Q Discuss the challenges of achieving just representation in Parliament. Examine the impact of electoral systems on fostering inclusive and equitable political representation. (GS 2)
Q Discuss the challenges of achieving just representation in Parliament. Examine the impact of electoral systems on fostering inclusive and equitable political representation. (GS 2)
| Structure of Answer
Introduction · Mention about the situation of political representation in India. Body · Mention Challenges of Achieving Just Representation in Parliament · Mention Impact of Electoral Systems on Inclusive Representation · Mention Strategies for Fostering Inclusive Representation Conclusion · Mention the future of inclusive representation envisions every voice contributes to shaping the collective destiny. |
Answer-
“Equal representation is not just about fairness, it’s about strength. A society that excludes the voices of its citizens is a society that is weakened.” ~ Eleanor Roosevelt
The pursuit of just representation in Parliament, an ideal that embodies equal political voice and influence for all citizens, remains a persistent challenge in many democracies. While considerable progress has been made in expanding voting rights and establishing democratic institutions, several factors continue to hinder the realization of truly representative Parliaments.
Challenges of Achieving Just Representation in Parliament
- Societal Divisions and Marginalization: Societal disparities based on factors such as income, education, gender, caste, ethnicity, and other markers of identity can create barriers to equal representation. Example: Scheduled Castes account for around 16% of the population but only 7.5% of Lok Sabha members and 14.6% of Rajya Sabha members.
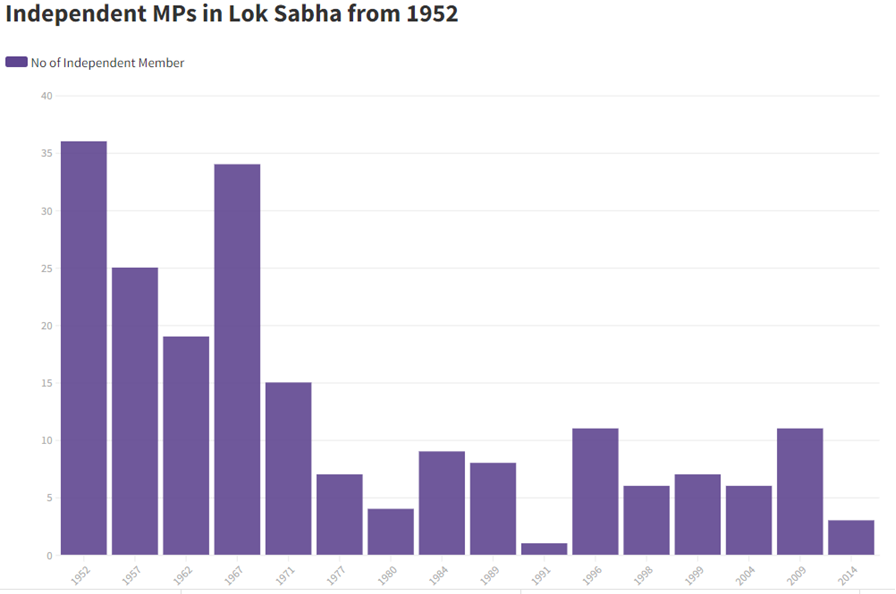
- Political Party: The dominance of major political parties often overshadows the voices of smaller parties and independent candidates, making it difficult for diverse perspectives to gain representation in Parliament. Example: Smaller parties and independent candidates secured a meager 5.9% of seats, highlighting the dominance of larger parties under the FPTP system.
- Money and Politics: The influence of money in politics can significantly distort the electoral process and hinder the representation of marginalized groups. The ability of wealthy candidates and parties to dominate campaigns can limit the opportunities for diverse voices to be heard, making it more challenging for them to gain representation.
- Media Bias and Representation of Diverse Voices: Media coverage and portrayal of candidates and political parties can influence public perceptions and impact election outcomes. Bias or inadequate representation of marginalized groups in the media can further hinder their chances of gaining representation in Parliament.
- Patriarchal Structures: Deep-rooted patriarchal structures persist in many societies, influencing political institutions. These structures can perpetuate gender biases, limiting the participation and representation of women in political processes.
Source: Deccan herald
Impact of Electoral Systems on Inclusive Representation
- The Women’s Reservation Bill: The recent passage of the Women’s Reservation Bill is a landmark development. This legislation reserves 33% of seats in Parliament for women, aiming to address the historical underrepresentation of women in politics. Its impact depends on effective implementation and addressing associated challenges.
- Regional Dynamics: Understanding regional dynamics is crucial in assessing the impact of electoral systems. In some regions, cultural factors may significantly influence political representation, posing unique challenges for the effective implementation of measures like the Women’s Reservation Bill.
- Reserved Seats for Marginalized Groups: Affirmative action through reserved seats for SCs and STs aims to address social inequalities, but debates persist on its effectiveness in ensuring genuine empowerment.
- Coalition Politics Impact Inclusivity: Coalition governments in India present both challenges and opportunities for inclusivity. While they require compromise, there’s a risk of major partners dominating decision-making, affecting smaller parties and marginalized communities.
Strategies for Fostering Inclusive Representation
- Encourage Political Party Diversity: Promote the formation and growth of political parties that represent the interests of marginalized groups, expanding representation options.
- Limit the Influence of Money in Politics: By reducing the financial advantage of wealthy candidates and parties, more diverse candidates can compete effectively.
- Promote Responsible Media Coverage: Accurate representation and diverse coverage in media can amplify the voices of marginalized groups and foster inclusive political discourse.
- Electoral Reforms: Exploring and implementing electoral reforms, such as proportional representation or mixed-member systems, can enhance inclusivity by providing a more accurate reflection of the diverse political landscape and reducing barriers for smaller parties and independent candidates.
The future of inclusive representation envisions a political landscape that harnesses the full potential of technology, embraces diversity in its myriad forms, and facilitates a participatory democracy where every voice contributes to shaping the collective destiny.
Source:https://www.deccanherald.com/india/from-36-to-3-where-are-independent-ls-members-729138.html