NavIC: India’s Crucial Satellite Navigation System Journey
Why in the news?
ISRO reported a partial failure of its navigation satellite NVS-02 (IRNSS-1K) due to engine malfunction, marking the latest setback in India’s indigenous NavIC system aimed at providing reliable navigation for defense and civilian purposes.
Introduction and Development:
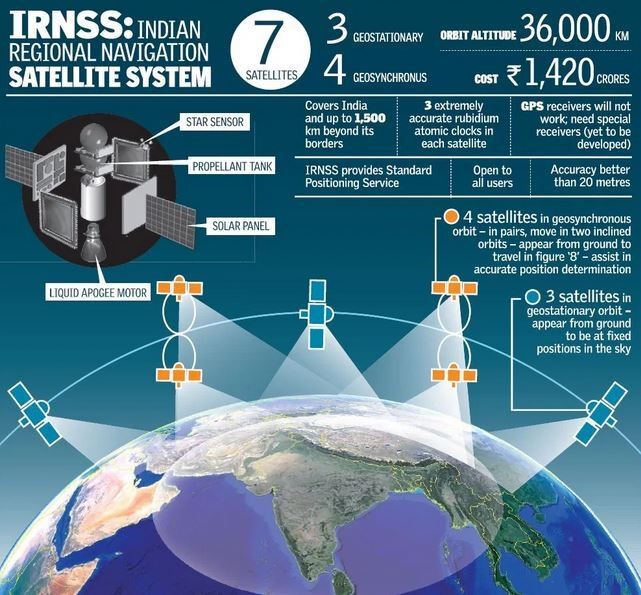
- NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation) is an indigenous satellite navigation system developed by ISRO to meet defense and civilian needs.
- Conceived after the Kargil War (1999) when India faced restrictions accessing GPS, it aimed for full deployment by 2016.
- The first satellite, IRNSS-1A, was launched in 2013, with a total of 11 satellites deployed by January 2025.
Setbacks and Technical Hurdles
- Only five satellites are currently operational, with several facing failures.
- A key issue has been the malfunctioning atomic clocks, which impacted multiple satellites, including IRNSS-1A.
- The recent engine failure of NVS-02 (IRNSS-1K) resulted in a sub-optimal orbit.
- Despite modifications, hardware challenges persist, causing partial failures in 6 out of 11 satellites launched.
Significance and Future Plans
- NavIC provides Standard Positioning Service (commercial) and Restricted Service (defense) over India and surrounding regions.
- It ensures position accuracy better than 20 meters, vital for military reliability over global systems like GPS.
- In 2023, Qualcomm agreed to support NavIC in its chipsets.
- ISRO plans to launch three more second-generation satellites (NVS-03, 04, and 05) to enhance services despite recent setbacks.
NavIC vs GPS:
- Accuracy:
- NavIC provides accuracy within 5 meters, while GPS offers accuracy within 20 meters.
- Coverage:
- NavIC is a regional system covering India and 1,500 km beyond its borders.
- GPS is a global system accessible worldwide.
- Development:
- NavIC was developed by ISRO (India).
- GPS was developed by the US Department of Defense.
- Satellite Constellation:
- NavIC operates with 7 satellites, while GPS uses 31 satellites.