REFORMS NEEDED IN THE VOTING PROCESS
Syllabus:
- GS 2: Salient features of the Representation of People’s Act.
- Constitution of India —historical underpinnings, evolution, features, amendments, significant provisions and basic structure.
Focus:
- The Supreme Court has agreed to hear petitions for 100% verification of Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT) slips against Electronic Voting Machine (EVM) counts, spotlighting concerns over election transparency and EVM integrity.
Source: Hinduustan Times
The integrity and efficiency of the voting process are critical to the health of any democracy. As technology evolves and societies become more complex, the need for reforms in the electoral process becomes increasingly evident. Here we explore several key areas where improvements can ensure more robust and transparent elections.
Reforms Needed in the Voting Process
Enhancing Voter Verification
- Introduction of Advanced Verification Technologies: Implement biometric verification to ensure that the person voting is indeed the registered voter.
- Upgraded Voter Education Programs: Increase voter awareness about the verification process and the importance of participation in a democracy.
- Transparent Voter Lists: Regular updates and audits of voter lists to prevent discrepancies and ensure all eligible voters are accurately listed.
- Real-Time Verification Systems: Use technology to provide real-time authentication at the polling stations to reduce fraud.
- Stronger Regulations for Voter ID: Enforce stringent criteria and checks for issuing voter IDs to minimize the risk of fraud.
Securing Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs)
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct frequent and thorough audits of the EVMs to ensure their integrity and security from external threats.
- Enhanced Physical Security Measures: Implement stricter physical security measures during transportation, storage, and use of EVMs.
- Advanced Encryption Techniques: Use state-of-the-art encryption technologies to safeguard data transmitted by EVMs.
- Robust Anti-tampering Mechanisms: Install mechanisms that make it virtually impossible to tamper with EVM hardware and software.
- Transparent EVM Handling Protocols: Publicize the protocols for EVM handling to build public trust in the electoral process.
Increasing Voting Accessibility
- Extended Voting Hours: Prolong polling hours to accommodate more voters, especially those who work long hours or live in remote areas.
- Mobile Voting Stations: Deploy mobile voting stations to rural and underserved areas to ensure everyone has the opportunity to vote.
- Enhanced Postal Voting Systems: Improve the reliability and security of postal voting to facilitate absentee voting.
- Online Voting Options: Explore secure online voting solutions for citizens living abroad or unable to physically reach polling stations.
- Accessibility for Disabled Voters: Ensure that all polling stations are equipped with facilities for disabled voters, making the voting process inclusive.
Improving Voter Education
- Comprehensive Educational Campaigns: Launch national campaigns to educate voters on their rights and the importance of their vote.
- School and Community Programs: Integrate voter education into school curriculums and community programs to engage citizens from a young age.
- Multilingual Support: Provide voting instructions and support in multiple languages to cater to diverse populations.
- Use of Media and Social Networks: Leverage traditional and social media to spread awareness and stimulate voter participation.
- Engagement with Civic Organizations: Collaborate with non-governmental organizations to facilitate workshops and seminars on civic responsibility.
Enhancing Transparency and Accountability
- Mandatory Audits of Vote Counts: Implement mandatory, random audits of precincts to ensure the accuracy of vote counts.
- Public Access to Voting Records: Allow public scrutiny of anonymized voting records to foster transparency.
- Legislation for Electoral Integrity: Pass robust laws that penalize electoral fraud and protect whistleblowers.
- International Observers: Invite international observers to oversee elections and validate the fairness of the process.
- Real-Time Results Reporting: Develop systems for the real-time reporting of electoral results to reduce the risk of manipulation during delay periods.
Conclusion
To maintain public trust and uphold the democratic process, it is essential to continuously evaluate and reform the electoral system. By implementing the proposed changes in voter verification, EVM security, accessibility, and transparency, we can significantly enhance the effectiveness and fairness of elections, ensuring that every vote counts and is counted correctly.
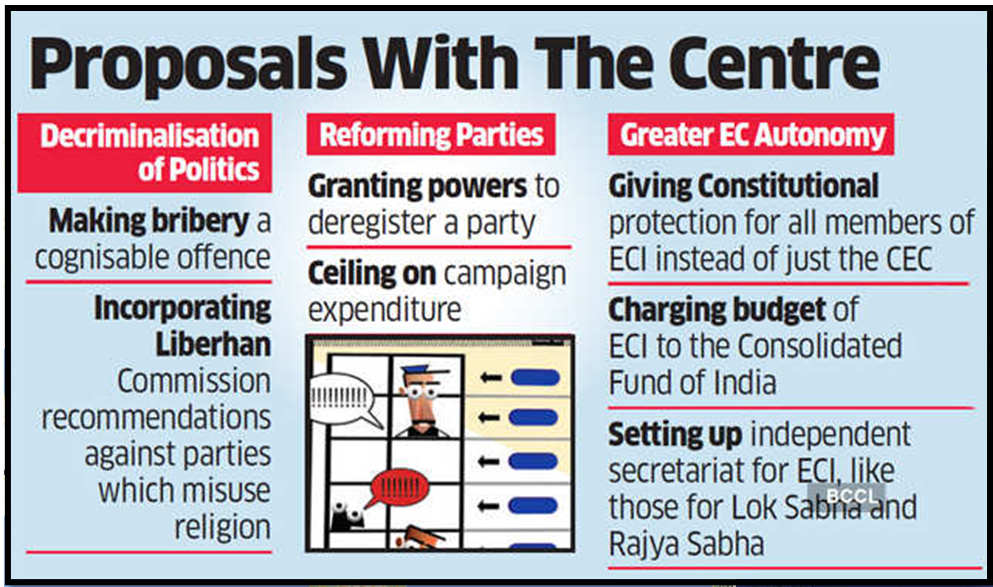
Electoral Reforms before 1996:
Electoral Reforms of 1996:
Electoral Reforms after 1996:
Electoral Reforms since 2010:
|
Source:The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
“Discuss the necessity for electoral reforms to enhance the transparency and integrity of the voting process in India. Suggest at least five innovative reforms that could be implemented to address the current challenges faced by the electoral system. Evaluate the potential impacts of these reforms on the democratic process in India.” (250 marks)
Associated Articles:
https://universalinstitutions.com/enhancing-representation-for-a-just-electoral-system/
https://universalinstitutions.com/comprehensive-reforms-needed-for-municipal-elections/