PARLIAMENT’S INTERVENTION AND PERFORMANCE
Syllabus:
- GS 2: Parliament and State legislatures—structure, functioning, conduct of business, powers & privileges and issues arising out of these.
Focus:
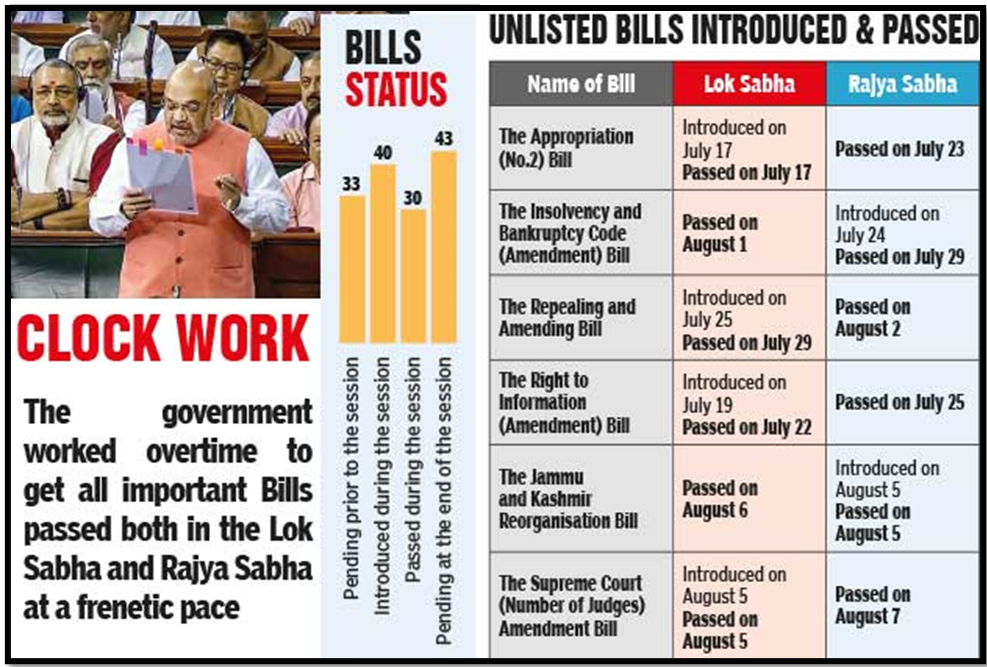
- 17th Lok Sabhas concluded its proceedings with extended sessions
Source: The Hindu
In the ever-evolving landscape of parliamentary dynamics, the functioning of legislative bodies offers invaluable insights into the changing priorities and challenges faced by nations. The reflection on past parliamentary sessions provides a lens through which we can gauge shifts in focus, engagement, and the pursuit of accountability within the corridors of power.
Historical Reflections:
- Extended Sessions: Both the 17th and previous Lok Sabhas concluded their proceedings with extended sessions, hinting at historical parallels.
- Precedent Setting: As the nation prepares for the upcoming general election, it raises questions about whether history will repeat itself or new precedents will be set.
- Shifts in Working Schedule: The departure from the usual five-day working schedule in the 17th Lok Sabha marked a notable change, prompting reflection on the evolving dynamics of parliamentary functioning.
Performance of Ministries:
- Prime Minister’s Office: The Office of the Prime Minister witnessed a decrease in the number of questions addressed, reflecting a declining interest in seeking answers from the executive office.
- Prominence of Ministries: Ministries of Health and Family, and Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare have emerged as the top two Ministries with the highest number of questions, indicating shifting parliamentary priorities.
- Decline in National Security Focus: Declining interest in matters of national security and internal affairs, with the Ministry of Home Affairs fading into obscurity, raises concerns about national priorities.
- Legislative Activity: Despite being the Ministries with the most number of questions, there is a marginal decline in the number of questions in the House of the People, indicating a shift in parliamentary focus.
- Impact of COVID-19: Scrutiny of the country’s health-care system preceded the COVID-19 pandemic, highlighting consistent monitoring by representatives, and indicating an increased awareness of public health concerns.
Legislative Engagement:
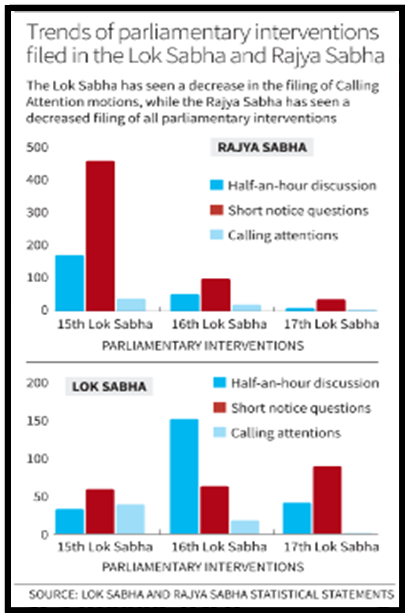
- Trends in Parliamentary Interventions: Trends show a decline in the filing of various parliamentary interventions, highlighting the need for revitalization of legislative engagement and constructive debate.
- Ministry of Finance: Despite decreased parliamentary interest, there is a promising increase in questions admitted for deliberation, signaling a commitment to transparency.
- Education Sector: Education remains a significant topic for parliamentary discourse, albeit with an increase in disallowed questions, raising concerns about oversight efficacy.
- Utilization of Interventions: Zero Hour has seen a significant increase in usage, reflecting a heightened focus on addressing pressing issues and seeking clarifications.
- Dwindling Usage of Other Interventions: Other interventions such as ‘Half-an-Hour Discussions’, ‘Short Notice Questions’, and ‘Calling Attention’ have witnessed dwindling usage, necessitating a balance in leveraging different platforms for debate and solution-seeking.
| Question Hour:
· Definition: The first hour of every parliamentary sitting designated for questioning is termed as Question Hour, as per the Rules of Procedure of the House. Types of Questions: · Starred Questions: Marked with an asterisk, these require oral answers allowing for supplementary questions. · Unstarred Questions: Demand a written response and do not allow for supplementary questions. · Short Notice Questions: Address urgent matters of public importance, requiring oral answers and a notice period of less than ten days. Zero Hour: · Description: An Indian parliamentary innovation not formally outlined in parliamentary rules, where Members of Parliament (MPs) can raise urgent matters without prior notice. · Timing: Occurs immediately after Question Hour and extends until the regular business of the House for the day begins, termed as the ‘Zero Hour.’ Half-an-Hour Discussion: · Purpose: Intended for discussing matters of significant public importance that have undergone considerable debate and require factual elucidation. · Frequency: The Speaker can allocate three days in a week for such discussions, without the need for formal motions or voting. Short Duration Discussion: · Alternate Name: Also referred to as a ‘Two-hour Discussion’ due to the maximum time limit of two hours. · Nature: Members of Parliament can initiate discussions on urgent matters of public importance, allocated for two days a week by the Speaker. · Historical Context: Established in 1953, this device serves as a platform for swift deliberations on pressing issues without formal motions or voting procedures. |
Overlooked Opportunities:
- Instances of Oversight: Despite notable performance, instances of oversight such as failure to raise privilege motions and missed discussions on crucial issues highlight the need for increased accountability and proactive engagement.
- Winter Session, 2023: The missed discussion on the sensitive issue of ‘Suicides among students due to competitive exams’ during the Winter Session, 2023 of the Rajya Sabha underscores a failure to address societal concerns through parliamentary channels.
- Need for Accountability: Changing parliamentary dynamics emphasize the importance of seizing every opportunity to ensure accountability, foster constructive debate, and prioritize the welfare of the nation and its citizens.
- Role of Opposition: There was a time when a strong Opposition could ensure the withdrawal of Bills, indicating the significance of an active and engaged Opposition in parliamentary proceedings.
- Policy Enactment: Revitalizing legislative engagement is essential for enacting policies that prioritize the welfare of the nation and its citizens, especially in the face of evolving challenges and priorities.
Conclusion:
As we navigate the complexities of governance and democratic processes, the analysis of parliamentary trends underscores the importance of adaptability, transparency, and proactive engagement. By learning from past experiences and embracing a renewed commitment to constructive debate and accountability, nations can strive towards more effective governance and better serve the interests of their citizens.
| Functions of Parliament:
· Representation of Society: Enables diverse sections of society to voice concerns and participate in decision-making processes. · Ensuring Accountability: Upholds collective responsibility of the Council of Ministers to the Lok Sabha and the citizens of India, facilitating control over elected executives. · Tools for Accountability: Provides mechanisms such as Zero Hour, Question Hour, Motions, and Resolutions to extract accountability from the government. · Coalition Building: Allows fragmented political opinions to converge into stable coalitions to address various issues. · Platform for Deliberation: Serves as the highest forum for deliberating over national issues. · Constitutional Amendments: Exclusive authority to carry out amendments to the Constitution. · Enactment of Laws: Empowered to enact laws under the Union List, Concurrent List, and, under special circumstances, the State List of the 7th Schedule of the Constitution. · Scrutiny through Committees: Parliamentary Committees facilitate effective scrutiny of government functioning, finances, and legislation. · Budget Approval: Union Budget is presented before Parliament for approval, ensuring financial accountability and oversight. · Impeachment Authority: Holds the power of impeachment for the President and removal of judges from the Supreme Court and High Courts. · Election Processes: Responsible for the election of the President and Vice-President, ensuring democratic electoral procedures. |
Source:
https://epaper.thehindu.com/reader
Mains Practice Question:
“Reflecting on the historical trajectory of parliamentary sessions and their evolving dynamics, discuss the significance of past trends in shaping contemporary governance. Analyze the shifting priorities, legislative engagement, and oversight challenges highlighted in the performance of Ministries and parliamentary interventions. Furthermore, evaluate the implications of missed opportunities and the role of parliamentary accountability in fostering effective governance. (250 words)”
Associated Articles
https://universalinstitutions.com/budget-session-of-parliament/