MPOX OUTBREAK: A GLOBAL HEALTH CONCERN WITH IMPLICATIONS FOR INDIA
Relevance
- GS 2 – Health and Governance
- GS 3 – Science and Technology
Focus
- This article investigates the global implications of the recent Mpox outbreak, which was declared a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) by the World Health Organization.
- It explores the outbreak’s causes, potential hazards to India, and global ramifications for public health and pandemic preparedness.
Context
- The WHO’s designation of mumps as a PHEIC underscores the mounting apprehension regarding the virus’s transcontinental spread.
- Significant public health issues have arisen as a result of the outbreak, especially in nations with weak healthcare systems.
- Mpox symptoms might be less severe than smallpox symptoms, including as fever, rash, and enlarged lymph nodes.
- However, it is now a top concern for global health surveillance due to the possibility of widespread transmission and the ensuing healthcare burden.
Key Issues
- Global Spread and Containment Challenges:
- Global Spread: As of mid-2024, over 100 countries have recorded occurrences of mpox, with the bulk of cases occurring in Africa and several regions of Europe. This extensive dispersion emphasizes how difficult it is to manage viral outbreaks in a society where everything is connected.
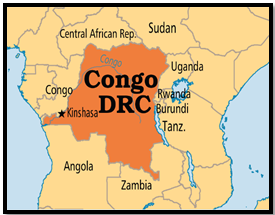
- Health System Strain: The outbreak has proven difficult to control in nations with less developed healthcare systems, notably those in sub-Saharan Africa. The healthcare system in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), where mpox is common, is severely overburdened, which raises mortality rates and slows the response to new cases.
About DRC
|
- Distribution of vaccinations: Despite the availability of Mpox vaccinations, their distribution has been unequal worldwide. The majority of doses that are currently available have been acquired by high-income nations, while shortages still affect low- and middle-income nations. According to WHO estimates, due to insufficient vaccination coverage, at least 25% of the world’s population is still considered high risk.
- Public Health Impact:
- Fatality and Morbidity: By mid-2024, the worldwide outbreak had led in about 99,176 confirmed cases and 208 deaths, with considerable regional variations in fatality rates.
- Economic Burden: The Mpox outbreak has had a significant negative economic impact. According to World Bank projections, the pandemic may cause a 1.2% decline in the world GDP in 2024, mostly as a result of higher healthcare expenses and lower worker productivity.
- Social Stigma: Mpox, like other contagious diseases, is stigmatized in society, which may discourage people from getting treatment in a timely manner. In areas where there is a lot of disinformation and mistrust of public health organizations, this stigma is more prominent.
- Vaccine Availability and Efficacy:
- Limited Vaccine availability: Not all at-risk populations can be adequately immunized with the existing global availability of Mpox vaccines. In order to guarantee that vulnerable people receive sufficient protection, the WHO has recommended for higher production and more fair distribution.
- Efficacy Concerns: Although the current vaccinations are successful in preventing serious illness, it is unclear how well they will work in the long run to combat newly developing Mpox strains. Research is still being conducted to determine whether booster doses are necessary and to produce vaccinations for the next generation.
- Impact on Vulnerable Populations:
- At-Risk Groups: Because of their high rates of comorbidities and restricted access to healthcare, vulnerable populations particularly those in Africa are more likely to experience severe results. There have been reports of up to 10% case fatality rates for mpox in nations like Nigeria and the Central African Republic.
- Children and the elderly: These populations have greater rates of hospitalization and mortality and are especially vulnerable to serious illness. Nearly 30% of Mpox-related deaths in Africa have been reported to be in children under the age of ten.
- Is India at Risk?
- Growing Concerns: Despite the fact that there haven’t been many cases of Mumps documented in India, the nation is nonetheless vulnerable because of its dense population and good connections to other countries. India is classified by the WHO as a “moderate risk” nation, meaning that if preventive measures are not successfully put in place, there may be localized outbreaks.
- Preparedness: India’s experience with prior epidemics, like COVID-19, has strengthened its preparedness. There are still holes in the rural healthcare system, too, and it is difficult to obtain immunizations and testing equipment. To reduce the possibility of an outbreak, the Ministry of Health has started targeted surveillance and public awareness initiatives.
- Government Reaction: In an effort to identify and contain possible cases of Mumps, the Indian government has instituted screening at significant international airports and seaports. However, timely vaccination availability and public collaboration are prerequisites for these efforts to be effective.
Case Studies
Statistical Data
|
Way Forward
- Enhancing Global Health Systems: To improve health systems in at-risk areas, international cooperation is required. To reach rural locations, this entails the deployment of mobile health units, more money, and technical assistance.
- Improving Vaccine Distribution: It’s critical that the Mpox vaccine be distributed fairly. High-income nations should contribute to international efforts by investing in low-income regions’ manufacturing capability and exchanging vaccine supply.
- Campaigns for Public Awareness: Thorough public education programs are necessary to inform communities about the dangers of mpox and the significance of vaccination. These advertisements ought to be presented in a variety of languages and customized for regional settings.
- Research and Development: It is imperative to allocate more funds towards investigating alternative medicines and next-generation vaccines. This includes researching novel treatment approaches and creating vaccinations that are effective against newly emerging Mpox strains.
- Global Cooperation: To manage mpox epidemics, the international community has to work together on surveillance, data sharing, and the creation of standardized methods. This involves more financing for pandemic preparedness and frequent updates to the WHO’s global health recommendations.
Conclusion
The worldwide health community is seriously threatened by the mpox outbreak, especially in areas with weak healthcare infrastructures. Even if it is not the outbreak’s epicenter right now, India needs to respond with vigilance and initiative. We can lessen the effects of Mpox and stop further outbreaks by bolstering health systems, improving vaccination programs, and raising public awareness.
Mains Question
Analyse the effects of the Mpox outbreak on public health throughout the world, paying particular attention to India’s risks and readiness. What steps ought to be done to stop similar epidemics in the future? (250 words)
Source: The India Express