New Research Redefines Dodo’s Extinction Story
Why in the news?
Recent studies reveal the dodo was not slow or unintelligent but a swift bird. The extinction was due to human-induced factors, not dietary preferences.
New Insights into Dodo’s Extinction:
- Revised Understanding:
- Researchers challenge the notion that dodos were slow and unintelligent.
- Findings suggest dodos were swift, thriving forest birds, not just clumsy creatures.
- New evidence, including anatomical studies, indicates dodos were capable runners.
- Reasons for Extinction:
- Dodos did not go extinct due to being prized as food.
- Extinction caused by invasive species: pigs ate eggs, rats and cats preyed on chicks, goats trampled nests.
- Human impact, including habitat destruction and introduction of predators, led to rapid extinction.
- Current Research and Lessons:
- Modern technology is used to reconstruct dodo life and movement.
- Study aims to understand past bird evolution to protect current species.
- Highlights the need for humans to be more mindful of their environmental impact.
About the Dodo:
- Scientific Name: Raphus cucullatus
- Description: Large, flightless bird, 3 feet tall, weighing 20-23 kg. Greyish-brown plumage, hooked beak, vestigial wings.
- Behaviour: Herbivorous, fed on fruits and seeds. Lack of natural predators led to no fear of humans.
- Habitat: Dense forests of Mauritius, endemic to the island.
- Extinction: Late 17th century due to human hunting and introduced animals destroying nests.
- Significance: Symbol of human-induced extinction and biodiversity loss.
About Germ Cells:
- Definition: Cells that give rise to gametes (sperm and eggs).
- Characteristics: Haploid, crucial for sexual reproduction, located in gonads.
- Development: Formed during embryonic development, undergo meiosis to create gametes.
- Role: Vital for genetic diversity and reproduction.
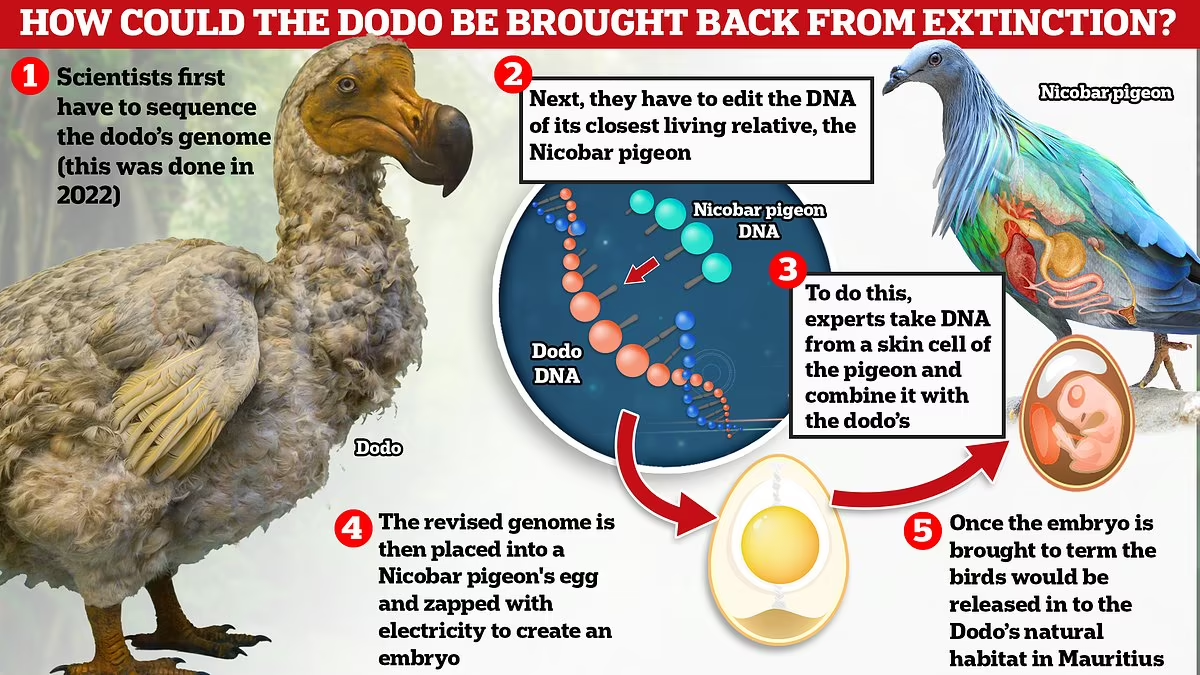
About Genome Sequencing:
- Definition: Process of determining an organism’s complete DNA sequence.
- Techniques: Includes Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) like Illumina and PacBio.
- Stages: Sample collection, DNA extraction, library preparation, sequencing, assembly.
- Applications: Human genetics, evolutionary biology, agriculture, microbial genomics.
- Challenges: Cost, accuracy, ethical concerns.
- Future: Technology advancements, single-cell sequencing, clinical integration.
Sources Referred:
PIB, The Hindu, Indian Express, Hindustan Times