MANY ELECTIONS, AI’s DARK DIMENSION
Syllabus:
GS3 :
- Awareness in the fields of IT and issues
- Artificial Intelligence
- Science and Technology- Developments and their Applications
Why in the News?
- With the announcement of the general election in India and numerous other countries in 2024, the role of AI in electoral dynamics cannot be overlooked.
Focus:
- Rapid advancements in Generative AI, simulating real-world interactions, pose new challenges and opportunities for electoral processes globally.
- The upcoming elections serve as a litmus test to gauge AI’s potential to influence electoral behaviors and outcomes, with AI models like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Copilot already making their presence felt in various sectors.
| Understanding Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, primarily computer systems. It involves the development of algorithms and models that enable computers to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, problem-solving, decision-making, and perception. AI impacts various sectors : 1. Healthcare: · Positive: AI assists in medical image analysis, improving accuracy and speed of diagnosis. · Negative: Dependence on AI may lead to reduced human interaction, affecting patient-doctor relationships. 2. Finance: · Positive: AI-driven algorithms enable faster and more accurate financial decision-making, leading to improved efficiency. · Negative: Over-reliance on AI may increase the risk of algorithmic errors or biases, potentially leading to financial losses. 3. Transportation: · Positive: AI-powered autonomous vehicles enhance road safety and reduce accidents by eliminating human error. · Negative: Adoption of AI in transportation may lead to job displacement for drivers and related workforce. 4. Retail: · Positive: AI-driven personalized recommendations improve customer satisfaction and increase sales. · Negative: Overuse of AI in retail may raise privacy concerns related to consumer data collection and tracking. 5. Manufacturing: · Positive: AI-driven predictive maintenance minimizes downtime and reduces maintenance costs for machinery. · Negative: Increased automation through AI may lead to job losses for human workers in manufacturing industries. 6. Agriculture: · Positive: AI-powered precision farming techniques optimize resource usage and increase crop yields. · Negative: Dependence on AI solutions may widen the digital divide, disadvantaging farmers with limited access to technology. 7. Education: · Positive: AI-based adaptive learning platforms personalize education, catering to individual student needs and improving learning outcomes. · Negative: Over-reliance on AI tutors may undermine the role of human teachers, reducing the quality of education. 8. Cybersecurity: · Positive: AI enhances threat detection capabilities, identifying and mitigating cyber threats in real-time. · Negative: Sophisticated AI-driven cyberattacks may outpace traditional cybersecurity measures, posing significant challenges to digital security. |
The Evolution of AI:
- Breakneck Pace: The development of AI has accelerated at an unprecedented rate, driven by advancements in machine learning algorithms and computational power.
- From Narrow to General AI: AI has evolved from narrow applications focused on specific tasks to more general intelligence capable of complex reasoning and decision-making, blurring the line between human and machine cognition.
- Deep Learning Revolution: Deep learning techniques, such as neural networks, have revolutionized AI research, enabling systems to learn from vast amounts of data and improve performance over time.
- Ethical Considerations: The rise of AI has raised ethical questions regarding its impact on society, including concerns about job displacement, algorithmic bias, and the concentration of power in the hands of tech giants.
- Collaborative Efforts:
Multidisciplinary collaboration between researchers, policymakers, and industry stakeholders is essential to address ethical, legal, and societal implications of AI development and deployment.
AI’s Influence on Electoral Landscapes:
Data-driven Campaigning: AI-powered analytics empower political campaigns to segment voters, tailor messages, and optimize outreach efforts based on demographic, behavioral, and psychographic data.
Targeted Messaging: AI algorithms enable microtargeting of voters through personalized advertisements, social media content, and messaging strategies, influencing voter perceptions and preferences.
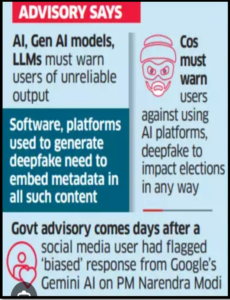
Deepfake Threat: The proliferation of deepfake technology poses a significant challenge to electoral integrity, as AI-generated audiovisual content can be used to spread misinformation, manipulate public opinion, and undermine trust in electoral processes.
Predictive Analytics: AI-driven predictive models analyze historical data, polling trends, and social media sentiment to forecast election outcomes, providing valuable insights for campaign strategists and political analysts.
Regulatory Gaps: The rapid adoption of AI in electoral campaigns has outpaced regulatory frameworks, highlighting the need for robust oversight mechanisms to ensure transparency, fairness, and accountability in political advertising and communication.
Challenges and Opportunities in AI Governance:
- Ethical Guidelines: Developing and enforcing ethical guidelines for AI research and development is crucial to ensure that AI technologies adhere to principles of fairness, transparency, and accountability.
- Bias Mitigation: Addressing algorithmic bias and discrimination is essential to prevent AI systems from perpetuating existing social inequalities and marginalizing underrepresented groups.
- Regulatory Frameworks:
Governments must establish comprehensive regulatory frameworks to govern the deployment of AI in electoral processes, including transparency requirements, data protection measures, and accountability mechanisms.
- International Cooperation:
Collaborative efforts between governments, intergovernmental organizations, and civil society are essential to harmonize AI governance standards, share best practices, and address cross-border challenges.
- Public Engagement: Enhancing public awareness and engagement on AI governance issues is critical to ensure democratic oversight and accountability in the development and deployment of AI technologies in electoral contexts.
Way Forward (Mitigating Disinformation and Deepfake Threats):
- Media Literacy: Promoting media literacy and critical thinking skills among citizens is essential to empower them to identify and combat disinformation and deepfake content.
- Technological Solutions: Developing AI-driven tools and algorithms to detect and flag deepfake videos and misinformation campaigns can help mitigate their impact on electoral integrity and public discourse.
- Regulatory Measures: Governments should enact legislation to hold platforms accountable for hosting and disseminating harmful or deceptive content, imposing fines and penalties for violations of electoral integrity.
- Fact-Checking Initiatives: Investing in independent fact-checking organizations and initiatives can help verify the accuracy of information circulating online and counter false narratives during electoral campaigns.
- International Cooperation: Collaborating with other countries and international organizations to share information, resources, and expertise is essential to combat global threats to electoral integrity posed by disinformation and deepfake technologies.
India’s Role in AI Governance and Electoral Integrity:
- Digital Innovation Hub: India’s thriving tech sector and skilled workforce position it as a global leader in digital innovation, providing an opportunity to develop AI governance frameworks and solutions tailored to the country’s unique context.
- Policy Leadership: The Indian government must take proactive steps to formulate and implement AI ethics guidelines, regulatory frameworks, and electoral integrity measures to address emerging challenges and opportunities in the digital age.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborative partnerships between government agencies, tech companies, academia, and civil society organizations are essential to drive innovation, build capacity, and promote responsible AI deployment in electoral processes.
- Capacity Building: Investing in AI research, education, and training programs can build the technical expertise and institutional capacity needed to develop and deploy AI solutions that enhance electoral integrity and democratic governance.
- International Engagement: Engaging with international partners and forums to share best practices, exchange knowledge, and coordinate efforts to address common challenges in AI governance and electoral integrity can amplify India’s impact on the global stage.
Conclusion:
The rise of AI presents both unprecedented opportunities and daunting challenges for global electoral dynamics. As nations navigate the complexities of AI governance and electoral integrity, it is essential to uphold democratic values, protect citizens’ rights, and ensure the integrity and fairness of electoral processes in the digital age.
Source:
Mains Practice Question:
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into various sectors has transformed societal dynamics, presenting both opportunities and challenges. Discuss the impact of AI on electoral landscapes globally, highlighting the opportunities for enhancing campaign efficiency and the challenges posed by disinformation and deepfake threats.