New Study Reveals Coronal Holes’ Thermal and Magnetic Structures
Why in News:
A recent study has provided crucial insights into the thermal and magnetic field structures of solar coronal holes, which impact space weather, Earth’s ionosphere, and satellite operations. These findings enhance forecasting and mitigation strategies for solar activity-related disruptions.
Discovery and Characteristics of Coronal Holes:
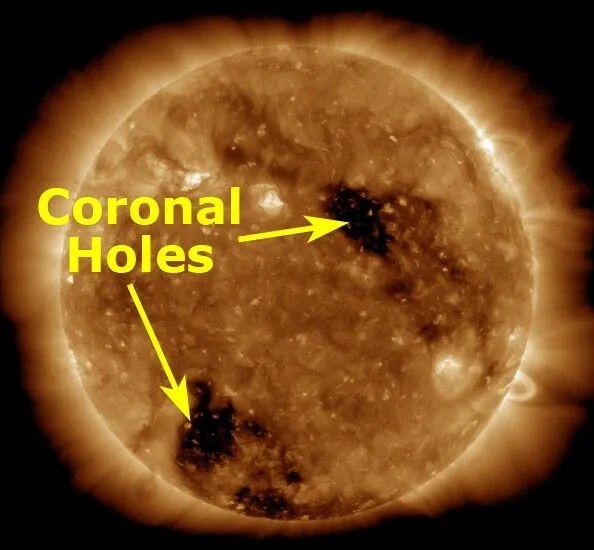
- Coronal holes are dark regions in X-ray and extreme ultraviolet images of the Sun, first discovered in the 1970s through X-ray satellites.
- These regions are cooler, less dense, and have open, unipolar magnetic fields that extend into space.
- Their magnetic field structure plays a key role in shaping the interplanetary medium and influencing space weather.
Lifespan and Solar Cycle Connection
- Coronal holes can last from a few weeks to several months, with longer durations during solar minimum periods when solar activity is low.
- They consistently appear throughout the Sun’s 11-year solar cycle, affecting space conditions around Earth.
Impact on Earth and Space Weather
- Coronal holes influence Earth’s ionosphere, potentially disrupting radio communications and satellite operations.
- Their effects on solar wind and geomagnetic storms have been linked to variations in the Indian summer monsoon rainfall.
- This study’s findings enhance forecasting solar activity’s impact on Earth, contributing to improved space weather predictions and mitigation strategies.
Solar Coronal Holes: Key Insights
About Coronal Holes:
- Dark regions in X-ray and extreme ultraviolet (EUV) images of the Sun.
- Discovered in the 1970s by X-ray satellites.
Features of Coronal Holes
- Cooler, less dense regions with open, unipolar magnetic fields.
- Appear throughout the Sun’s 11-year solar cycle and last from weeks to months.
- Persist longer during solar minimum (low solar activity phase).
Impact & Significance
- Cause geomagnetic storms and ionospheric disturbances, affecting radio communications.
- Influence space weather and Indian monsoon rainfall.
- Help in predicting solar activity and space weather effects.