LOOKING TO THE FUTURE ON ST. PATRICK’S DAY
Syllabus:
GS 3:
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Focus:
- 75 years of diplomatic relations between Ireland and India
Source:- The Hindu
75 Years of Diplomacy
- Celebrating 75 years of diplomatic relations between Ireland and India.
- Reflecting on both nations’ shared history in the struggle for independence from colonial rule.
- Honoring the historic exchanges between founding figures leading to the creation of modern republics.
- Recognizing the growing ties in trade, education, and personal connections.
St. Patrick’s Day Significance
- St. Patrick’s Day as a global celebration for those of Irish descent and friends of Ireland.
- Opportunity to showcase Irish culture and heritage worldwide.
Global Conflicts
- Addressing current global conflicts, including Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and the conflict in Gaza.
- Ireland’s stance on demanding accountability and supporting international humanitarian law.
- Calls for ceasefire and humanitarian assistance in conflict zones.
Youth and Innovation
- Young people’s leadership in addressing the climate crisis and advocating for international law.
- Ireland’s investment in young talent as a driver of economic success and innovation.
- The role of Irish educational institutions in fostering a vibrant, globally-connected workforce.
Economic Success and Talent Pool
- Home to major global companies, attracted by Ireland’s economic stability and skilled workforce.
- Support for young entrepreneurs and the welcoming environment for international students.
UN Human Development Index
- Ireland’s commitment to global citizenship reflected in its high UN Human Development Index ranking.
- The focus on peace, human dignity, and equality.
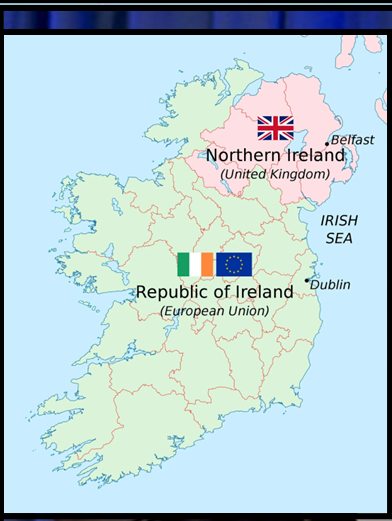
| Northern Ireland
· Location and Geography: Northern Ireland is situated in the northeastern part of the island of Ireland. It shares borders with the Republic of Ireland to the south and west, while the Irish Sea separates it from England and Wales to the east and southeast, and the North Channel separates it from Scotland to the northeast. · Political Status: As a constituent country of the United Kingdom, alongside England, Scotland, and Wales, Northern Ireland is not a sovereign state but operates with its own devolved government within the framework of the United Kingdom. · Capital and Major Cities: The capital city of Northern Ireland is Belfast, known for its modernity and industrial heritage, particularly in shipbuilding. Other significant cities include Londonderry (also called Derry) and Armagh. · Cultural Contributions: Northern Ireland has made notable contributions to global culture, especially in literature, music, and the arts. Renowned figures like poet Seamus Heaney and musician Van Morrison hail from this region. · Economy: While historically reliant on industries like shipbuilding and textiles, Northern Ireland’s economy has undergone diversification in recent years. It now focuses on sectors such as technology, tourism, and services to drive growth and development. · Demographics: Northern Ireland boasts a diverse population with various ethnicities, religions, and cultural backgrounds. Christianity predominates, with significant Protestant and Catholic communities shaping the region’s social fabric. |
India – Ireland
- Historical Ties: India and Ireland share historical connections dating back to the early 20th century when Indian nationalists sought support from Irish leaders during the struggle for independence from British colonial rule.
- Diplomatic Relations: Diplomatic relations between India and Ireland were established in 1947, following India’s independence. Ireland opened its embassy in New Delhi in 2005, and India opened its embassy in Dublin in 2012.
- Bilateral Trade: Bilateral trade between India and Ireland has been steadily increasing, with sectors such as pharmaceuticals, information technology, and agriculture driving economic cooperation. Efforts are ongoing to further enhance trade relations between the two countries.
- Investment Opportunities: Ireland serves as a significant destination for Indian investments, particularly in sectors such as technology, pharmaceuticals, and renewable energy. Indian companies have made substantial investments in Ireland, contributing to economic growth and job creation.
- Education and Research Collaboration: There is a growing collaboration between Indian and Irish educational institutions, fostering student exchanges, joint research projects, and academic partnerships. This collaboration enhances cultural understanding and promotes academic excellence.
- Cultural Exchanges: Cultural exchanges between India and Ireland are promoted through various initiatives, including film festivals, art exhibitions, and literary events. These exchanges help strengthen people-to-people ties and promote cultural understanding.
- Diaspora Connections: The Indian diaspora in Ireland plays a significant role in strengthening bilateral relations by contributing to various fields such as business, academia, and culture. Cultural festivals and community events further enhance ties between the two countries.
- Multilateral Cooperation: India and Ireland cooperate closely on various multilateral platforms, including the United Nations, where both countries share common interests and collaborate on issues such as climate change, peacekeeping, and sustainable development.
- Tourism: Tourism between India and Ireland is growing, with travelers from both countries exploring each other’s rich cultural heritage, natural landscapes, and historical sites. Efforts to promote tourism and enhance connectivity contribute to deepening bilateral relations.
- People-to-People Contacts: Increasing people-to-people contacts through tourism, business delegations, and cultural exchanges serve as a foundation for strengthening India-Ireland relations. Regular interactions at various levels foster mutual understanding and goodwill between the two nations.
Source:
https://epaper.thehindu.com/reader
Mains Practice Question:
“Discuss the challenges and opportunities associated with India’s research and development (R&D) funding landscape, considering its comparative position globally and the role of government and private sectors. Assess the impact of recent policy initiatives on incentivizing R&D investment and fostering innovation for economic growth.”