RBI’s Quality of Public Expenditure Index: Key Insights
Why in the News?
The RBI’s latest report on the Quality of Public Expenditure (QPE) Index highlights improved fiscal management in India. It assesses capital and revenue spending trends since 1991, showing better public expenditure quality, especially with a focus on capital investment post-COVID-19.
Context & Background:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has developed the Quality of Public Expenditure (QPE) Index using data since 1991 to assess how effectively the government spends public funds.
- India has focused on fiscal discipline, particularly after the introduction of the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act in 2003, which set limits on fiscal and revenue deficits.
- The aim is to enhance capital expenditure, which strengthens infrastructure and economic productivity, rather than excessive revenue spending like salaries and subsidies.
Key Findings & Implications
- The QPE Index evaluates capital outlay, development expenditure, and interest payments as a percentage of GDP.
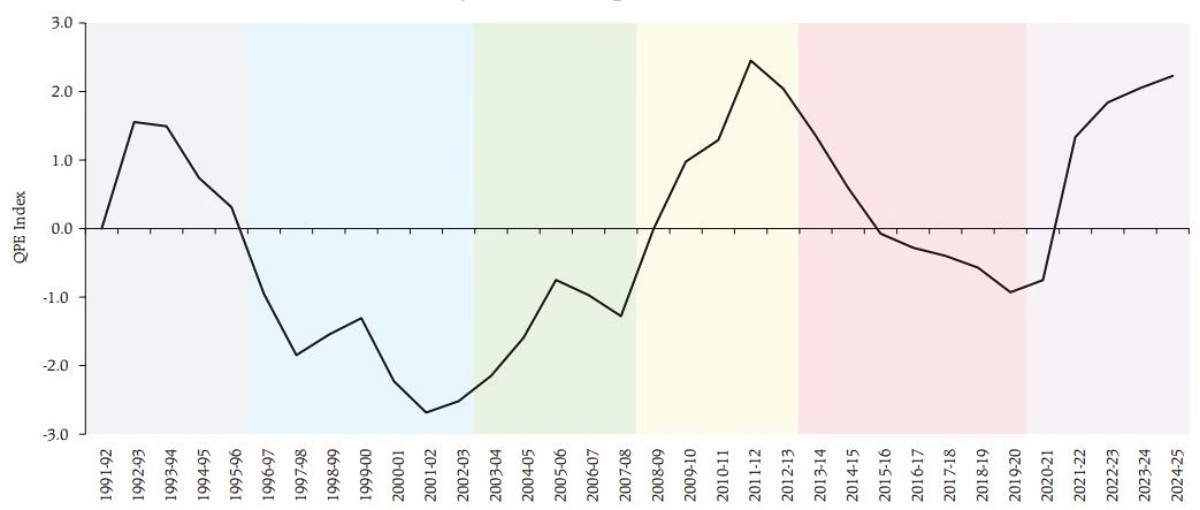
- Current spending quality is at its highest level since 1991 economic liberalization, indicating improved fiscal management.
- A continued emphasis on capital investment over revenue expenditure is crucial for long-term economic growth.
Trends in Public Expenditure:
- Phase 1 (1991-1996): Initial improvements in the Centre’s expenditure, but states struggled due to fiscal constraints.
- Phase 2 (1997-2003): Sharp decline due to increased revenue spending (higher salaries, interest payments) and lower capital outlay.
- Phase 3 (2004-2008): Growth rebounded with the FRBM Act’s implementation and strong economic expansion. States benefited from higher tax devolution.
- Phase 4 (2009-2014): Global Financial Crisis led to fiscal stimulus, increasing spending but also raising deficits.
- Phase 5 (2015-2019): States improved spending due to Finance Commission recommendations, while the Centre faced revenue-sharing challenges with GST implementation.
- Phase 6 (2020-present): The COVID-19 pandemic necessitated stimulus measures, but capital expenditure focus has improved spending quality.