PERMANENT STATUS: ON PALESTINE AND THE UN
Relevance: GS 2 – Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
Why in the News?
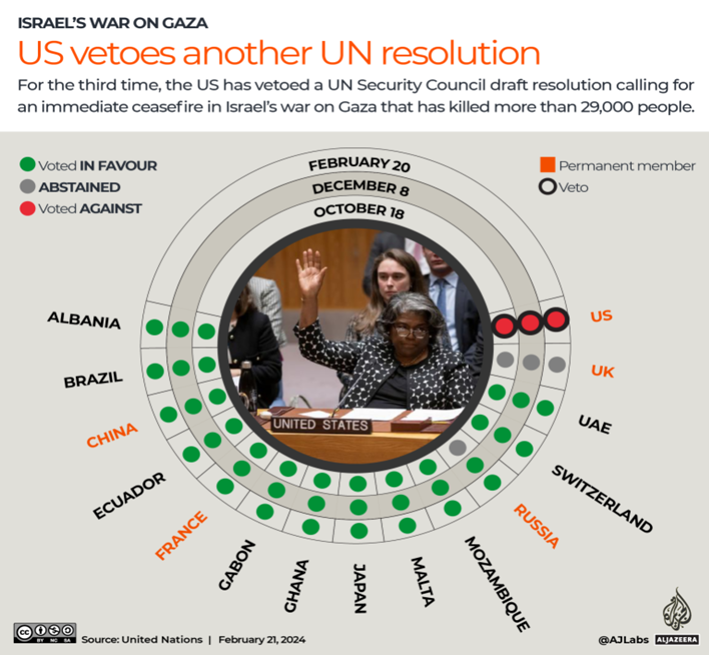
- The UN Security Council resolution proposing full-member status for Palestine was vetoed by the United States.
- The resolution, put forward by Algeria, aimed to fulfill the promise made in 1947 to partition the then-mandated Palestine into two states: one Jewish and one Arab.
- Currently, only Israel has full membership in the UN since 1949.
Historical Background
- The “Question of Palestine” has been debated for decades.
- In 2012, Palestine received permanent observer status at the UN.
- In 2019, Palestine had temporary powers of a full member while chairing the G-77 and China grouping.
U.S. and Israeli Stance
- The S. vetoed the UNSC resolution despite support from 12 of 15 UNSC members.
- The S. believes Palestine should achieve membership through direct negotiations between the parties.
- The Israeli Ambassador opposed granting Palestine membership, citing the recent terror attacks by Hamas on October 7 as reason to deny membership.
Current Situation
After the October 7 terror attacks by Hamas, Israel has conducted bombings in the Gaza Strip and the West Bank.
- Israel has continued its operations despite a UNSC ceasefire resolution, which the U.S. also signed.
- Israel now threatens another offensive on Rafah, highlighting the urgent need for Palestine to have a stronger voice on the multilateral stage
Need for Recognition
- Self-Determination: Palestinians have a right to self-determination under the U.N. Charter. Membership acknowledges this right and grants them a voice on their future.
- Two-State Solution:N. recognition could bolster the two-state solution as the accepted framework for Israeli-Palestinian peace.
- Legitimacy and Equality: Inclusion in the U.N. affirms Palestine’s legitimacy as a state and promotes equality with other member nations.
- Accountability: Membership strengthens Palestine’s ability to hold Israel accountable for actions deemed violations of international law.
- International Cooperation:N. membership facilitates access to international organizations and resources for development, humanitarian aid, and human rights protections.
- Economic Benefits: Formal recognition allows Palestine to participate in international trade agreements and attract foreign investment, potentially boosting its economy.
- Psychological Boost:N. membership could provide a significant morale boost for the Palestinian people, fostering hope for a brighter future.
- However, it’s important to acknowledge complexities:
- Israeli Security Concerns: Israel fears U.N. membership could embolden Palestinian actions against them. Negotiations are seen as crucial.
- Palestinian Unity: Internal divisions within the Palestinian leadership raise concerns about effective governance as a full member.
Reconsideration of U.S. Stance on Israel
- The U.S. should reconsider its unwavering support for Israel on all issues.
- The argument that Palestine should only achieve statehood through “dialogue between the parties” is flawed.
- Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu stated in January that he would never accept a Palestinian state and intended to retain “full Israeli security control over all the territory west of Jordan”.
Benefits of UN Membership for Palestine
Palestinian membership in the UN would bind the new state to the obligations of all UN members. Conflating all Palestinians with terrorist acts by Hamas is a gross injustice. Refusing to distinguish between combatants and non-combatants marginalizes all victims of violence.
- International Recognition:N. membership grants formal recognition of Palestine as a sovereign state. This strengthens its legitimacy and standing on the world stage.
- Political Participation: Palestine gains voting rights in the General Assembly, allowing it to influence U.N. resolutions and participate more actively in international discussions.
- Legal Tools: Membership unlocks access to the International Court of Justice (ICJ). Palestine could potentially pursue legal challenges against other states, including Israel.
- Diplomatic Leverage:N. membership enhances Palestine’s diplomatic standing. It can establish embassies and formal relations with other member states.
- Peace Process: Some argue U.N. involvement could pressure a more balanced approach to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
U.S. Role and UN Principles
- As the international order becomes more fractured, the U.S., as a global leader, should aim to build consensus rather than favoring one country.
- The U.S. approach contradicts the UN’s basic principle of sovereign equality for all nations.
- The current approach leans towards the primitive dictum that “might is right”.
Mains Question
Discuss the implications of the recent UN Security Council resolution on granting Palestine full-member status. Examine the U.S. stance and its alignment with UN principles on sovereign equality. (250 words)