LAYING FOUNDATION FOR A DEVELOPED ECONOMY
Syllabus:
- GS 3 : Government Budgeting
Focus:
- India’s economic strategy, characterized by fiscal prudence and capital expenditure-led growth, has garnered global acclaim for its effectiveness in navigating economic challenges while fostering inclusive development.
- Emphasizing fiscal responsibility alongside strategic investments in infrastructure and human capital, India’s approach aims to create a conducive environment for sustainable economic growth.
Historical Growth Trajectory:
Mid-2000s:
- Indian GDP surged at a remarkable 9% annually in the mid-2000s, fueled by robust global trade growth.
- However, unsustainable factors like a financial sector bubble contributed to this growth.
Global Financial Crisis:
- Growth decelerated to 6% post the 2007-08 global financial crisis as world trade slowed down abruptly.
2012-15:
- GDP growth fell to around 4.5% by 2012-13, but subsequent years saw a jump due to a revision in GDP calculation methodology in 2015.
- Despite the revision, real growth didn’t improve significantly.
2016-2018:
- Growth faced headwinds from demonetization and GST rollout.
- The collapse of the finance-real estate bubble post the IL&FS bankruptcy further dampened growth, reducing GDP to 3.9% in the year preceding the pandemic.
Pre-Covid Years:
- Demand Weakness: Private corporate fixed investment plummeted from 17% of GDP in 2007-08 to 11% in 2019-20, indicating subdued demand.
- Fearful of job prospects, domestic consumers curtailed spending, while foreign demand for Indian goods remained limited.
Covid Years:
- Economic Volatility:
- Amid the pandemic, the economy witnessed sharp declines, modest recoveries, severe slowdowns, and sporadic rebounds from late 2022 onwards.
Budget Highlights
Source: India Technology News
- Assessing the post-Covid phase requires evaluating the average growth rate over the entire period.
- Demand Indicators:
- Private corporate investment further decreased to 10% of GDP in 2021-22, indicating lingering demand weakness.
- The annual growth rate averaged around 4.2% over the latest four quarters compared to just over 2% when comparing the latest quarter pre-Covid.
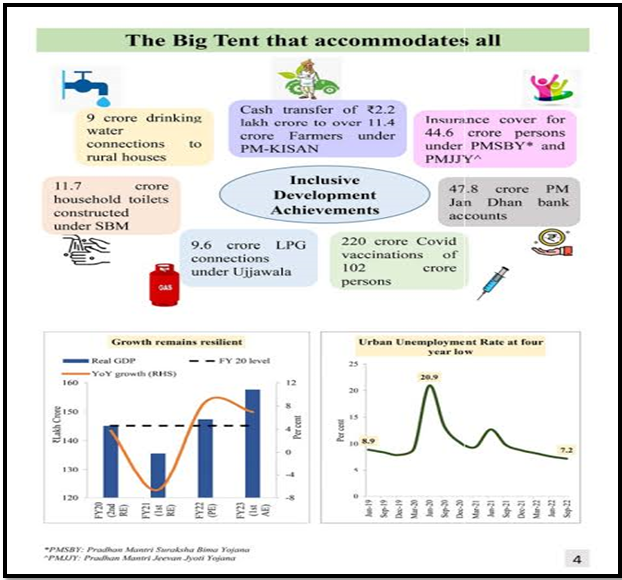
Welfare Paradigm Shift:
- India’s welfare programs have undergone a significant transformation, shifting from targeted interventions to universal access to basic amenities and services.
- By adopting a citizen-centric approach, India’s welfare initiatives prioritize the provision of essential services such as housing, electricity, healthcare, and education to all citizens, regardless of socio-economic status.
Budget Alignment with Expectations
- Confederation of Indian Industries (CII) Expectations:
- The CII’s expectations for the interim budget centered around fiscal discipline, investments in critical infrastructure, and measures to address socio-economic disparities.
- Anticipating a proactive approach to bolster economic resilience and foster inclusive growth, the CII sought initiatives aimed at supporting vulnerable segments of society while promoting long-term economic sustainability.
- Budgetary Outcomes:
- The interim budget’s alignment with the CII’s expectations underscores the government’s commitment to prudent fiscal management and inclusive development.
- With a focus on increasing capital expenditure and supporting key sectors, the budget reflects a comprehensive strategy to stimulate economic growth while addressing socio-economic challenges.
Capex Boost and Economic Resilience
- Significance of Capital Expenditure (Capex):
- Capital expenditure (capex) plays a pivotal role in driving economic growth by enhancing productive capacity, improving infrastructure, and fostering innovation.
- By prioritizing investments in infrastructure, healthcare, education, and technology, India aims to strengthen its economic foundation and enhance long-term competitiveness.
- Impact on Economic Resilience
- The emphasis on capex in the interim budget is expected to have a multiplier effect on economic resilience by stimulating demand, creating employment opportunities, and enhancing productivity.
- Through strategic investments in critical sectors, India seeks to build a robust economic framework capable of withstanding external shocks and fostering sustained growth.
Industry Support and Sustainability Focus
- Industry Stimulus Measures:
- The interim budget includes measures to support industries through access to credit, technology adoption, and regulatory reforms.
- By facilitating an enabling environment for businesses to thrive, India aims to promote entrepreneurship, innovation, and competitiveness in the global market.
- Sustainability Initiatives:
- Recognizing the importance of environmental sustainability, the budget allocates resources to promote renewable energy, enhance eco-friendly practices, and address climate change.
- Through investments in clean energy infrastructure, conservation initiatives, and green technologies, India demonstrates its commitment to building a sustainable future for generations to come.
| Understanding the Budget
The Union Budget is India’s annual financial statement presented on February 1st by the Finance Minister in the Lok Sabha. Budget Preparation: The Department of Economic Affairs, Ministry of Finance, prepares the Budget document. Budget Classification: · Revenue Budget: Covers expected income and expenses within a year, including taxes and regular sources of revenue. · Capital Budget: Manages government assets and liabilities, including major expenses like infrastructure development. Budget Parts: · Part A: Announces government schemes, priorities, and sector allocations. · Part B: Contains the Finance Bill, including taxation proposals like income tax revisions and indirect taxes. The Finance Bill is considered a Money Bill under Article 110 of the Constitution, subject to the Speaker’s approval. Constitutional Provisions Related to India’s Union Budget: · As per Article 112, the Union Budget is the government’s estimated receipts and expenditures, termed the Annual Financial Statement. · Key Budget documents include the Annual Financial Statement, Demands for Grants, Finance Bill, and Fiscal Policy Statements mandated by the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act (FRBM Act), 2003. · Additional explanatory documents presented include Expenditure & Receipt of Budget, Expenditure Profile, Budget at a Glance, and more. Objectives of Union Budget: · Economic Growth: Stimulate rapid and balanced economic growth nationwide. · Social Justice and Equality: Promote social justice and equality, ensuring equitable distribution of benefits. · Resource Allocation: Allocate resources effectively to minimize unemployment and poverty. · Fiscal Stability: Maintain fiscal stability by controlling prices, reducing wealth and income disparities, and reforming the tax system. |
India’s interim budget reflects a strategic vision aimed at laying the foundations for a developed economy characterized by fiscal stability, inclusive growth, and environmental sustainability. By prioritizing investments in critical sectors, supporting vulnerable populations, and promoting innovation, India reaffirms its commitment to building a resilient and prosperous nation.
Source:
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss India’s economic trajectory from the mid-2000s to the post-Covid era, analyzing the factors influencing growth and the role of fiscal policies.

 Source: India Technology News
Source: India Technology News

