective ICT-driven governance.” |