ON THE UPSIDE
(REVIVAL OF PRIVATE INVESTMENT)
Syllabus:
GS 3:
- Investment Models.
- Indian Economy and issues relating to Growth and Development.
Why in the News?
- India’s economic trajectory continues to outperform expectations, registering a robust 7.6% GDP growth in the National Statistical Office’s second advance estimate, surpassing earlier projections.
- This resilience, coupled with a government focus on fiscal consolidation, is pivotal for sustaining high growth rates.
Source: The Print
GDP Growth Dynamics:
- Surprising Upside:
- The revised GDP growth of 7.6% for the fiscal year signifies a positive economic momentum, driven by additional data and rising net taxes.
- Gross value added, excluding net tax impact, grew slightly lower at 6.9%.
- Year-End Projection:
- With the first three quarters averaging an 8.2% growth, the implied fourth-quarter growth is 5.9%.
- Despite being below pre-pandemic levels, India’s economy is on a trajectory towards 7% growth.
| Understanding Advance Estimates
Advance estimates of GDP are pivotal for economic planning and policy formulation. They provide early insights into the anticipated performance of key sectors, aiding decision-making processes. Formation Process: · Data Evaluation: Central Statistics Office (CSO) formulates advance estimates by analyzing data from previous years and conducting surveys across various ministries. · Sector-Specific Estimates: Advance estimates cover various sectors, including agriculture and horticulture, projecting production for the upcoming fiscal year. · Timeline: These estimates are released months before the end of the financial year, providing timely insights for planning and policy formulation. Types of Advance Estimates: 1. 1st Advance Estimates: Typically released in early January, these estimates set the initial forecast for GDP growth in the upcoming fiscal year. 2. 2nd Advance Estimates: Published in the last week of February, these estimates follow the annual budget announcement and provide updated GDP growth projections. 3. 3rd Advance Estimates: Specifically focusing on agriculture and horticulture, these estimates offer sector-specific insights based on data from states and surveys. 4. 4th Advance Estimates: The final quarterly estimates before the end of the financial year, these projections offer a comprehensive overview of agriculture production. Significance of Advance Estimates: · Budget Allocation: Advance estimates guide the finance ministry in allocating budgetary resources effectively. · Economic Planning: They offer a broad overview of the economy’s expected performance, aiding in policy formulation and decision-making processes. |
Factors Influencing Growth:
- Strengthened bank and corporate balance sheets contribute to improved growth performance.
- The government’s infrastructure focus enhances growth potential.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), projecting a 7% GDP growth for the next year, faces limitations due to high-interest rates and reduced fiscal impulse, potentially normalizing demand and net tax impact.
Private Consumption and Savings Analysis:
- Consumption Trends:
- Private consumption growth at 3% lags behind overall GDP growth.
- Rural consumption, affected by high food inflation, particularly suffers, impacting discretionary spending.
- Shifting Consumption Patterns:
- Data reveals a shift in household consumption towards non-food items, reflecting rising per capita income.
- Adjusting consumer price index weights becomes crucial, considering these changing consumption patterns.
- Savings Overview:
- Household savings, comprising 61% of total savings, have seen a decline in their GDP share to 18.4%.
- Net financial savings witness a dip, while physical savings rise, reflecting increased borrowings for acquiring assets like houses.
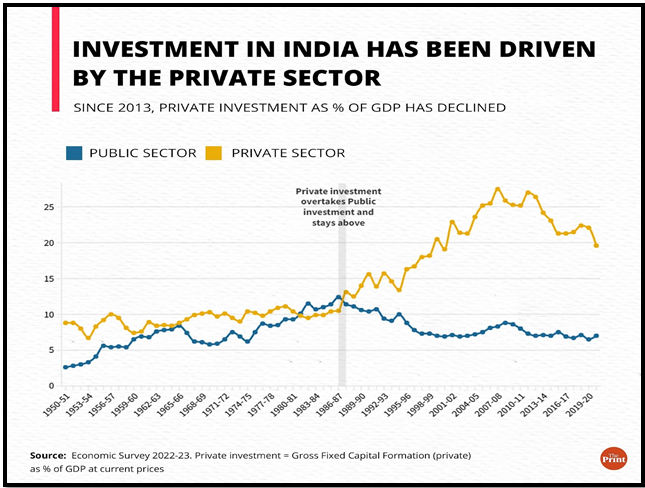
Investment Scenario:
- Corporate Investments:
- Comprehensive data on investments reveals public and household investments as leading contributors in fiscal 2022-23.
- Private corporate investment remains stagnant, highlighting the need for a definitive revival.
- Current Fiscal Dynamics:
- The ongoing fiscal year sees signs of corporate investment picking up, driven by the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, especially in pharmaceuticals and electronics.
- The shift towards core/capital-intensive segments is anticipated.
Government Initiatives to Attract Investments
Empowered Group of Secretaries (EGoS) and Project Development Cells (PDCs):
- Establishment: EGoS and PDCs set up by the Union Cabinet to expedite investments in collaboration with state governments.
- Objective: To enhance India’s pipeline of investable projects and attract more FDI and domestic investments.
National Monetization Pipeline (NMP):
- Launch: Introduced in 2021 to showcase available investment opportunities in infrastructure.
- Value: Over four years, the NMP’s indicative value for the Central Government’s core assets is estimated at Rs. 6 lakh crore.
Business Reforms Action Plan:
- DPIIT’s Business Reforms Action Plan ranks states/UTs based on their implementation of reform parameters.
- Reform Areas: The Business Reforms Action Plan by DPIIT streamlines rules, focuses on key areas, and ranks states and UTs based on designated reform parameters.
Investor-Friendly Strategy:
- Accessible FDI: Majority of sectors allow 100% FDI under the automatic route.
- Policy Revision: FDI policy is regularly updated after extensive consultations with stakeholders to maintain India’s attractiveness for investors.
Four Labour Codes:
- Streamlining: Government has consolidated 29 Central Labour Laws into four codes to simplify conducting business.
- Codes: Includes the Code on Wages, Industrial Relations Code, Code on Social Security, and Code on Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions.
Concessional Tax Rate:
- Extension: Concessional tax rate of 15% extended to new domestic companies setting up manufacturing units until March 31, 2024.
India Industrial Land Bank (IILB):
- Introduction: GIS-based portal providing comprehensive industrial infrastructure-related information.
- Features: Includes connectivity, infrastructure details, terrain information, vacant plot details, line of activity, and contact information.
Phased Manufacturing Programme (PMP):
- Promotion: Launched to promote domestic manufacturing of electric vehicles and related components.
- Objective: Encourage indigenous production of assemblies, sub-assemblies, parts, and inputs.
National Single Window System (NSWS):
- Launch: Introduced to streamline approvals and clearances for investors through a single window.
- Benefits: Enhances transparency, accountability, and responsiveness in the ecosystem.
PLI schemes
- Impact: Aimed at generating additional production worth Rs. 30 lakh crore and creating employment opportunities for 60 lakh people over the next five years.
Way Forward:
- Corporate Sector Preparedness: The private corporate sector, poised for investments, could benefit from reduced policy uncertainty and compliance costs, fostering a conducive environment for economic growth.
- Revival of Private Investments: A broad-based revival of private investments becomes crucial for sustained high growth rates, especially as the government moderates its investments, emphasizing fiscal consolidation.
Conclusion:
India’s economic landscape exhibits resilience and growth potential, driven by strengthened fundamentals. A strategic focus on private investments, coupled with addressing policy uncertainties, is imperative for navigating the path to sustained economic prosperity.
Source:
Mains Practice Question:
Analyse the challenges and opportunities associated with private sector revival and its implications for India’s economic trajectory.