OCEANS HAVE A FEVER – HERE’S WHY
Why in the news?
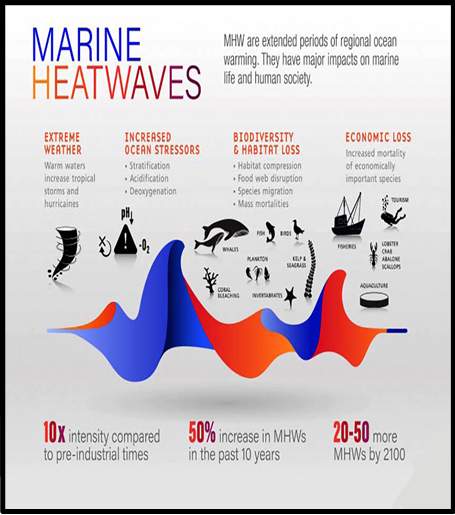
Record-high ocean temperatures pose severe threats to marine ecosystems, biodiversity, and weather patterns, urging urgent action on emissions reduction.
About Record-High Ocean Temperatures:
- Copernicus Climate Change Service reports the highest-ever average global sea surface temperature (SST) for February 2024 at 21.06°C, surpassing the previous record set in August 2023.
- Since March 2023, daily SST has consistently exceeded historical norms, indicating unprecedented ocean warming.
- Factors contributing to ocean warming include increased greenhouse gas emissions, reduced dust from the Sahara desert, and regulations on sulphur emissions from marine fuels.
- The World Meteorological Organization warns of a high likelihood of surpassing the 1.5°C threshold above pre-industrial levels between 2023 and 2027.
| What are Ocean currents?
● Continuous, directional movement of seawater influenced by various forces, akin to river flows in oceans. ● Movements: Horizontal currents, vertical upwellings or downwellings. ● Impact: Crucial for climate regulation, influencing weather patterns and biodiversity in the biosphere. What is Global warming? ● Earth’s temperature rises gradually due to increased greenhouse gases like CO2, CFCs. Consequences include climate change, habitat loss. About World Meteorological Organization (WMO): ● Intergovernmental organisation with 192 Member States and Territories. ● Origin: Evolved from the International Meteorological Organization (IMO) after the 1873 Vienna International Meteorological Congress. ● Established: Ratification of the WMO Convention on March 23, 1950, as a specialised agency of the United Nations. ● Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland. |