ISRO’S XPOSAT LAUNCH: UNVEILING X-RAY POLARIMETRY
Why in the News?
- India launched its first mission of the year , the C-58 ISRO’S XPoSat.
XPoSat Mission Overview:
- XPoSat, ISRO’s latest mission, is the world’s second dedicated satellite for X-ray polarimetry, following NASA’s IXPE.
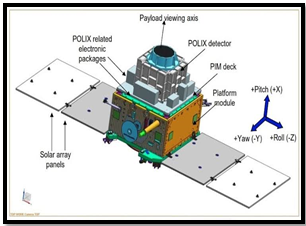
- Launched from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, it aims to study X-ray emissions from celestial sources, using two payloads: POLIX and XSPECT.
Source: ISRO
Payloads and Significance:
- POLIX, a medium X-ray instrument, measures polarisation in the 8-30 keV energy band, observing sources like black holes.
- XSPECT, focusing on soft X-rays (0.8-15 keV), targets diverse cosmic entities such as X-ray pulsars and magnetars.
- XPoSat’s significance lies in pioneering X-ray polarisation measurements, offering new insights into celestial processes.
About XPoSat:
- XPoSat, signifies India’s ground-breaking polarimetry mission.
- Objective: The mission’s primary objective is to investigate the diverse dynamics of astronomical sources under extreme conditions.
- XPoSat carries two significant payloads:
- POLIX (Polarimeter Instrument in X-rays) developed by the Raman Research Institute
- XSPECT (X-ray Spectroscopy and Timing) by the Space Astronomy Group of URSC, Bengaluru.
- Globally, it marks the second X-ray polarimetry mission, following NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) launched in 2021.
- XPoSat is a collaborative effort between ISRO and the Raman Research Institute (RRI) located in Bengaluru, Karnataka, showcasing joint expertise in space exploration and research.
| What is X-ray Polarisation?
· X-rays, consisting of electric and magnetic waves, are typically disorganized in motion. · Polarised X-rays occur when emitted by celestial sources like black holes. · During passage through materials, scattered photons change direction, and the resulting photon becomes polarised. · Polarisation measurements offer insights into the nature of X-ray-emitting sources and their complex radiation processes.. |

 Source: ISRO
Source: ISRO

