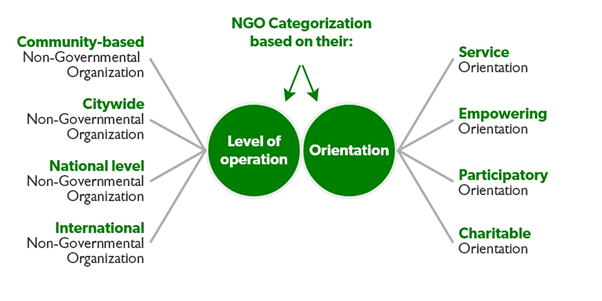
Non Governmental Organisation- 1.0
Relevance
- GS Paper 2 The role of NGOs, various groups and associations, institutional and other stakeholders.
- Tags: #governance #civilsocieties #ngo #goodgovernance #democracy.
Why do we need NGOs?
NGOs are essential for bridging gaps in services, advocacy, innovation, and community engagement. They empower communities, provide specialized expertise, and ensure inclusivity, promoting social change and development.
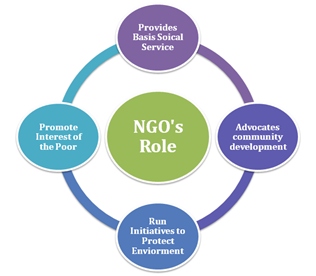
Some of the role played by NGOs in social upliftment are:
- Filling Gaps in Services: NGOs often provide critical services in areas where government resources are limited or inadequate, addressing issues such as healthcare, education, and social welfare. In India, NGOs like “Pratham” play a crucial role in supplementing government efforts in providing education to underprivileged children. Organizations like Médecins Sans Frontières (Doctors Without Borders) provide healthcare in crisis zones where state healthcare systems may be inadequate or non-existent.
- Advocacy and Accountability: NGOs act as watchdogs, advocating for human rights, environmental protection, and social justice. They hold governments and corporations accountable. NGOs like Transparency International India work to combat corruption and promote transparency in governance. Amnesty International advocates for human rights globally, holding governments accountable for abuses.
- Addressing Social Issues: NGOs engage communities in decision-making, empowering them to take an active role in addressing local challenges and promoting grassroots development. NGOs like “Goonj” address issues of poverty and sanitation by providing clothing and essentials to marginalized communities. The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation focuses on global health, poverty reduction, and education.
- Environmental Conservation: Many NGOs have specialized knowledge and expertise in niche areas, making them invaluable resources for solving specific problems. NGOs like the Wildlife Trust of India work to protect endangered species and their habitats. The World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) is a global organization dedicated to wildlife conservation and environmental protection.
- Disaster Relief: During emergencies and disasters, NGOs provide crucial humanitarian aid, including food, shelter, and medical care. NGOs like Khalsa Aid provide relief and aid to affected communities. The Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies offer disaster relief and support in various countries worldwide.
- Empowering Marginalized Groups: NGOs work to ensure that marginalized and vulnerable populations have a voice and access to essential services and rights. Organizations like SEWA (Self Employed Women’s Association) empower women through livelihood programs. The International Disability Alliance advocates for the rights of persons with disabilities.
- Innovation and Research: NGOs are often more flexible and can innovate and experiment with new approaches to solving societal problems, serving as laboratories for social change. NGOs like Pratham have pioneered innovative education models. The Gates Foundation invests in research to develop vaccines and improve healthcare in impoverished regions.
- Building Civil Society: NGOs contribute to civil society by fostering community engagement, volunteering, and social responsibility. NGOs worldwide help build vibrant civil societies by encouraging civic participation and activism.
- Research and Data Collection: NGOs often conduct research and collect data that inform policies, shape public opinion, and help in making evidence-based decisions.
- Global and Local Reach: NGOs operate at both local and global levels, bridging gaps in international development and addressing localized issues.
NGOs play a pivotal role in improving the well-being of communities, both in India and across the globe.
Role of NGO in development process
The role of Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) in the development process in India is multifaceted and critical. NGOs are instrumental in addressing various social, economic, and environmental challenges, supplementing the efforts of the government and promoting inclusive and sustainable development.
- Poverty Alleviation: NGOs in India often focus on poverty alleviation through various programs. They provide financial assistance, vocational training, and support to marginalized communities, empowering them to improve their living standards. Microfinance institutions, for instance, are a common NGO initiative that helps people access credit and start small businesses.
- Education and Skill Development: NGOs are instrumental in improving education and skill development in India. They establish schools, training centers, and scholarships for underprivileged children, promoting literacy and enhancing employment opportunities. NGOs like Teach For India work to bridge educational gaps.
- Healthcare Services: Many NGOs in India work to improve healthcare accessibility, particularly in rural areas. They set up clinics, conduct health awareness campaigns, and provide medical services to those in need. Notable examples include the Indian Red Cross Society and the Public Health Foundation of India.
- Women’s Empowerment: NGOs play a significant role in promoting gender equality and women’s empowerment. They offer support to women in various ways, including skill training, awareness programs, and advocacy against gender-based violence. NGOs like SEWA and Kudumbashree empower women economically and socially.
- Environmental Conservation: India faces significant environmental challenges, and NGOs are crucial in addressing them. Organizations like Greenpeace and The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI) work on issues related to climate change, renewable energy, and sustainable development.
- Human Rights Advocacy: NGOs in India actively advocate for human rights, civil liberties, and social justice. They work to protect marginalized communities from discrimination and exploitation. Notable organizations include Amnesty International India and the People’s Union for Civil Liberties (PUCL).
- Rural Development: India’s rural areas often lack access to basic amenities and infrastructure. NGOs are involved in various rural development projects, including building roads, providing clean drinking water, and promoting sustainable agriculture. The Swaminathan Foundation, for instance, focuses on rural development and agriculture.
- Disaster Relief and Rehabilitation: In times of natural disasters or emergencies, NGOs play a crucial role in providing immediate relief and aiding in long-term rehabilitation efforts. Organizations like Goonj and the National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) are involved in disaster relief.
- Advocacy and Policy Change: NGOs engage in advocacy efforts to influence policy changes at the national and local levels. They work to hold the government accountable and push for more inclusive and equitable policies and practices.
- Social Welfare Programs: Many NGOs run social welfare programs aimed at uplifting the underprivileged, such as orphans, street children, and the elderly. They provide shelter, food, and healthcare to those in need.
- Research and Data Collection: NGOs often conduct research and collect data on various developmental issues, which can inform both government and private sector initiatives. This research helps in the formulation of evidence-based policies.
- Promotion of Sustainable Practices: NGOs promote sustainable development practices, such as eco-friendly farming methods, waste management, and renewable energy adoption, contributing to environmental conservation and long-term economic stability.
- Community Mobilization: NGOs work closely with communities, mobilizing them to actively participate in their own development. They foster a sense of ownership and encourage self-reliance.
|
Compliance Requirements NGOs in India are subject to various compliance requirements to maintain their legal status and ensure accountability:
Legislation used by NGOs
This comprehensive regulatory framework for NGOs in India serves the dual purpose of promoting their important developmental work while also ensuring that they operate transparently, responsibly, and within the bounds of the law. |
| Mains Question
In the context of socio-economic development, critically analyze the significance of Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) and their role in addressing governance gaps and fostering inclusive growth in contemporary society. |