Researchers Discover TB Bacteria’s Immune Evasion Strategies
Why in the news?
New research reveals how Mycobacterium tuberculosis survives in immune cells, highlighting the importance of cysteine synthases in its resistance and potential antibiotic treatment advancements.
TB Bacteria’s Immune Evasion Strategies:
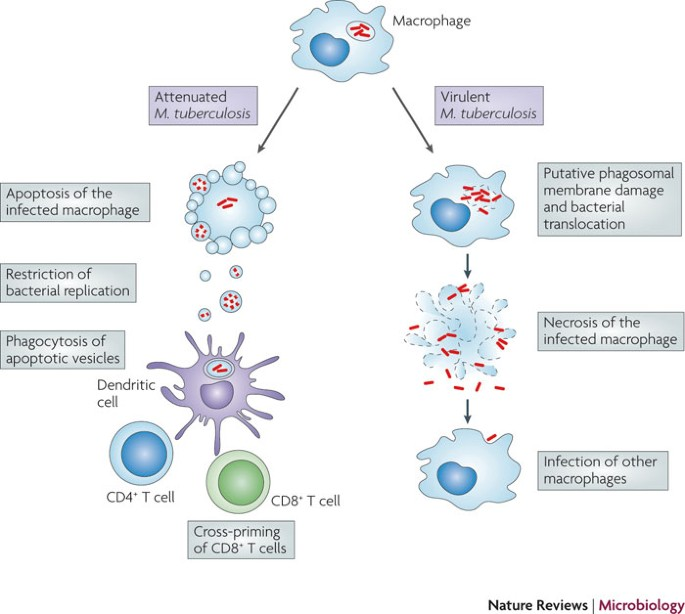
- Survival Mechanism: Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) forms clusters called tubercles in the lungs, protected by lipids.
- It can remain dormant in cells for decades without causing disease.
- Co-evolution with Humans: Mtb has coevolved with humans for about 70,000 years, allowing it to adapt and evade the immune response, particularly by thriving within macrophages—key immune cells that usually destroy pathogens.
- Oxidative Stress Resistance: Mtb withstands the oxidative stress created by macrophages, which typically helps in destroying invading microbes.
Research on Cysteine Synthases
- Cysteine Synthase Enzymes: Researchers are studying Mtb’s cysteine synthase enzymes, which aid in synthesising cysteine, an amino acid that helps counter oxidative stress.
- Experimental Findings: A recent study found that two specific cysteine synthase enzymes, CysK2 and CysM, are crucial for Mtb’s survival under nutrient-deprived and oxidative stress conditions.
- Inhibitors of these enzymes could enhance the effectiveness of existing antibiotics.
Future Directions in TB Treatment:
- Broad Research Focus: Scientists are also exploring Mtb’s metabolic pathways, cell wall strength, and mechanisms for evading macrophage memory, which could lead to new treatments.
- Need for Human Studies: To translate these findings into effective therapies, research must shift towards human cell studies, highlighting the need for sustained efforts in combating TB.
About Tuberculosis (TB):
- Definition: TB is a bacterial infection primarily spread through inhalation of droplets from an infected person’s cough or sneeze.
- Affected Areas: Mainly affects lungs but can impact other body parts, including abdomen, glands, bones, and nervous system.
- Seriousness: Potentially serious but treatable with the right antibiotics.
Symptoms of TB:
- Persistent cough (over 3 weeks) with possible blood
- Weight loss
- Night sweats
- High temperature
- Fatigue and tiredness
- Loss of appetite
- Swellings in the neck
Types and Treatment:
- Pulmonary TB: Contagious type affecting lungs; requires prolonged exposure.
- Latent TB: No symptoms; bacteria inactive but present in the body.
- Active TB: Symptoms develop if the immune system fails to contain the infection.
- Treatment: Cured with a course of antibiotics (6-18 months).
TB in India
- Statistics: 33 lakh cases in 2021; 24.22 lakh in 2022.
- Goal: End TB epidemic by 2025; National Strategic Plan for Tuberculosis Elimination (2020-2025) launched for this aim.
Associated Article: