Mars’ Missing Atmosphere: New Study Insights
Why in the news?
A recent MIT study reveals how water and Martian rocks interacted to reduce the atmosphere, providing clues about Mars’ environmental evolution and potential future resource utilisation.
About Mars’ Historical Atmosphere:
- Mars, now a cold and barren desert, once had flowing water on its surface, indicating a thick atmosphere that prevented water from freezing.
- Approximately5 billion years ago, the atmosphere, rich in carbon dioxide, thinned dramatically, leading to the drying up of water.
- Understanding this transition is crucial for scientists studying Mars’ history.
New Research Findings
- A study published in Science Advances on September 24 by MIT geologists Joshua Murray and Oliver Jagoutz offers insights into this atmospheric loss.
- The researchers propose that water interacted with olivine, a common Martian rock, triggering a slow chain reaction that removed carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and converted it into methane.
Key points :Mars
- Position: Fourth planet from the Sun and second-smallest in the solar system.
- Appearance: Soil contains iron oxide, giving it a reddish hue (hence, Red Planet).
- Surface Features: Covered with craters, valleys, volcanoes, and canyons.
- Atmosphere: Very thin, primarily carbon dioxide; lacks a magnetic field, exposing the surface to high radiation levels.
- Notable Landmark: Olympus Mons, the tallest mountain in the solar system.
- Water Presence: Evidence suggests liquid water may have existed; ice caps are present at the poles.
- Moons: Two small, irregularly shaped moons—Phobos and Deimos—likely captured asteroids.
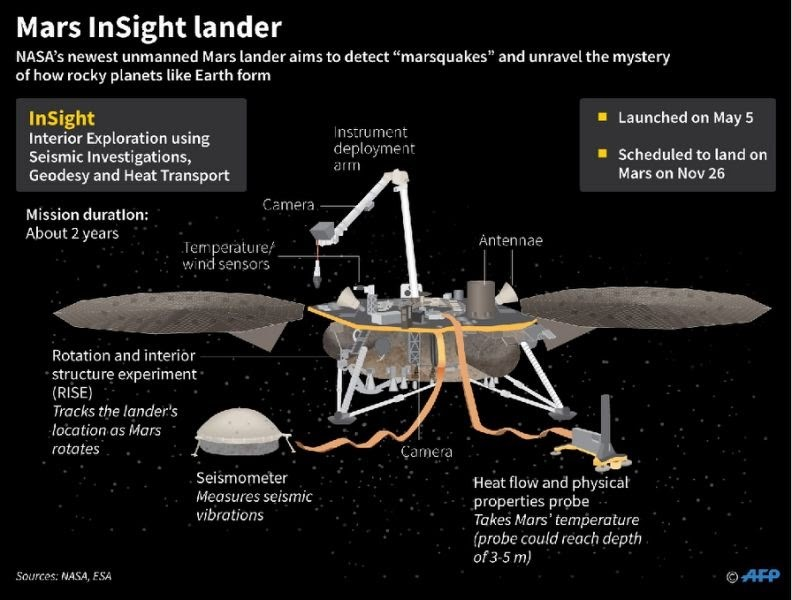
InSight Mission:
- Launch: Robotic lander launched by NASA in 2018.
- Purpose: To study Mars’ seismic activity, core, and crust for evolutionary insights.
- Key Instruments:
- Seismometer for detecting Marsquakes.
- Heat flow probe for measuring internal heat.
- Findings: Evidence of a liquid magma ocean in Mars’ past, indicating a dynamic geological history.
Other Significant Mars Missions:
- Viking 1 & 2: First successful landers searching for signs of life.
- Mars Pathfinder: Deployed the first rover, Sojourner, on Mars.
- Mars Exploration Rovers: Spirit and Opportunity studied geology and past water evidence.
- MAVEN: Ongoing orbiter studying atmospheric changes.
- ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter: Ongoing study of atmosphere and potential life signs.
- Perseverance Rover: Collecting rock samples for return to Earth.
- Mangalyaan (2013-2022): India’s first interplanetary mission, studying ionosphere and atmospheric composition; exceeded its expected mission life.
NASA Missions:
- Lander: InSight (studies seismic activity)
- Rovers: Curiosity (geological studies) and Perseverance (collecting rock samples)
- Orbiters: Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, Mars Odyssey, MAVEN (atmospheric studies)
- Tianwen-1 (2021): China’s Mars mission, including an orbiter and rover.
- Hope Mars Mission (2021): UAE’s first interplanetary mission.
- Mars 2 and Mars 3 (1971): Soviet Union missions, first to reach Mars’ surface.