Modernizing India’s Defence Production Amidst Global Shifts
Syllabus:
GS 2:
- India and its neighbourhood relations
- Bilateral , Regional and Global Agreements involving India
- Defence
Why in the News?
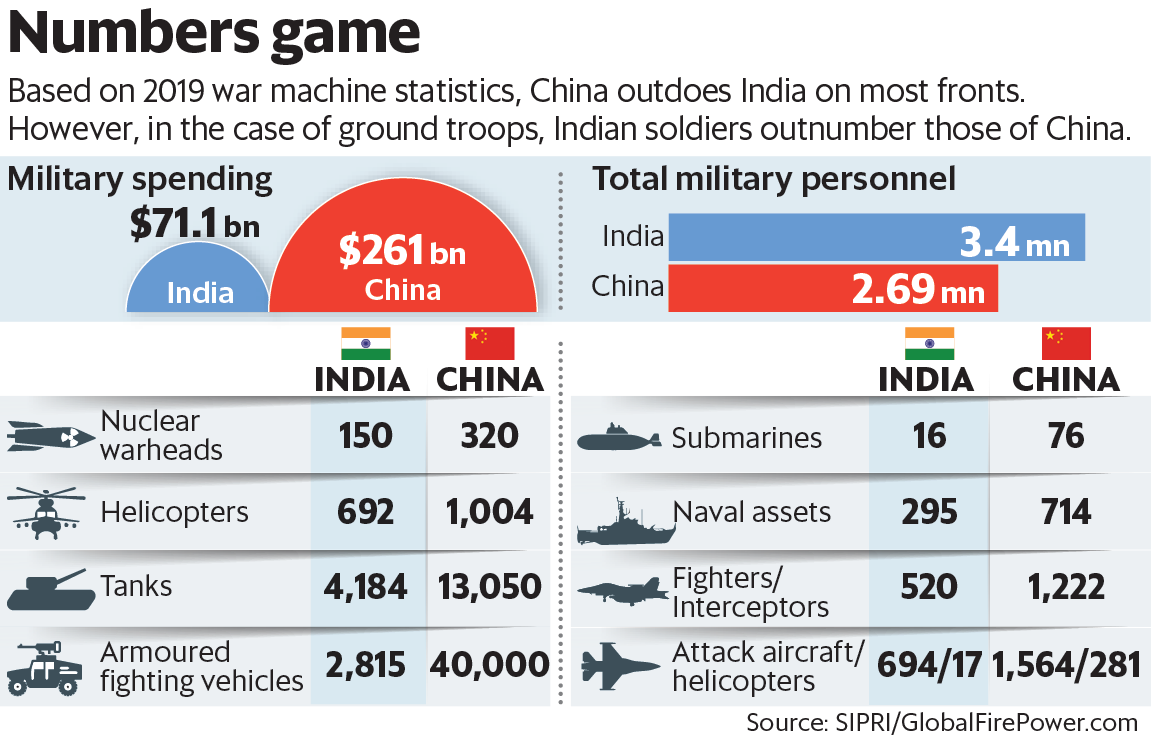
India is fostering defence cooperation agreements and accelerating the modernization of its defence production system amidst China’s growing military dominance and global shifts in defence supply chains.
Strengthening Defence Cooperation in Asia
- Enhanced partnerships: Agreements with Australia (air refueling) and Japan (stealth equipment production) are boosting India’s interoperability and advancing defence collaboration in response to shared security challenges.
- Geopolitical needs: These partnerships reflect a strategic alignment to counter Chinese assertiveness, ensuring collective defence measures in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Building networks: Asian countries increasingly see value in forging regional defence networks, supported by India, to stabilize the regional security architecture.
- S. military role: Recognizing U.S. importance, regional actors, including India, prioritize the American military presence to balance China’s rising military power.
- Expanding outreach: India continues military diplomacy with partners like France, Italy, and ASEAN nations to strengthen joint production and deepen defence partnerships.
China’s Growing Military Dominance
- Defence expenditure: China’s military spending surpasses that of its regional neighbors, including India, with massive investments in modernization and defence R&D.
- Unprecedented production: China’s commissioning of 70 submarines in 25 years demonstrates its industrial might, unmatched since World War II.
- Local focus: While China concentrates its defence resources on its immediate neighborhood, India faces broader strategic and resource challenges.
- Qualitative shifts: Despite U.S. qualitative superiority, China’s quantitative advantage is reshaping the regional military balance.
- Strategic unpredictability: China’s mix of diplomatic charm and military aggression creates uncertainty, demanding preparedness from its neighbors.
Decline of the U.S. Military-Industrial Complex
- Aging infrastructure: Many U.S. defence production facilities are outdated and struggle to meet the growing global demand for advanced weaponry.
- Global commitments: Unlike China, the U.S. is stretched across Asia, Europe, and the Middle East, diluting its focus on Indo-Pacific security.
- Supply chain issues: The U.S. faces challenges in mass-producing arms, such as drones and missiles, required for existing and potential conflicts.
- Allied dependence: The U.S. seeks collaboration with partners like Japan and South Korea, despite their own constraints, to bolster defence capabilities.
- Sustainability concerns: Balancing commitments across multiple theatres challenges the effectiveness and sustainability of U.S. military operations.
Opportunities for India’s Defence Modernization
- Global supply shifts: The restructuring of defence supply chains creates opportunities for India to position itself as a key global player in arms production.
- Private sector role: Greater participation from India’s private sector can enhance efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness in the defence manufacturing ecosystem.
- Collaborative frameworks: India’s roadmaps with France, Italy, and the U.S. aim to foster co-production, exports, and technology transfers.
- Restructuring DRDO: Overhauling the Defence Research and Development Organization is critical for innovation and improving defence production capabilities.
- Military diplomacy: India’s proactive engagement with global powers reinforces its role as a regional and global security partner.
Challenges
- Capability gap: India lags behind China in military modernization, posing challenges to its ability to counter Beijing’s growing defence dominance.
- Resource constraints: Limited investments and infrastructure hinder India’s ability to match global production standards in arms and equipment.
- Bureaucratic inertia: Delayed policy reforms and inefficiencies in defence production slow the pace of modernization efforts.
- Export limitations: India struggles to compete in global arms markets, limiting its potential as a significant arms exporter.
- Technological dependence: Heavy reliance on imports for advanced technology undermines India’s goal of achieving self-reliance in defence production.
Way Forward
- Accelerate reforms: Swift restructuring of defence policies and organizations like the DRDO is essential for India’s defence modernization goals.
- Indigenous focus: Strengthening local manufacturing capabilities and reducing dependence on imports are crucial for self-reliance.
- Strengthen R&D: Investing in cutting-edge research and fostering innovation will enhance India’s global competitiveness in defence technology.
- Expand partnerships: Collaborating with global allies for joint production and technology transfer is vital to build a robust defence ecosystem.
- Boost exports: Developing globally competitive arms and expanding markets will establish India as a significant defence exporter.
Conclusion
India has the opportunity to modernize its defence industry and become a global leader. By addressing capability gaps, fostering partnerships, and accelerating reforms, it can achieve self-reliance and strengthen its security architecture amidst evolving global dynamics.
Mains Practice Question
Discuss how India can bridge the defence capability gap with China. Analyze the challenges in modernizing its defence production system and suggest ways to enhance self-reliance in the defence sector.
Associated Articles:
https://universalinstitutions.com/india-as-global-player-in-defence-sector/