RBI CONCERNS, US RECESSION FEARS, AND GLOBAL ECONOMIC CHALLENGES
Syllabus:
GS 3:
- Changes in Industrial Policy and their Effects on Industrial Growth.
- Indian Economy and issues relating to Planning, Mobilization of Resources, Growth, Development and Employment.
Why in the News?
Reliance Industries’ significant workforce reduction and slower hiring pace in FY24 have garnered attention, reflecting the company’s strategic adjustments amid economic uncertainties. The substantial decline in Reliance Retail’s headcount, coupled with a cautious hiring approach, highlights the company’s focus on operational efficiency and cost management.
Workforce Reduction at Reliance Industries
- Significant Reduction: Reliance Industries cut its workforce by 42,052 employees in FY24, with Reliance Retail seeing the largest drop of 38,029 employees. Voluntary separations were lower than the previous year.
- Hiring Slowdown: The company hired 171,116 new staff, 35% less than the previous year, reflecting a cautious approach to workforce expansion.
- Strategic Adjustment: The workforce reduction and slower hiring indicate a strategic focus on optimizing efficiency and managing costs in a challenging environment.
- Retail Sector Impact: The large reduction in Reliance Retail’s workforce suggests shifts in the retail sector, possibly due to changes in consumer behavior or operations.
- Focus on Efficiency: Reliance Industries is aligning workforce levels with current market conditions, emphasizing operational efficiency and future growth.
RBI’s Concern Over Credit-Deposit Mismatch
- Structural Liquidity Risks: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has raised concerns about the growing mismatch between credit growth and deposit growth, which has forced banks to rely on alternative, non-deposit sources of funding. This trend could expose the banking system to structural liquidity issues.
- Short-Term Funding Risks: RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das warned that banks’ increasing dependence on short-term non-retail deposits and other financial instruments to meet rising credit demand could create vulnerabilities in the banking system’s liquidity structure.
- Call for Household Savings: Governor Das emphasized the importance of banks focusing on mobilizing household financial savings as a more stable and sustainable source of funding to address the credit-deposit mismatch.
- Potential Impact on Banking Sector: The RBI’s concerns suggest that the banking sector may need to adjust its strategies to ensure long-term stability, particularly by aligning deposit mobilization efforts with credit expansion.
- Policy Implications: These developments highlight the need for careful monitoring and potential policy adjustments to mitigate risks associated with the credit-deposit mismatch, ensuring the resilience of the banking sector.
Recession Fears in the US
- Rising Recession Probability: Goldman Sachs has raised the probability of a recession in the US next year to 20%, up from 15%, following data showing unemployment rates hitting a near three-year high of 4.3%. This has sparked concerns about the potential for an economic downturn.
- Global Market Impact: Recession fears in the US have caused turbulence in global markets, with investors questioning whether the Federal Reserve has been slow in responding to economic conditions by adjusting interest rates.
- Interest Rate Concerns: The Bank of Japan’s rare interest rate hikes have contributed to market volatility, particularly by triggering the unwinding of the yen carry trade, further unsettling financial markets.
- Economic Uncertainty: The rising likelihood of a US recession adds to global economic uncertainty, with potential spillover effects on other economies, including emerging markets.
- Monitoring Developments: As recession risks grow, ongoing developments in the US economy and central bank policies will be closely watched for their broader implications on global economic stability.
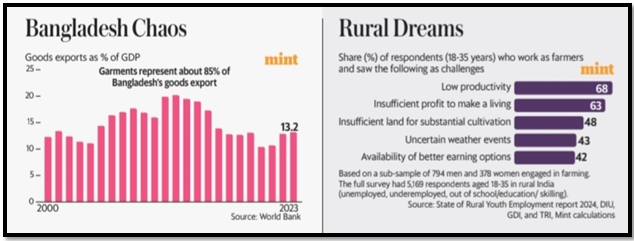
Bangladesh in Crisis
- Political Turmoil: Bangladesh has entered a period of political crisis, with Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina being forced to resign and flee the country following massive protests against government job quotas. This marks a significant turn in the nation’s recent political and economic history.
- Economic Challenges: Despite Bangladesh’s remarkable economic growth, particularly in the ready-made garments sector, the country has begun to face limitations in its export-led growth model, with its share in GDP declining in recent years.
- Comparison with Neighbors: Bangladesh’s economic success had previously allowed it to surpass India and Pakistan in terms of per-capita income, but recent political instability may jeopardize its progress.
- Impact on Exports: The crisis raises concerns about the future of Bangladesh’s export sector, which has been a key driver of its economic turnaround, potentially affecting its position in the global market.
- Uncertain Future: The political and economic upheaval in Bangladesh underscores the fragility of its growth model, with potential long-term implications for the region’s economic dynamics.
Challenges in Rural Employment
- Agriculture Dominance: Agriculture remains the primary source of employment in rural areas, but a majority of young people are increasingly seeking salaried jobs instead, driven by dissatisfaction with the challenges in farming.
- Low Productivity Concerns: A survey by Development Intelligence Unit, Global Development Incubator, and Transforming Rural India found that over 60% of young respondents cited low productivity and insufficient profits as key reasons for wanting to leave agriculture.
- Limited Land and Market Access: Additional challenges include insufficient land for substantial cultivation and limited access to markets, which further discourage young people from pursuing agriculture as a viable career.
- Debt Traps for Small Farmers: Many small farmers face debt traps, adding to the financial pressures and making agriculture an unattractive option for the younger generation in rural areas.
- Shift in Employment Aspirations: The findings highlight a significant shift in employment aspirations among rural youth, indicating a growing need for alternative job opportunities outside of agriculture to address these challenges.
Medical Education Expansion
- Increase in Medical Seats: The Union government plans to add additional undergraduate medical seats in response to recent criticism over the medical entrance exam fiasco, bringing the total number of seats to 115,000.
- Approval of New Colleges: The National Medical Commission has approved the establishment of 28 private medical colleges, aimed at increasing the availability of medical education and addressing the growing demand for healthcare professionals.
- Response to Criticism: This expansion is part of the government’s broader efforts to address concerns about access to medical education and ensure that more students have the opportunity to pursue careers in healthcare.
- Impact on Healthcare Sector: The increase in medical seats is expected to have a positive impact on the healthcare sector, helping to meet the rising demand for doctors and improving the overall quality of medical services.
- Educational Reforms: The government’s decision to expand medical education reflects its commitment to reforming the sector and addressing the challenges highlighted by recent controversies.
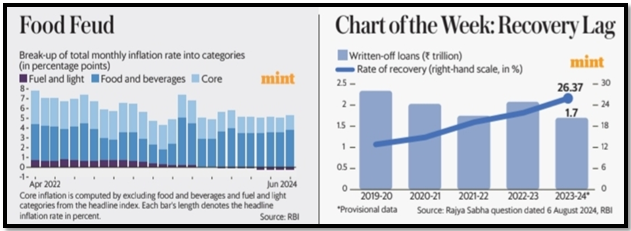
Food Inflation Debate
- Excluding Food Inflation: The Economic Survey 2024 proposed excluding food inflation from the overall inflation target, a suggestion that has sparked debate among economists and policymakers.
- Impact on Inflation Targeting: A Mint analysis argues that excluding food inflation may not be practical, as large and persistent food price shocks significantly influence non-food prices and household inflation expectations.
- Close Linkages: The close alignment between food prices and overall inflation suggests that food inflation cannot be ignored in the broader context of inflation management.
- Flexible Approach Needed: The analysis advocates for a flexible, situation-driven approach to managing inflation, similar to the current strategy employed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- Policy Considerations: The debate underscores the complexities of inflation targeting and the need for careful consideration of all factors, including food prices, in the formulation of monetary policy.
Recovery Lag in Indian Banks
- Low Recovery Rates: Indian banks have managed to recover only a fifth of bad loans over the past five years, with an average recovery rate of 19% between FY20 and FY24, during which loans worth ₹9.9 trillion were written off.
- Gradual Improvement: Despite the low overall recovery rate, there has been a gradual improvement, with the rate increasing from 12.8% in FY20 to 26.4% in FY24, indicating some progress in addressing non-performing assets.
- Challenges in Bad Loan Recovery: The data highlights the ongoing challenges faced by Indian banks in recovering bad loans, which continue to weigh heavily on their balance sheets and profitability.
- Policy Implications: The slow pace of recovery underscores the need for more effective strategies and policy interventions to deal with the issue of bad loans in the banking sector.
- Future Outlook: The improvement in recovery rates offers some hope, but sustained efforts will be necessary to achieve meaningful progress in reducing the burden of bad loans on the banking system.
Conclusion
Reliance Industries’ workforce strategy in FY24 underscores its adaptability to evolving market conditions. By reducing its workforce and slowing down hiring, the company aims to enhance operational efficiency and align its human resources with current and future business needs, ensuring sustainable growth in a challenging economic landscape.
Source:The Mint
Mains Practice Question
Discuss the implications of workforce reductions and hiring slowdowns by major conglomerates like Reliance Industries on the broader economy and employment landscape in India. How should companies balance operational efficiency with employment generation?
Associated:
https://universalinstitutions.com/workers-await-benefits-of-recovery/