RBI’S LIQUIDITY NORMS AND POTENTIAL IMPACT ON CREDIT GROWTH
Why in the News?
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has introduced new guidelines requiring banks to hold a higher stock of liquid assets to address potential bank runs.
- The guidelines focus on deposits made through digital channels, which are considered less stable and prone to quick withdrawals.
Source: BS
Key Provisions and Requirements
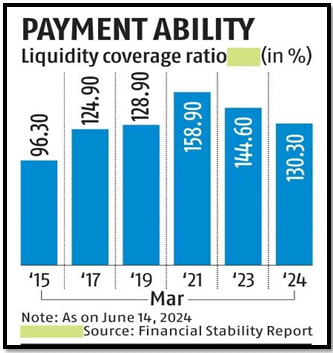
- Banks must maintain a Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR) of 100%, holding high-quality liquid assets (HQLA) like government securities.
- New rules mandate higher liquidity for digital deposits, increasing the run-off factor to 10% for stable retail deposits and 15% for less stable deposits via internet and mobile banking.
- Banks are also required to apply relevant haircuts on assets while calculating the LCR.
Potential Impacts and Industry Response
- The guidelines are seen as conservative, potentially forcing banks to invest more in government securities and slow credit growth.
- Banks might need to keep deposit rates elevated and temper growth to align with the new funding requirements.
- Analysts predict an 8-11% reduction in banks’ LCR, assuming varying levels of deposit linkage to internet and mobile banking, with moderate impacts on mid-cap banks and public sector banks.
| Understanding the Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR)
Key Concepts
Requirements
Current Status:
Associated Article: https://universalinstitutions.com/rbi-and-monetary-policy-in-india/ |