PANCHAYAT
Focus:
- Panchayat Revenue Sources
About Panchayat Revenue Sources:
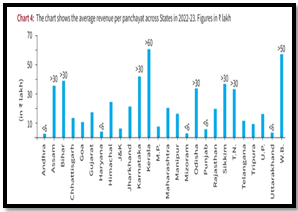
- Only 1% of panchayats’ revenue was generated internally, with the majority sourced from grants by the Central and State governments.
- Central government grants contributed 80% of the revenue, while State government grants accounted for 15%.
Source: TH
About Panchayats
The 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992, known as the Panchayati Raj Act introduced the system of panchayats in India.
- Three-tier System: Establishes a three-tier system of panchayats in rural areas: gram panchayat, panchayat samiti, and Zilla parishad.
- Population Criteria: Requires the formation of a village-level panchayat for every village with a population of at least 500 persons.
- Elections: Mandates regular elections to panchayats, ensuring democratic processes in line with the Act’s provisions.
- Reservation:
- Specifies reserved seats for scheduled castes, scheduled tribes, and women at all panchayat levels.
- Reserves the office of chairpersons for Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and women at the village and intermediate levels.
- State Finance Commission: Constitutes finance commissions to review panchayats’ financial positions and recommend fund devolution, grants-in-aid, and taxes.
- Powers and Functions: Defines powers, authority, and responsibilities of panchayats, empowering them in economic development, social justice, and sector-specific schemes.
- State Election Commission: Establishes a State Election Commission to conduct elections for local governments across the three tiers.


 Source: TH
Source: TH

