LIGHT-EMITTING DIODES (LEDS): ILLUMINATING THE FUTURE
Focus: Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
Source: openworldlearning
What are LEDs ?
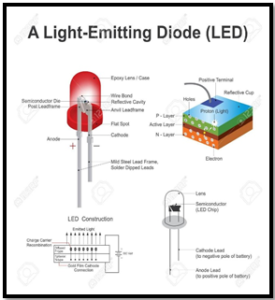
- Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are tiny semiconductor devices that convert electricity directly into light.
- Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are electronic components with a p-n junction that emits light when an electric current passes through.
- Electrons recombine with holes, releasing energy in the visible spectrum
Understanding Diodes:
- Diode Basics: Electronic component with anode and cathode, enabling one-way current flow via a p-n junction.
- P-n Junction: Interface of p-type (holes) and n-type (electrons) materials creating diode asymmetry.
- Diodes emit light due to electron-hole recombination.
- Band gap determines the energy emitted as visible light.
Advantages and Applications:
- More efficient, durable, and cost-effective than traditional bulbs.
- Applications range from smartphones to greenhouses.
- LEDs can produce various colours by combining red, green, and blue.
- Widely used in industry, electronics, and households.
- Replacing incandescent bulbs and fluorescent lamps.

 Source: openworldlearning
Source: openworldlearning

