PENSION CONCERNS: ON THE EPFO RECOMMENDATION
Relevance:
- GS 2 – Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
- GS 3 – Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
Why in the News?
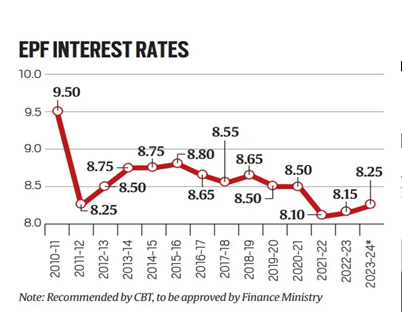
- The Central Board of Trustees of the Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) has recommended a higher interest rate of 8.25% for the financial year 2023-24.
- It has recommended a 1-percentage-point increase in PF deposits for 2023-24.
- The proposed rate marks the highest interest rate for EPF subscribers in the past three years.
- This interest rate applies to EPF subscribers, totaling over 29 crore, with approximately8 crore being active contributing subscribers.
Comparison with Previous Years
- The recommended interest rate of 8.25% for 2023-24 is 0.4-percentage points lower than the rate in 2018-19.
- Notably, 2018-19, like 2023-24, was a pre-election year.
- Financial Implications: If approved by the Union Finance Ministry, the recommendation would involve transferring a record ₹1,07,000 crore to EPF members.
Minimum Pension Implementation
- Since September 1, 2014, a minimum pension of ₹1,000 per month under the EPS has been provided through budgetary support, benefiting around 20.5 lakh pensioners.
- Though, the BJP advocated for a ₹3,000 minimum pension, when in opposition.
- This information was disclosed in an action taken report (ATR) presented recently in the Rajya Sabha, alongside the response of a query regarding the status of implementing recommendations from the 147th report of the Committee on Petitions, also known as the Bhagat Singh Koshyari Committee report.
- Implementation of Recommendations:
- The government considered panel recommendations and implemented feasible ones administratively and financially.
Concerns Regarding Minimum Pension
- Increasing the minimum pension: The government should consider that the difference between the minimum and original pension amounted to approximately ₹970 crore for 2022-23.
- Doubling the minimum pension would not impose a significant financial strain based on this calculation.
- Equating the amount of spouse pension with what a member-pensioner receives.
- Rules regarding higher PF pension were formulated after a 2022 Supreme Court judgment, potentially leaving out most pre-2014 retirees;
- There are approximately four lakh applications for higher pension pending.
- Adopting a more comprehensive approach to PF pension matters would benefit senior citizens.
Finance Ministry’s Views
- The Finance Ministry rejected a proposal to double the minimum pension, citing concerns about the substantial increase in budgetary support required under the Employees’ Pension Scheme (EPS), 1995.
- The budgetary support also includes the Central government’s contribution at 1.16% of wages up to ₹15,000 a month.
- For FY 2024-25, the Ministry projects ₹10,950 crore as budgetary support, compared to the revised estimate of ₹9,760 crore for the current year.
- The Ministry argues that a 100% rise in the minimum pension would lead to a disproportionate increase in overall budgetary support, considering that many pensioners received less than ₹1,000 as monthly pension until 2014.
Employees’ Pension Scheme (EPS) Nature
- The government described the EPS as a “Defined Contribution-Defined Benefit” social security scheme in the Rajya Sabha.
- It asserted that all benefits were funded through contributions, highlighting an actuarial deficit based on the fund’s valuation as of March 31, 2019.
- However, the EPFO’s annual report for 2022-23 contradicts this argument, suggesting that the actuarial deficit claim is not substantial.
| Definition of Actuarial Deficit
● Actuarial deficit is the shortfall between future Social Security obligations and the income rate of the Social Security Trust Fund at present. ● It represents the variance between the anticipated payouts from the Social Security program in the future and the existing income rate of the program’s trust funds. |
Significant Improvement in Actuarial Deficit
- The Central government has reported a “significant drop” in the actuarial deficit of the Employees’ Pension Fund (EPF).
- This improvement is attributed to enhancements in data quality concerning members of the Employees’ Pension Scheme (EPS), 1995.
- Amendments based on recommendations from the actuarial valuation report and suggestions from the Union Finance Ministry have contributed to this achievement.
| Some recommendations of Bhagat Singh Koshyari Committee
Amendments to Pension Scheme ● It included changes in the calculation of pensionable salary, which shifted to a 60-month average instead of a 12-month average. ● Eligible service determination was modified to base on contributory service rather than simple length of service. Improvements in Data Collection and Valuation ● Special efforts were made to gather information on members, leading to better data quality. ● Valuation exercises for 2011-12, 2012-13, and 2013-14 utilized data from almost 60% of active contributing members and 100% of pensioners, enhancing reliability. Replace EPS ● Despite suggestions to conduct valuation every three years and replace EPS with a Provident Fund-cum-Pension Annuity Scheme, no consensus was reached during CBT meetings in September 2010 and January 2014. ● Annual valuation was deemed necessary, and annuity-based scheme proposal was not pursued further. Addressing Inflation and Efficient Management ● Price rise neutralization in pension amounts to offset inflation was deemed infeasible due to the funded scheme’s features of defined benefits and defined contribution. ● EFPO appointed fund managers in September 2008 for better corpus management, adhering to investment patterns prescribed by the Union Finance Ministry and guidelines set by EPF’s CBT. |
Mains question
In the context of the recent Employees’ Provident Fund rate hike recommendation, discuss the potential socio-economic impact and the government’s role in balancing the interests of EPF subscribers. (250 words)