Nepal Contracts Chinese Firm for Currency with Disputed Territories
Why in the news?
Nepal Rastra Bank hired a Chinese firm to print 100-rupee notes featuring disputed territories, asserting its territorial claims, which may impact India-Nepal diplomatic relations.
Highlights of the Nepal Contracts Chinese Firm for New 100-Rupee Notes:
- Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB) has engaged China Banknote Printing and Minting Corporation to print 300 million 100-rupee notes.
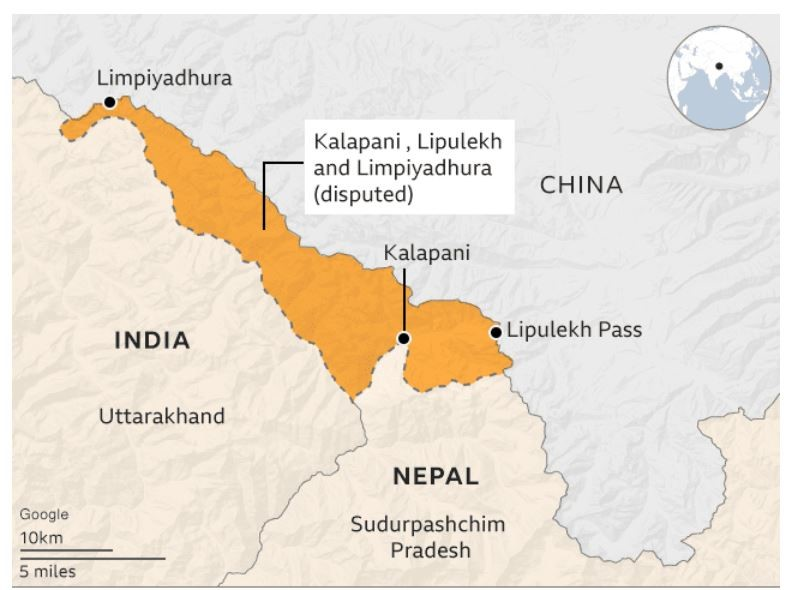
- The currency design will feature Nepal’s updated political map, which includes the disputed territories of Lipulekh, Limpiyadhura, and Kalapani.
- Approved by the Nepalese government in 2020, this map reinforces Nepal’s claim to these areas, which India administers as part of Uttarakhand.
Cost and Scope of the Printing Contract:
- The NRB’s contract with the Chinese firm is valued at approximately USD 8.99 million, costing about 4 Nepali rupees per note.
- This agreement covers the full spectrum of currency production, including the design, printing, supply, and delivery of the banknotes.
- By outsourcing this project, Nepal aims to ensure the efficient and high-quality production of its revised currency.
Geopolitical Implications of Updated Currency Map:
- The Kalapani region, positioned at the tri-junction of India, Nepal, and Tibet, is strategically significant in the region’s geopolitics.
- Nepal’s inclusion of these areas on its currency underscores its assertion of territorial claims, adding another layer to India-Nepal relations.
- The move highlights Nepal’s stance on its disputed borders, with the new currency intended to affirm its claim over these sensitive territories.
About the regions of border dispute between India and Nepal primarily include:
- Kalapani-Limpiadora-Lipulekh Trijunction:
- Located in the northwestern part of Nepal, this 35-square-kilometre area is near the tri-junction of India, Nepal, and China.
- Kalapani is administered by India as part of Uttarakhand and serves as an observation post on the Kailash Mansarovar route.
- Susta Area:
- Situated in the West Champaran district of Bihar, this region is also claimed by both countries, leading to tensions over its control.
- Discrepancies in River Source:
- The Kali River, which demarcates the border, is central to the dispute. Both countries contest the location of its source, leading to conflicting territorial claims.
- Historical Context:
- The Treaty of Sugauli (1816) established the Kali River as Nepal’s western boundary, but ambiguities regarding the river’s source have contributed to ongoing disputes.
These disputed areas highlight the complex historical and geographical factors affecting India-Nepal relations.
About Treaty of Thapathali:
- Treaty of Thapathali: Signed between the Tibetan government of Ganden Phodrang (under Qing protection) and the Kingdom of Nepal.
- Location and Context: Signed at Thapathali Durbar in Kathmandu after the Nepal-Tibet War (1855–1856).
Sources Referred:
PIB, The Hindu, Indian Express, Hindustan Times