Obesity: The Core of the Non-Communicable Disease Epidemic
Syllabus:
GS – 3 – Health and non communicable diseases , technology in healthcare , Lifestyle
Focus :
The article discusses obesity as a global health crisis and a major contributor to non-communicable diseases (NCDs) like diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular ailments. It highlights the alarming trends of obesity across age groups, especially in India, its impact on mental and physical health, and the economic burden it poses. Solutions through lifestyle changes, medical interventions, and preventive measures are also explored.
Introduction
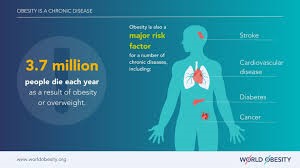
- Obesity is a chronic disease marked by excessive fat deposits harmful to health.
- Increases risks of diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, cancers, and mobility issues.
- Globally, one in eight people are obese, and one in three are overweight.
Obesity as a Catalyst for NCDs:
- Obesity drives the epidemic of non-communicable diseases like diabetes and cardiovascular issues.
- Obesity in younger generations signals future health challenges.
Causes of Obesity
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Reduced physical activity due to sedentary lifestyles.
- Increased availability of high-calorie processed foods.
- Cultural and Economic Shifts:
- Transition from active, labor-intensive lives to urban sedentary living.
- Economic prosperity increasing access to unhealthy food.
- Genetic and Hormonal Factors:
- Certain individuals are genetically predisposed to obesity.
- Hormonal imbalances may also contribute.
Global Obesity Trends
- Rising Statistics:
- Worldwide adult obesity has doubled since 1990; adolescent obesity has quadrupled.
- Over 300 million children aged 5-19 years are overweight, with 160 million categorized as obese.
- Regional Variations:
- WHO’s BMI criteria adjusted for the Asia-Pacific region:
- Overweight: BMI > 23 kg/m²
- Obesity: BMI > 25 kg/m²
- WHO’s BMI criteria adjusted for the Asia-Pacific region:
Childhood Obesity
- Health Implications:
- Childhood obesity leads to early-onset diabetes, hypertension, and poor mental health.
- India ranks second globally for childhood obesity prevalence.
- Causes:
- High consumption of fast food, sugary drinks, and processed snacks.
- Decreased physical activity due to digital entertainment and academic pressures.
- Consequences:
- Increased likelihood of adult obesity.
- Social stigma, low self-esteem, and depression.
Obesity in India
- Current Scenario:
- 13% obesity prevalence; India ranks third after China and the USA.
- “Normal Weight Obesity” and “Sarcopenic Obesity” emerging as distinct challenges.
- TOFI Phenomenon (Thin Outside, Fat Inside):
- Individuals with normal BMI but high waist circumference and internal fat deposits.
- Higher risk of NCDs despite appearing lean.
- Economic Burden:
- Direct medical costs for obesity-related diseases.
- Indirect costs like productivity loss, absenteeism, and premature mortality.
Impact of Obesity
- On Health:
- Increases risk of chronic diseases.
- Affects bone health, sleep, and mobility.
- On Mental Health:
- Linked to low self-esteem, eating disorders, and depression.
- On Society and Economy:
- Increased healthcare expenditure.
- Reduced workforce productivity.
Addressing Obesity
- Preventive Measures:
- Encourage healthy eating habits: Reduce high-calorie, processed foods and sugary drinks.
- Promote physical activity: Aiming for 6,000-8,000 daily steps and regular exercise.
- Behavioral Interventions:
- Lifestyle modifications such as avoiding elevators, walking short distances, and limiting screen time.
- Companies can introduce walking targets and wellness programs.
- Medical Interventions:
- Newer medications and bariatric surgery options.
- Awareness of long-term nutritional supplements and costs associated with treatments.
- Public Policy and Advocacy:
- Government campaigns to create awareness about healthy living.
- Taxing unhealthy foods and providing subsidies for healthier alternatives.
Conclusion
- Obesity is a multifaceted challenge with far-reaching consequences on individuals, families, and societies.
- Preventing and addressing obesity requires a collaborative approach, integrating personal responsibility, medical advancements, and government interventions.
- Lifestyle changes and societal awareness are key to combating this growing epidemic and ensuring healthier futures for coming generations.
Associated Article
https://universalinstitutions.com/tackling-the-fatty-liver-disease-epidemic/
Mains UPSC Question GS 3
Discuss the rising prevalence of obesity in India and its impact on public health, society, and the economy. Suggest comprehensive strategies to address this epidemic effectively.(250 words).