RBI MONETARY POLICY HIGHLIGHTS
Why in the News?
- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) unanimously maintains key interest rates.
Source: BankGyan
Key Highlights:
- GDP :The MPC raises the GDP growth projection for 2023-24 from 6.5% to 7%.
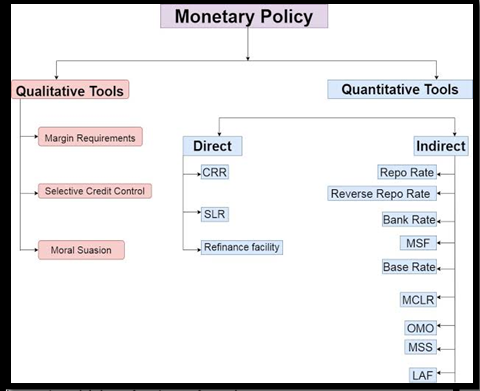
- Repo rate : The repo rate remains at 6.5%, offering no immediate relief to borrowers.
- Inflation : Average inflation forecast retained at 5.4%.
Cautionary note on potential inflation spikes in November and December.
Headline inflation remains volatile, influenced by supply shocks.
- Food Inflation Impact: Despite moderation in food inflation from double-digit levels in July to 6.2% in October, uncertainties persist.
Factors Influencing Inflation:
- Potential surge in consumer price index (CPI) inflation due to increased vegetable prices.
- Monitoring of crop output and concerns over elevated global sugar prices.
About Monetary Policy Committee (MPC):
- Origin:
- Enacted under Section 45ZB of the amended RBI Act, 1934, in 2016.
- Empowers the central government to establish a six-member Monetary Policy Committee (MPC).
- Objective: Section 45ZB specifies that the MPC is tasked with determining the Policy Rate to achieve the inflation target.
- Decision Authority: The decisions made by the Monetary Policy Committee are binding on the Bank.
- Composition:
- The MPC is comprised of six members as outlined in Section 45ZB.
- Members include the RBI Governor as the ex-officio chairperson, the Deputy Governor in charge of monetary policy, an officer nominated by the Central Board of the Bank, and three individuals appointed by the central government.
- Appointment Criteria: Persons appointed by the central government must possess “ability, integrity, and standing,” along with knowledge and experience in economics, banking, finance, or monetary policy.

 Source: BankGyan
Source: BankGyan

