RESPONDING TO COVID-19 SUB-VARIANTS
The Issue:
- Since the initial report of the novel coronavirus in 2019, the virus has undergone numerous changes, resulting in over 1,000 subvariants and recombinant sub-lineages.
- The emergence of the JN.1 sub-variant of the Omicron variant is part of the expected evolution of the virus, with genetic alterations in its genome leading to new classifications.
Source: COVID communication Network
Key Highlights:
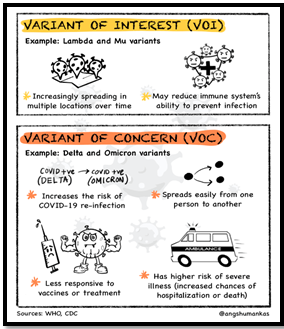
- Status :1, designated a Variant of Interest (VoI), triggers increased genomic sequencing and monitoring by health agencies.
- Health Hazards : While JN.1 does not currently show evidence of causing severe disease or immune escape.
- Vaccine Response : Current scientific evidence supports existing COVID-19 vaccines and hybrid immunity from natural infections against sub variants.
- Impact : Globally, cases emerge in the US, Europe, Singapore, and China.
- Impact on India: India reports JN.1 cases from Kerala and Goa.
Public Health Impact and Vaccines:
- WHO states no evidence of additional public health risk from JN.1, but with the winter onset, it could heighten respiratory infections globally.
- Assures existing vaccines continue to protect against severe illness and death caused by JN.1.
| About Genome Sequencing
· Process of determining the order of nucleotides in an organism’s DNA. · Involves breaking DNA into fragments, sequencing them, and assembling the sequence. · Enables identification of genes, variations, and understanding genetic codes. · Essential in various fields, including medicine, genetics, and evolutionary biology. |

 Source: COVID communication Network
Source: COVID communication Network

