NEED FOR A FOOD BUFFER POLICY
Why in the news?
- Open market sales of wheat and chana from buffer stocks have mitigated soaring inflation rates, maintaining price stability despite supply challenges.
- Increasing climate-induced supply shocks have highlighted the necessity for expanding buffer stocks to include other essential food items.
Case for Buffering Staple Foods
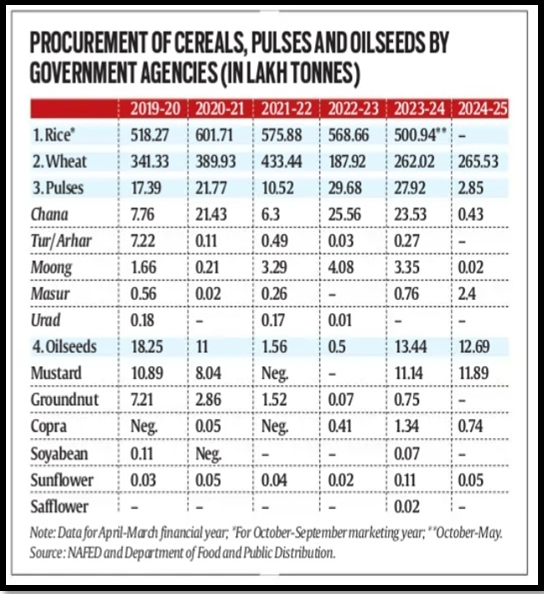
Buffering Wheat Stocks
- Government offloaded 34.82 lakh tonnes of wheat in 2022-23, stabilizing prices through open market interventions.
- Sales reduced cereal inflation from 16.73% to 8.69% by May 2024.
Impact of Chana Buffering
- NAFED’s procurement of chana at MSP during surplus years helped stabilize pulse prices despite erratic monsoons.
- Buffer stocks of 37.21 lakh tonnes alleviated inflation pressures by supplying chana at controlled prices.
Source: Phys
| What is Buffering?
Buffering refers to the practice of maintaining reserves of goods, such as food or commodities, to mitigate fluctuations in supply and demand, ensuring stability and preventing price volatility. Food Corporation of India (FCI) Role:
|