Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana- 1.0
Relevance
- GS Paper 2 Important aspects of governance, transparency and accountability, e-governance, applications, models, successes, limitations, and potential;
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Tags: #pmmy #Mudra #refinance #scheme #currentaffairs #upsc
MUDRA (Micro Units Development and Refinance Agency)
- MUDRA was established by the Government of India as a wholly owned subsidiary of the Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) with 100% capital contribution from SIDBI.
- As of the present, MUDRA’s authorized capital stands at ₹5000 crores, with a paid-up capital of ₹1675.92 crores, fully subscribed by SIDBI. Additional capital infusion is expected to further enhance MUDRA’s operations.
- MUDRA’s core responsibility is to develop and refinance the micro-enterprise sector by offering support to financial institutions engaged in lending to micro and small businesses in manufacturing, trading, and service activities.
- Micro Finance serves as an economic development tool aimed at providing income-generating opportunities to individuals at the grassroots level, offering not only credit but also additional services like financial literacy and social support.
What Is Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana and Its Objectives?
The PM MUDRA Yojana is a flagship scheme of the Government of India launched on 8th April 2015. The primary aim of PMMY is to offer collateral-free access to credit for micro enterprises, particularly in the non-farm sector.
- This scheme targets income-generating micro enterprises involved in manufacturing, processing, trading, or services, providing loans up to Rs. 10 lakh.
- MUDRA works with financial intermediaries to extend loans to non-corporate, non-farm sector activities of micro and small entities.
- These entities encompass a wide range of businesses, including small manufacturing units, service providers, shopkeepers, vendors, truck operators, food-service units, artisans, and more in both rural and urban areas.
- Loans under the MUDRA scheme are accessible through various banking and lending institutions, such as
- Public sector banks,
- Private sector banks,
- State-operated cooperative banks,
- Rural banks,
- Microfinance institutions, and
- Non-bank financial companies.
- The implementation of financial inclusion in India is based on three key pillars:
- Banking the Unbanked
- Securing the Unsecured
- Funding the Unfunded
- These three objectives are attained by harnessing technology and embracing a collaborative approach that involves multiple stakeholders, all while catering to those who have historically been overlooked and underserved.
- Funding the Unfunded, one of these pillars, is exemplified by PMMY, which aims to provide credit access to small entrepreneurs.
- This is achieved through a collaborative approach that leverages technology and involves multiple stakeholders to serve those who have traditionally been unserved and underserved.
Features of PMMY
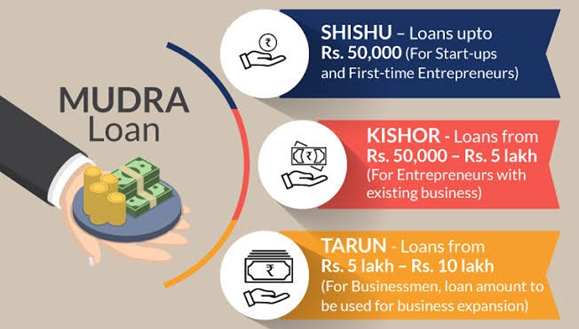
The scheme offers benefits categorized into ‘SHISHU,’ ‘KISHOR,’ and ‘TARUN,’ representing the various stages of growth and funding requirements for micro units and entrepreneurs.
These categories not only serve as a reference point for their growth trajectory but also ensure a balanced distribution of credit. It is guaranteed that a minimum of 60% of the credit will be directed to Shishu Category Units, with the remaining portion allocated to Kishor and Tarun Categories.
While PMMY loans do not come with a subsidy, they can qualify for inclusion if the loan proposal is associated with a government scheme offering capital subsidies.
- SHISHU: For individuals in the early stages of their business or those requiring minimal capital to commence their venture. Eligible for a credit amount of up to Rs. 50,000
- KISHOR: Targeted at entrepreneurs needing funding between Rs. 50,000 and Rs. 5 lakh. Includes individuals who have already initiated their business and seek additional funds for expansion.
- TARUN: Geared towards entrepreneurs with a funding requirement of up to Rs. 10 lakh, representing the maximum loan amount available for start-up businesses.
The interest rates are determined by lending institutions according to RBI guidelines. For working capital facilities, interest is only levied on the funds held overnight by the borrower.
MUDRA Card
- MUDRA Card is an innovative credit product designed to offer borrowers a hassle-free and flexible means of accessing credit.
- It provides borrowers with a working capital arrangement in the form of an overdraft facility, making it easier to manage their finances.
- This card functions as a RuPay debit card, allowing users to withdraw cash from ATMs or Business Correspondents, as well as make purchases using Point of Sale (POS) machines.
- Borrowers also have the convenience of repaying the borrowed amount whenever they have surplus cash, thereby reducing the overall interest cost.
MUDRA App – “MUDRA Mitra”
- “MUDRA MITRA” is a mobile phone application accessible through Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
- This app is a valuable resource for individuals seeking information about the “Micro Units Development and Refinance Agency Ltd. (MUDRA)” and its various products and schemes.
- It serves as a guide for loan seekers who wish to approach a bank for obtaining a MUDRA loan under the Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY).
- Users of the app can access a wealth of loan-related material, including sample loan application forms, making it a comprehensive tool to facilitate the loan application process.
Beneficiaries of PMMY
PMMY loans cater to both term loans and working capital needs for income-generating activities in sectors like manufacturing, trade, and services, including allied agricultural activities such as poultry, dairy, and beekeeping.
Borrowers who qualify for the scheme include:
- Individuals.
- Proprietorship concerns.
- Partnership firms.
- Private Limited Companies.
- Public Companies.
- Other legally recognized entities.
Applicants must not have a history of defaulting on loans from banks or financial institutions and should maintain a satisfactory credit track record.
- Individual borrowers may be required to demonstrate the necessary skills, experience, or knowledge required for their proposed business activity.
- The need for any specific educational qualifications, if applicable, will be determined based on the nature and requirements of the proposed activity.
Sectors covered
In order to expand the reach of the program and tailor financial products to meet the specific needs of various business activities, sector-focused schemes will be introduced. Initially, these schemes are being proposed for the following sectors based on the higher concentration of businesses:
- Land Transport Sector/Activity: This will support businesses in acquiring transport vehicles for both goods and personal transportation, including auto-rickshaws, small goods transport vehicles, three-wheelers, e-rickshaws, passenger cars, and taxis.
- Community, Social & Personal Service Activities: These include businesses such as salons, beauty parlors, gyms, boutiques, tailoring shops, dry cleaning services, cycle and motorcycle repair shops, DTP and photocopying facilities, medicine shops, and courier agents, among others.
- Food Products Sector: This sector encompasses activities like making papads, pickles, jams, agricultural produce preservation at the rural level, sweet shops, small food stalls, daily catering services, cold chain vehicles, cold storages, ice-making units, ice cream production, biscuit and bread making, and more.
- Textile Products Sector/Activity: Support is provided for various activities within the textile industry, including handloom and powerloom operations, chikan work, zari and zardozi work, traditional embroidery, dyeing and printing, apparel design, knitting, cotton ginning, computerized embroidery, stitching, and the production of textile non-garment products such as bags, vehicle accessories, and furnishing accessories.
To Enhance Scheme Implementation
- Handholding Assistance: Providing dedicated support to assist loan applicants in the process of submitting their loan applications. This guidance ensures that potential borrowers can navigate the application process with ease.
- Online Application Facilities: Introducing the convenience of online application submission through platforms such as PSBloansin59minutes and Udyamimitra portal. This digital approach streamlines the application process, making it more accessible.
- Extensive Public Awareness Campaigns: Launching robust publicity campaigns to increase awareness of the scheme among all relevant stakeholders. These campaigns aim to promote greater visibility and understanding of PMMY.
- Streamlined Application Forms: Simplifying the loan application forms to make them more user-friendly and less complex, thus reducing barriers to entry for potential borrowers.
- Appointment of MUDRA Nodal Officers: Designating MUDRA Nodal Officers within Public Sector Banks (PSBs) to oversee and facilitate the implementation of the scheme. These officers serve as points of contact for borrowers and play a crucial role in ensuring smooth operations.
- Ongoing Performance Monitoring: Regularly monitoring the performance of Public Sector Banks in relation to the Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY). This monitoring process helps in assessing the effectiveness and efficiency of the scheme’s implementation, allowing for necessary adjustments and improvements.
Mains question
Analyze key objectives of the Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana and assess its impact on micro-enterprises and economic development in India.