Ovarian Cancer- Symptoms, Causes, Screening
Syllabus:
GS 2: Women health
Why in the News?
Month of September is celebrated as Ovarian Cancer Awareness Month highlighting the importance of early detection, preventive strategies to improve women health.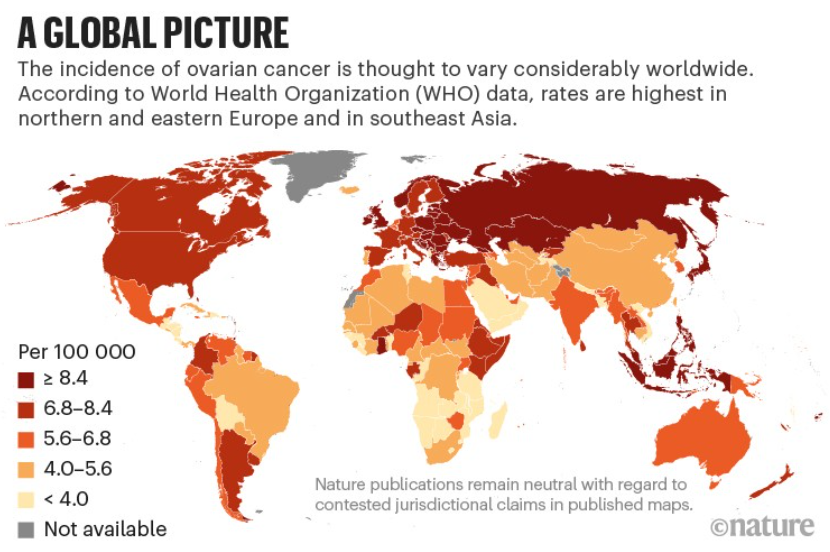
Introduction
- Ovarian cancer, famously called as “silent killer,” is the deadliest of women’s cancers because of its often-overlooked understated symptoms.
- These hidden symptoms make early detection tough, there is need for increased awareness of risk factors and symptoms can enable women to seek appropriate treatment and improve health outcomes.
Ovarian Cancer – Overview
- Ranked as most deadly cancer among women.
- Accounting for 6.6% of all cancers among women in India and therefore ranks among the top 3 cancers.
Concerning Realities
- 47,333 new cases of ovarian cancer and 32,978 deaths in recorded in India in 2022
Symptoms and Difficulty in Diagnosis
- Ovarian cancer symptoms are Unclear; hence, the disease is hard to detect at its early stage.
- The following are the most common symptoms:
- o Bloating Pelvic or abdominal pain
o Loss of appetite
o Frequent urination
o Indigestion, constipation, fatigue,
o back pain
o Postmenopausal vaginal bleeding - Due to lack of awareness above mentioned symptoms are often mistaken for normal conditions, thus delaying diagnosis.
Study Highlights
- A 2004 study illustrated that women with ovarian cancer have above symptoms almost 20 to 30 times in a month, and they are also more severe compared to women without the disease.
Need to be Aware - It is, therefore, of paramount importance that health professionals are on alert for persistent symptoms, early diagnosis, and treatment so that a better projection may follow.
Subtypes of Ovarian cancer
- Cancer Subtypes
- The two major subtypes of ovarian cancer include:
- o Type I Tumours: Less common, they are said to be those cancers which are detected early and usually have a better prognosis.
o Type II Tumours: More aggressive, later stages of detection with most of the deaths associated with them.Survival Rates
- The rate of survival is totally dependent on the stage of detection and quality of treatment.
- The 2022 research study estimated that, with optimal surgery and platinum-based chemotherapy, in 2022, 20 percent of patients with advanced ovarian cancer could remain disease-free for at least ten years, presumably being cured.
Limitations of Screening
- Unlike menaces of the breast or cervix, ovarian cancer currently has no effective screening test.
- CA125 blood test, while useful as a monitor after diagnosis, is not recommended for routine screening because its limited sensitivity and specificity may result in the detection of benign conditions by an unnecessary surgery.
Importance of Awareness
- This means awareness of symptoms and risk factors in the absence of reliable screening.
- Regular check-ups, together with family medical history discussions, will help in their early detection and management for ovarian cancer.
Ovarian cancer causes
- Genetic Implications
- Ovarian cancer is hereditary, and with BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes mutations contribute 65-85% of hereditary cases.
- Women with BRCA1 mutations have up to a 50% increased risk for life, while women with BRCA2 mutations have a 15% risk of developing ovarian cancer.
- Though most important are BRCA mutations are, other genes also play a role in hereditary cancer.
Testing and risk management
- Genetic testing helps identify high-risk women and allows individualized approaches, e.g.
o Clinical monitoring for women’s responsive healthcare.
o Preventive medicine to reduce prevalence of ovarian cancer risk.
o Preventive surgery (such as hysterectomy) to prevent ovarian cancer in high-risk women.Endometriosis and endometrial cancer
- Endometriosis, a health condition in which uterus-like tissue grows outside the uterus, is associated with an increased risk of certain types of uterine cancers, such as endometrioid and clear cell cancer
- But risk is very minimal, and prophylactic surgery for endometriosis-related ovarian cancer is rarely recommended without other significant risk factors.
Lifestyle implications
Talc powder
- Recently there has been controversy regarding the possible association of talcum powder exposure, especially during vaginal intercourse, with cervical cancer.
- Historical talcum powder has asbestos, a carcinogen, but modern talc does not contain asbestos.
- Currently, there are mixed evidences on talcum powder, with experts like the American Cancer Society advocating for further research to clarify the risk.
Hair products
- Hairs-dyes: have been studied suggest a possible link between long-term hair use and the risk of cervical cancer.
- Hair straightener and soothing: Formaldehyde, a known carcinogen, is generally responsible for increasing the risk of cervical cancer
Further research is needed
- Further research is needed to drive a specific association between lifestyle factors and the risk of the presence of cervical cancer.
- Recent studies done on ovarian cancer are unsatisfying, highlighting the need for research and studies to better understand these potential risks.
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
- HRT is a symptoms to treat meno-pause, it has been linked to an increased incidence of ovarian cancer even when used for a period of less than 5 years.
- women considering HRT Postmenopausal must deliberate the risks and benefits with their healthcare providers to make well-informed choices.
Genetic Consultation
Genetic Consultation
- Genetic counseling is often appropriate for women with family history related to ovarian or breast cancer.
- Risk Management: It enables the identification of high-risk groups because of hereditary causes and conveys to them specific methods of prevention and prognosis.
- Benefit: genetic counselling improves the overall outcome, it lowers the possibility of developing ovarian cancer through early interventions in prevention and treatment.
Conclusion
Awareness of lesser-known aspects of cervical cancer can lead to earlier detection and management, helping in adopt ion of preventive measures and attain timely medical interventions.
Source:The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
Analyse how lifestyle and hereditary factors influence risk of ovarian cancer, suggest preventive measure taken by Government of India in ensuring women health.



