REGIONAL TURMOIL IN WEST ASIA
(THE NEED FOR SECURITY EQUILIBRIUM)
Relevance :
GS 2:
- Issues of national And International Importance ,
- Effect of Policies and Politics of Developed and Developing Countries on India’s interests, Indian Diaspora.
Why in the News ?
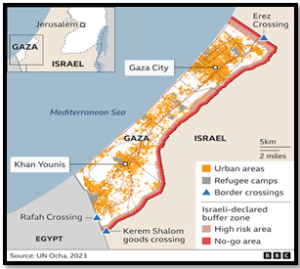
- The Gaza conflict transcends Israel-Hamas, extending to Lebanon and Syria. Targeted strikes by Israel hit Hezbollah, Hamas, and Iranian commanders.
- Hezbollah engages Israeli forces in southern Lebanon, while Iran-backed militias attack the U.S. in Syria and Iraq.
- Yemen’s Houthis, backed by Iran, intensify conflict in the Red Sea. U.S. retaliates with airstrikes against Shia militias in Iraq, Syria, and Yemen.
Source: BBC
Escalating Anarchy and Unilateral Measures
- Widespread chaos prompts Sunni Islamist militants to target Iran, resulting in over 100 casualties.
- Iran retaliates by claiming destruction of Israeli intelligence outpost in Iraq and Sunni Islamist training camps in Syria and Pakistan.
- Regional anarchy prevails as countries pursue unilateral military actions, challenging international laws and sovereignty.
- Risk of a broader all-out war looms, jeopardizing the fragile security landscape.
Ignored Crisis: Palestine’s Reemergence
- Despite recent regional shifts, the age-old crisis of Israel’s occupation of Palestinian territories resurfaces.
- October 7 Hamas attack and Israel’s forceful response refocus attention on Palestine.
- Non-state actors’ involvement and the absence of off-ramps complicate the security crisis.
- After a 100-day war, Israel’s impact on Gaza remains limited, raising questions about the effectiveness of its actions.
Background: The Israel-Palestinian Issue
Origin of Conflict
- Roots trace back to pre-First World War, with a demand for a Jewish homeland in Palestine.
- Balfour Declaration in 1917 supported the establishment of a Jewish homeland in British-controlled Palestine.
- UN General Assembly’s 1947 recommendation to partition Palestine intensified Arab-Jewish conflict.
Escalation of Conflict
- 1948 establishment of a Jewish state led to Arab League opposition and the 1948 Arab-Israeli war.
- Six-Day War in 1967 saw Israel capturing the West Bank and Gaza Strip.
- Oslo Accords (1993) allowed Palestinian authority in the West Bank and Gaza Strip.
- Subsequent rise of Hamas in 2006 and control over Gaza in 2007.
Current Status
- Presently, Hamas governs the Gaza Strip, while the West Bank is under Fatah’s control.
- Ongoing tensions and distinct equations persist between both factions and Israel.
About the Recent Israel-Hamas Conflict
Attackers and Reasons
- Hamas militants attacked Israeli troops and civilians in response to Israeli raids in the West Bank and violence at al-Aqsa Mosque.
- Over 5,000 rockets launched from Hamas-controlled Gaza Strip.
- Israel’s Operation ‘Iron Swords’ initiated in retaliation for unprecedented attacks.
Impact of the Conflict on the World
- Potential rise in global shipping charges due to increased insurance premiums.
- Risk of a global oil crisis impacting crude oil costs.
- Possibility of regional instability escalating into a broader war.
- Further strain on the global economy already affected by the Ukraine conflict.
- Shift towards bipolarity between the Western world and the Russia-China axis.
- Potential reversal of Israel’s normalization efforts with the Arab world.
Challenges in Achieving Peace
- Jerusalem remains a contentious issue for both Israel and Palestine.
- Presence of proxy groups in Palestinian territories hampers a peaceful solution.
- Arab countries’ historical demand for Israeli withdrawal acts as a barrier.
- Right-wing politics in both Israel and Palestine obstruct compromise.
Impact on India:
- Economic Consequences
- Indian exporters face increased insurance costs, potentially impacting competitiveness.
- Current trade worth $10.7 billion could suffer significant impact.
- Diplomatic Stand
- India, advocating a two-state solution, may need to adapt its diplomatic stance.
- Condemnation of attacks on civilians already expressed.
- Citizen and Diaspora Concerns
- Evacuation needs for stranded Indian citizens in Israel.
- Potential impact on the Indian diaspora residing in the conflict zone.
- Defence and Trade
- Israel is a major source of Indian defence equipment.
- Concerns over potential delays in India’s defence consignments.
- Regional Projects and Shipping Routes
- Potential hindrance to India’s planned projects, including the India-Middle East-Europe economic corridor.
- Possible disruption of shipping along the Suez Canal affecting India’s trade with Europe.
Way Forward:
- West Asia requires a fresh security balance amid the crumbling old order.
- Urgent call for a Gaza ceasefire, positioning peace between Israel and Palestinians as a foundation for broader regional security talks.
- Main stakeholders—Israel, Arab nations, Iran, the U.S., and their allies—should engage in meaningful dialogue.
- Addressing the Palestinian issue becomes a pivotal step in forging a comprehensive and lasting security equilibrium in the region.
- Peace between Israel and Palestinians could serve as a foundation for broader regional security talks.
West Asia demands a strategic reset to establish a new security equilibrium, emphasizing dialogue and cooperation among major players for lasting stability.
| Hamas
· Origins: Formed in the late 1980s during the First Intifada. · Purpose: Emerged as a resistance movement against Israeli occupation. · Nature o Dual Identity: Functions as both a militant and political organization. o Roots: Rooted in the Palestinian branch of the Muslim Brotherhood. · Objective o Islamic State: Aims to establish an Islamic state in historic Palestine. o Rejection of Israel: Rejects the existence of Israel and advocates for Palestinian rights. · Goals and Ideology o Anti-Israel Stance: Strong ideological opposition to Israeli presence in Palestinian territories. o Territorial Liberation: Seeks the liberation of Palestinian lands, including East Jerusalem. o Capital Aspiration: Envisions East Jerusalem as the capital of a future Palestinian state. |
Source: The Hindu
Mains Practice Question
“Critically analyze the recent resurgence of regional turmoil in West Asia, focusing on the escalating conflict between Israel and Hamas, its wider regional implications, and the challenges of attaining a sustainable security equilibrium.”

 Source: BBC
Source: BBC

