LEAN INTO THE LEVANT, DELHI
(INDIA’S STRATEGIC STAKES IN WEST ASIA)
Syllabus:
GS 2:
- India and its Neighborhood- Relations.
- Effect of Policies and Politics of Developed and Developing Countries on India’s interests.
Focus:
- The editorial “Lean Into the Levant, Delhi” emphasizes India’s increasing involvement in the conflict in West Asia and the need for strategic engagement with Iran and Israel.
Source: The Economist
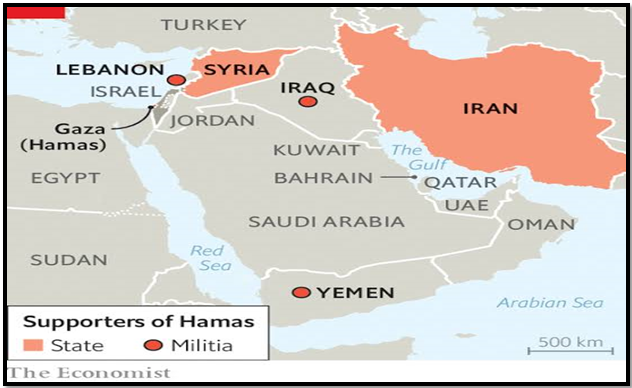
Understanding Israel Iran Relation:
- Historical Alliance: Israel and Iran were allies since the 1950s under Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi’s rule.
- Early Relations: Before the alliance’s collapse, the Shah’s envoy visited Israel in 1977, signing “oil for arms” contracts and initiating a military co-production line involving missile technology transfer from Israel to Iran.
- Shift in Alliance: The alliance ended abruptly in 1979 with Iran’s Islamic Revolution, leading to a stridently anti-Israel stance by the new leadership.
- Anti-Israel Stance: Iran denounced Israel as a regional colonial entity and supported organizations like Hamas and Hezbollah, known for their opposition to Israel.
- Nuclear Threat Perception: Israel perceives Iran’s nuclear weapons development as a threat to its survival, leading to suspicions of Israeli involvement in sabotaging Iran’s nuclear program.
- Shadow War: The Iran-Israel proxy conflict, lasting over three decades, involves threats from Iran’s leaders to destroy Israel, supporting labeled terrorist organizations, and engaging in a broader geopolitical struggle.
- Israel’s Defensive Measures: Due to Iran’s hostility, Israel takes precautions against Iran’s nuclear and missile programs, working to counter Iranian proxies and influence in Syria, a sworn enemy of Israel.
- Missile Deal: Israel agreed to provide Iran with ballistic surface-to-surface missiles with a 700 km range and a nuclear warhead as part of the military co-production agreement.
| Case Study : Octopus Doctrine
Origin of the “Octopus Doctrine”: · Coined by former Israeli Prime Minister Naftali Bennett. · Advocates striking the head of an octopus rather than its tentacles. Meaning of the Doctrine: · Refers to targeting Iran (the head) rather than its proxies in places like Syria, Lebanon, Gaza, and Iraq (the tentacles). Connection to Policy Shift: · Reflects a shift towards a more aggressive policy approach. · Failure to revise or renew the “Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action” aligns with this approach. · The JCPOA aimed to prevent Iran from acquiring nuclear weapons. |
India’s Role in Mitigating Conflict:
- Historically, India has played a role in managing tensions in West Asia through diplomatic efforts and humanitarian aid.
- However, recent developments, including terror attacks and disruptions to regional connectivity projects, have heightened India’s security concerns and economic interests in the region.
- The Indian Prime Minister’s discussions with key regional players, including the UAE and Iran, underscore India’s commitment to promoting peace and stability in West Asia.
- India recognizes the importance of engaging with Iran to address security threats and safeguard its economic interests in the region.
The Role of External Actors
China’s Position:
- China’s reluctance to intervene in the conflict reflects its policy of non-confrontation and disengagement.
- While China may benefit from US discomfort, its stance limits its potential contribution to resolving the crisis.
India’s Position:
- India’s willingness to respond militarily to threats against its ships demonstrates its commitment to safeguarding its energy security and economic interests.
- India’s clear message to Iran underscores the importance of maintaining stability in the region for mutual benefit.
Challenges :
- Iran’s geopolitical significance and radical ideology pose challenges to regional stability.
- The collapse of the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) and Iran’s nuclear ambitions raise concerns about its destabilizing actions in the region.
| Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA)
Negotiation Process: · Also known as the 2015 Iran Nuclear Deal. · Negotiated between Iran and P5+1 (China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, the United States + Germany) from 2013 to 2015. Iran’s Commitments: · Iran agreed to significant reductions in centrifuges, enriched uranium, and heavy-water stocks, crucial for nuclear weapons. · Implemented a protocol allowing IAEA inspectors access to nuclear sites to prevent secret weapon development. Sanctions Relief: · Western countries lifted sanctions related to Iran’s nuclear activities. · Sanctions on human rights abuses and Iran’s ballistic missile program remained. · The US lifted sanctions on oil exports but maintained restrictions on financial transactions, hindering international trade. Economic Impact: · Iran’s economy stabilized after years of recession, currency depreciation, and inflation. · Exports increased substantially after the deal’s implementation. US Withdrawal: · In 2018, the US abandoned the deal and reinstated banking and oil sanctions. · Iran responded by ramping up its nuclear program, regaining about 97% of its pre-2015 nuclear capabilities. |
Way Forward:
- Regional powers must take the lead in finding lasting solutions to the conflict in West Asia.
- Outsider-imposed solutions are no longer viable, and the withdrawal of the US from the region necessitates greater regional cooperation.
- India must step up its diplomatic efforts and collaborate with diverse stakeholders to mitigate the conflict’s humanitarian and security implications.
- India’s engagement with Qatar, a key mediator with influence in Iran, holds promise for advancing regional peace initiatives.
- As a key stakeholder in West Asia, India must actively engage with regional powers to promote peace and stability.
- By leveraging its diplomatic ties and advocating for multilateral solutions, India can contribute to resolving the conflict and safeguarding its strategic interests in the region.
Conclusion
India’s engagement with Iran and other regional players demonstrates its commitment to pursuing a balanced and pragmatic foreign policy in West Asia.
Source:
Mains Practice Question:
Analyze India’s evolving role in the West Asia conflict, emphasizing its strategic engagement with Iran and Israel.

 Source: The Economist
Source: The Economist

