RBI MAINTAINS RATES AMID PERSISTENT INFLATION CONCERNS
Why in the news?
The RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee kept interest rates unchanged to address rising retail inflation, driven by escalating food prices, impacting consumer confidence and economic stability.
source:paisabazaar
About RBI Maintains Interest Rates Amid Persistent Inflation:
- Monetary Policy Decision:
- The RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) decided to keep benchmark interest rates unchanged for the ninth consecutive meeting.
- The decision aims to address retail inflation, which has remained above the 4% medium-term target for 57 months.
- Persistent inflation is affecting consumer confidence and poses risks to broader monetary policy credibility.
- Inflation Concerns:
- Food Prices: Elevated food prices, especially vegetables, have contributed to persistent inflation. For example, tomato prices surged by 62%, onions increased by nearly 23%, and potatoes rose by 18%.
- Impact on CPI: Food prices make up about 46% of the Consumer Price Index (CPI), significantly affecting household budgets.
- Projection Adjustments: The MPC raised its retail inflation projection for the July-September quarter to 4%, up from the previous 3.8%. The forecast for the third fiscal quarter also increased to 4.7%.
| What is the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)?
Formation:
Members:
Functions:
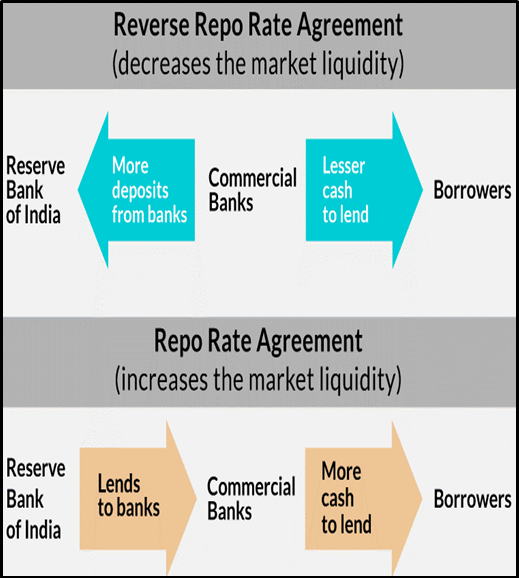
What is the repo rate? Definition: The repo rate is the interest rate at which a central bank, like the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), lends money to commercial banks for short-term needs. Purpose:
Associated Article: https://universalinstitutions.com/rbi-likely-to-maintain-repo-rate-amid-persistent-food-inflation/ |