LOOSE ENDS: UKRAINIAN MILITARY’S SURPRISE ATTACK ON KURSK
Syllabus:
GS 2:
- India and its neighbourhood relations.
- Effect of global politics on India.
Focus:
Kiev’s military forces had carried out a surprize ground invasion of Russian territory in the Kursk region which had been first in Ukrainian history since the Second World War. This has taken Moscow by surprise and people have started questioning Russia’s espionage abilities and the conflict situation might just be turned on its head.
Source: TH
An unexpected attack and its implications:
- Surprise Invasion: On 6 August Ukraine declared a ground attack on Russia’s southwestern province Kursk ending the non-aggression status of Ukraine since World War II.
- Moscow’s Unpreparedness: The attack caught the Russian authorities by surprise therefore sparking an intelligence failure. Soon the regional government informed the inhabitants and stated extensive losses in Sudzha because of shelling.
- Breach of Defense: Even though Russia’s Ministry of Defence said the raids were repelled by Russian forces, geolocation of the videos showed that the Ukrainians had penetrated 10 kilometers into the Russian territory.
- Operational Security: In several instances including the above one, the Ukrainians showed great operational security throughout and this raised doubts over Russia’s preparedness and intelligence.
- Political Reactions: Russian President Vladimir Putin said that Ukraine conducted a “large scale provocation”, while the Chief of the General Staff tried to comment on the situation as relatively stable and controllable.
Strategic Advancements by Ukraine
- Continued Offensive: After the first assault, Ukrainians attacked and liberated several settlements and also eliminated the bridges over the Seim River.
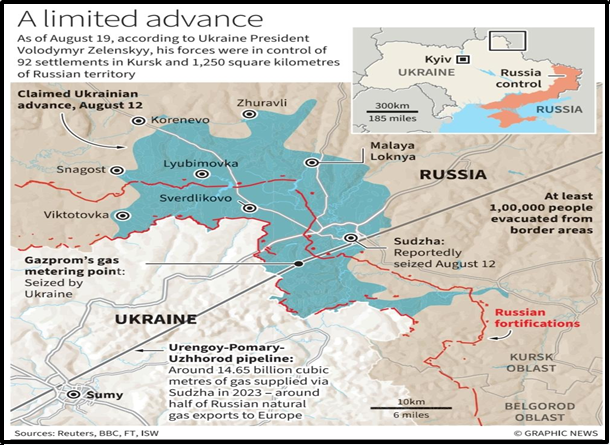
- Territorial Gains: In the occupied regions, Ukraine now holds 92 settlements and 1,250 square kilometers of Russian territory in Kursk as of August 19, Zelenskyy said.
- Evacuations: The Russian government claimed that more than 1,33,000 people were evacuated from those zones and that shows the extent of Ukraine’s territorial advancement.
- Changing Battle Dynamics: This was a significant change in the war, especially after Ukraine losses in Kharkiv earlier this year when the country looked for change in the course of the conflict.
- Long-term Goals: Ukraine might have a leverage in future negotiations with Moscow thanks to the success in Kursk, especially taking into account that the Western support might become less persistent in the future.
Strategic motivation for the invasion:
- Diversion Tactic: The attack on Kursk can be viewed as an attempt to make Russia spread her forces and more specifically pull back from the continuous advances in eastern Ukraine, especially around Kharkov.
- Geographical Significance: Kursk itself is quite close to the border with Sumy and its control will allow undermining the Russian movements towards Kharkiv.
- Buffer Zone Creation: In Zelenskyy’s words, the main goal was to create a buffer zone so that there were no other attacks across the border from Russia and Kursk was preparing to launch artillery strikes on Sumy.
- Negotiation Leverage: Keeping the buffer zone could be of major value for Ukraine as a key bargaining chip in case of future negotiations , also given the increasing doubts regarding the U. S. support.
- Timing Considerations: As the US elections were approaching, and support from other countries could shift, Kyiv regarded this attack as important in order to consolidate its positions while it has the support that it needs.
Agreements between Russia and Ukraine:
Minsk agreements, the main parameters of which are the preservation of the territorial integrity of Ukraine and the start of the process of decentralization, the holding of new elections and the establishment of a tomorrow mechanism for resolving the state’s political crisis.
Minsk I (2014):
- In September 2014, Ukraine and the Russian-backed separatists signed 12-point ceasefire in Minsk, Belarus.
- These comprised prisoners’ swap, supply of humanitarian assistance and demobilization of heavy weapons.
- The deal intended to reduce tension between the two parties on the conflict in Eastern Ukraine.
- However the violation of the agreement was seen on both sides and the ceasefire was brought to a halt.
- The Minsk I agreement did not help in achieving sustainability in the conflict issues that is why in order to establish long-term peace other agreements were made.
Minsk II (2015):
- Minsk II was signed in 2015, to prevent an extension of the open warfare with France and Germany acting as co-chairs.
- The agreement concerned cessation of the fighting in the territories controlled by the rebels and the return of the border to the Ukrainian national forces.
- The participants of these agreements comprised of representatives from Russia, Ukraine and the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)together with leaders of two breakaway regions of Ukraine.
- The OSCE, the world’s largest security related IGO, stands for the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe and it was primarily in charge of monitoring the implementation of the agreement.
- The Minsk II was intended at providing stability to the region and this is yet to be fully implemented.
Russian Response and Strategy
- Initial Downplay: First of all, being under pressure in the Kursk area, Russia tried to play it down specially by the official comments that everything was under control.
- Focus on Eastern Front: Contrary to expectations, Moscow retained its focus on place where it was already having some successes, mainly around the town of Pokrovsk, an important communication center in eastern Ukraine.
- Territorial Gains: Russia said it made major advances in the east; pro-Russian fighters seized Niu-York, a supply base near Pokrovsk, which may strengthen its grip on Donetsk.
- Defensive Measures: In response to Ukraine’s focusing on Kursk, Russia has strengthened its positions by shifting some forces from Kharkiv but at the same time it dilutes them.
- Strategic Calculations: To Putin, territorial improvements in the east may keep the domestic pressure from slips in Kursk and sustain motion in the expansive war.
Future Implications and Uncertainties:
- Shift in Narrative: Ukrainian action in temporarily changing the dynamics of the war means that it can reach into the Russian depths, thus disrupting Russia’s invincibility complex.
- Diplomatic Leverage: Kyiv expected that territorial gains made in Kursk would offer a bargaining asset in the future negotiations about the rights of the Ukrainian and Russian-speaking population, albeit the long-term capabilities of such territorial gains.
- Potential Counteroffensive: Current position is still somewhat dynamic and it may happen that the counterattack by Russia will shift the balance
- Western Support Uncertainty: As there are the forthcoming elections to the U. S. congress and possible shifts in the foreign support, it can be assumed that the considerations of the Ukrainian strategists may be driven by the goal to seize some benefits while they are on top.
- Long-term Outcomes: Thus, the further outcome can be discussed either as the turning point in the Kursk offensive or as a momentary success depending on how the further development of the confrontation and the concrete actions of Russia will be organized.
Conclusion
The attack of Ukraine in Kursk is another milestone in the ongoing conflict as it attacks Russia’s presumed infallibility. Although this step could give Kyiv some advantages in future negotiations with Russia and other neighbours, the long–term effects still remain unpredictable, particularly taking into consideration the dynamics in regional foreign policies and the fluctuations of the west’s support to Ukraine.
Source:The Hindu
Mains Practice Question
Explain why Ukraine’s entry into the Kursk region in Russia and how further negotiations can be conducted . To what extent is it possible to assert that this development may contribute to shifting the power in favour of Ukraine against Russia?