ISRO’s Indigenous Stellite Nozzle Cuts Import Costs
ISRO’s Indigenous Stellite Nozzle Cuts Import Costs
Why in News ?
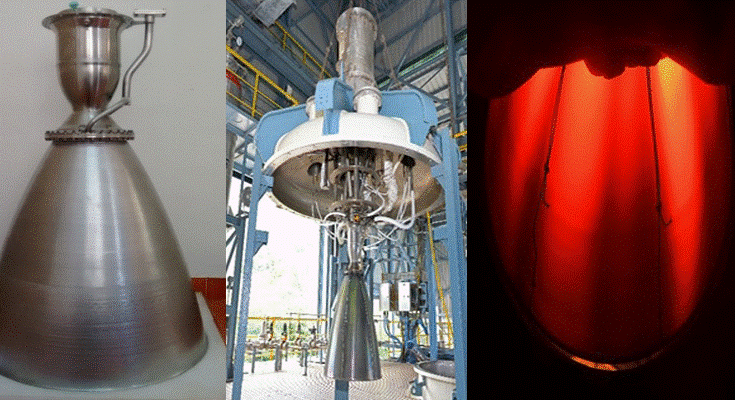
ISRO has successfully developed an indigenous Stellite nozzle divergent for the PSLV’s fourth stage, replacing imported Columbium and reducing costs by 90%. The component passed its final hot test on April 8 at Mahendragiri, Tamil Nadu.
Indigenous Material Breakthrough for PSLV:
- ISRO has developed a Stellite-based nozzle divergent for the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), replacing imported Columbium material.
- Stellite, a cobalt-based alloy with Chromium, Nickel, Tungsten, and Iron, offers high-temperature strength up to 1150°C.
- This move boosts ISRO’s Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliance) mission in space hardware.
Successful Testing Milestone at Mahendragiri:
- The nozzle underwent three rounds of prior testing and passed a final hot test lasting 665 seconds on April 8.
- Tests were conducted at ISRO Propulsion Complex (IPRC) in Mahendragiri, Tamil Nadu.
- The indigenous nozzle will cut import costs by 90%, enhancing both cost-efficiency and strategic independence.
Strengthening Human Spaceflight Program
- ISRO also successfully tested the human-rated Vikas Engine, designed for the Gaganyaan mission.
- The LVM-3 G launch vehicle will use two Vikas engines to carry astronauts to space.
- The engine honors Vikram Sarabhai, the pioneer of India’s space journey.
What is Nozzle Divergent ?● The nozzle divergent is the expanding section of a rocket nozzle that boosts gas flow to supersonic speeds, increasing thrust. ● It is part of the Convergent-Divergent (CD) nozzle structure: ○ Convergent: Narrows for speed increase. ○ Throat: Gas reaches Mach 1. ○ Divergent: Expands to produce maximum thrust. Stellite Nozzle Divergent Innovation ● ISRO developed a Stellite-based nozzle (KC20WN), replacing costly imported Columbium. ● Stellite withstands temperatures up to 1150°C. ● Testing: 3 preliminary hot tests + 1 final 665-second test (April 8, 2025). ● Achieves 90% cost savings. |