LET US PROHIBIT UNSAFE CRACKERS IN ALL STATES
LET US PROHIBIT UNSAFE CRACKERS IN ALL STATES
Relevance: GS3– Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
Tags: #Pollution #Crackers #GS1 #GS3 #UPSC
Why in the News?
The Supreme Court declared that limitations on firecrackers extend beyond the Delhi-National Capital Region (NCR) and are applicable nationwide, emphasizing a comprehensive approach to regulate firecracker usage across the country.
What is Diwali and the use of Firecrackers?
- Diwali originates from the Sanskrit word “Deepavali,” translating to “row of lights.”
- The festival is symbolized by clay lamps, signifying inner light dispelling spiritual darkness.
- Inclusivity Across Religions: It is celebrated beyond Hinduism, with Jainism marking Lord Mahavira’s spiritual awakening. Sikhism commemorates Guru Hargobind Ji’s release, and Buddhists in India also partake in Diwali festivities.
- Cultural Practices: Common theme across celebrations is the triumph of good over evil. Festivities unite people, transcending geographical and cultural boundaries.
- History behind Firecrackers wrt Diwali:
- Post the discovery of gunpowder, fireworks were initially a luxury limited to the affluent or royalty.
- During the Mughal era, fireworks symbolized prosperity and grandeur, reserved for special occasions. Maratha rulers are believed to have organized fireworks for the general public during this period.
- After India gained independence, the manufacturing of firecrackers by Indian industries began. This era witnessed the popularization of firecrackers among the general public during festive celebrations.
Impact of Diwali Fireworks on Air Quality
- Concentration of PM2.5 Particles: A report by the Centre for Science and Environment noted a consistent rise in PM2.5 particles during Diwali in each of the last four years leading up to 2021. Larger fireworks tend to contribute more PM2.5 particles.
- Increased levels of PM10 particles, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, ozone, iron, lead, manganese, copper, beryllium, nickel were observed during Diwali.
- The Central Pollution Control Board lists 15 hazardous and toxic substances in fireworks. Some Indian states have banned fireworks during Diwali, but enforcement has been weak.
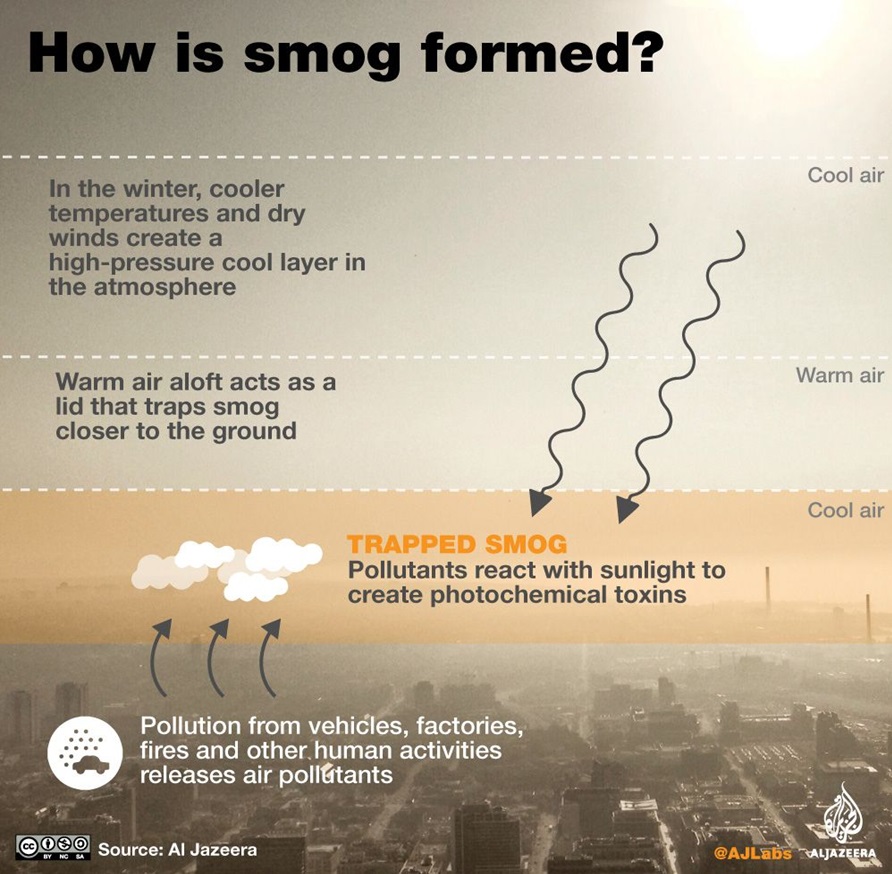
What is Smog?
- Smog is a mixture of smoke and fog.
- Today’s prevalent type is photochemical smog, formed when sunlight reacts with nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
- Components of Photochemical Smog
- Nitrogen oxides, from sources like car exhaust, coal power plants, and factories.
- VOCs released from gasoline, paints, and cleaning solvents.
- Sunlight triggers a reaction, forming airborne particles and ground-level ozone, constituting photochemical smog.
- Geographical Factors Influencing Smog
- Common in big cities with high industrial activity and traffic.
- Cities in basins surrounded by mountains may experience trapped smog due to geographical features hindering wind dispersion.
- Health Impact
- Ground-level ozone poses health risks, damaging lung tissue and causing eye irritation, especially for those with respiratory illnesses.
- Detrimental effects on plant life and contributes to an unsightly brown or gray sky.
- The correlation between Diwali celebrations and smog formation underscores the need for sustainable and responsible festivities.
Year-round Celebration with Firecrackers
- Firecrackers are not limited to festive seasons; they are used in various celebrations like sports victories, birthdays, weddings, and even funerals.
- The diverse occasions for firecracker use pose a continual threat to public health and the environment.
- Health Hazards Beyond Festivities
- Short-term exposure to chemical-laden firecrackers leads to lung diseases, asthma, and acute bronchitis.
- Individuals with heart diseases face an elevated risk of heart attacks and arrhythmias due to firecracker smoke.
- Distress in Animals: High-decibel crackers cause distress not only in humans but also in animals.
- Contribution to Air Pollution:
- Live Air Quality Index (AQI) data reveals alarming pollution levels, with eight of the world’s ten most polluted cities located in India.
- Delhi, ranking fourth globally, records an AQI more than ten times the country’s accepted safe level in recent days.
- State Initiatives to Control Hazardous Firecrackers: Karnataka State Pollution Control Board and the GST Council set up check-posts to prevent the entry of harmful firecrackers.
- This proactive approach needs replication across all states to create a comprehensive regulatory framework.
- To curb harmful firecracker usage a multi-faceted approach is needed. From legal measures to public awareness and sustainable alternatives, addressing this issue requires a concerted effort from various stakeholders.
Green Firecrackers
- They are characterized by Reduced shell size, elimination of ash, and minimized raw material usage. They utilize additives as dust suppressants to reduce emissions, particularly particulate matter (PM).
- Excludes barium compounds known for contributing to air and noise pollution and responsible for their distinctive green hue.
- Green crackers incorporate dust suppressants, minimizing emissions during ignition.
- Upon ignition, green crackers produce water vapor. This water vapor significantly reduces dust emissions, contributing to a cleaner environment.
- They generate noise ranging from 110 to 125 decibels which is notably lower than traditional firecrackers (160 decibels), resulting in nearly 30% less noise.
- Identifying green firecrackers involves recognizing the CSIR-NEERI and PESO green logo, accompanied by a QR code.
- They are categorized into SWAS, STAR, and SAFAL
- SWAS (Safe Water Releaser): Emits water vapor to minimize dust, reducing particulate matter by 30%, devoid of sulfur and potassium nitrate.
- STAR (Safe Thermite Cracker): Contains no potassium nitrate or sulfur, resulting in lower particulate matter emissions and reduced sound levels.
- SAFAL (Safe Minimal Aluminum): Uses less aluminum, more magnesium, producing less noise compared to traditional firecrackers.
Ineffectiveness of ‘Green’ Firecracker Appeals
- Persistent bursting of ear-shattering and health-hazardous firecrackers despite regulatory efforts. Challenges in enforcement highlight the gap between legislation and effective implementation.
- Multiple court rulings have targeted firecrackers due to their role in air and noise pollution and orders promoting ‘green’ firecrackers.
Recommendations for Mitigation
- Strict enforcement of restrictions on hazardous firecrackers is imperative to safeguard public health. Policymakers should consider more stringent regulations and penalties for violating firecracker restrictions.
- Comprehensive awareness campaigns should educate the public on the health and environmental consequences of firecracker use.
- Role of Education and Schools: Integrating education on the hazards of firecrackers into school curricula. Fostering a sense of responsibility among students to discourage firecracker use and promote sustainable celebrations.
- Sustainable Celebrations: Promoting alternative, less harmful ways to celebrate events, reducing the reliance on firecrackers.
- Public-Private Partnerships for Change: Collaboration between government agencies, private sectors, and NGOs to drive collective action against hazardous firecrackers.
- Incentivizing businesses to invest in and promote eco-friendly alternatives.
- Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation: Establishing mechanisms for continuous monitoring of air quality and health impacts related to firecrackers. Regular evaluations of the effectiveness of implemented measures to adapt strategies accordingly.
- Community Participation: Encouraging community-led initiatives to raise awareness and advocate for responsible celebration practices.
- Grassroots Initiatives: Empowering local communities to enforce regulations and ensure compliance.
Source:
- https://www.newindianexpress.com/opinions/editorials/2023/nov/10/let-us-prohibit-unsafe-crackers-in-all-states-2631597.html
- https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/smog/
- https://www.bbc.com/news/world-46138064
- https://www.cnbctv18.com/india/diwali-2022-is-bursting-firecrackers-a-diwali-tradition-14946691.htm
- https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/karnataka/what-are-green-firecrackers-and-how-to-recognise-them/article67505393.ece
Mains Question
How can a nationwide prohibition on unsafe firecrackers be effectively implemented across all states in India? Analyze its regulatory challenges. (250 words)