INNOVATION TO BRIDGE THE PENSION DIVIDE
Relevance:
GS 2
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Why in News:
- There have been debates on the Old Pension Scheme and the NPS.
Source- HDFC
The quest for a secure retirement plan transcends societal and economic boundaries, affecting everyone from the local chaiwala to the corporate executive. The National Pension System (NPS) offers a solution but is fraught with complexity and uncertainty. This analysis explores innovative solutions to make retirement planning accessible and predictable for all, spotlighting the potential of inflation-linked, deferred-income, annuity-like securities (InDIAS) as a transformative tool.
| What is InDIAS
InDIAS, or Inflation-Linked, Deferred-Income, Annuity-Like Securities, are government-issued financial instruments designed to provide individuals with a secure and predictable retirement income that is protected against inflation. They simplify the retirement planning process by linking current savings directly to future, inflation-adjusted income, ensuring financial stability and predictability for retirees. InDIAS offers an accessible and straightforward solution for retirement savings, catering to both financially sophisticated individuals and those with minimal financial knowledge. |
The Challenge of Current Pension Systems
- Complexity in Planning: Traditional pension systems, like the NPS, require individuals to navigate complex calculations to forecast retirement savings, making it challenging for the average person to plan effectively.
- Market Volatility: Pension schemes tied to market performance, such as the NPS, expose individuals to significant financial risk, including the impact of inflation and interest rate fluctuations, which can erode the value of their retirement savings.
- Lack of Predictability: Unlike the OPS, which offered predictable and indexed benefits, current systems fail to provide a clear picture of future financial standing, making it difficult for individuals to plan for a certain standard of living in retirement.
- Inflation Risk: Current pension schemes do not adequately protect against inflation, risking a decrease in purchasing power and living standards for retirees over time.
- Accessibility Barriers: The complexity and eligibility criteria of existing pension systems can be prohibitive for informal sector workers, leaving a significant portion of the workforce without adequate retirement planning options.
- Inadequate Financial Inclusion: The reliance on financial literacy and access to banking services as prerequisites for participation in current pension schemes limits their reach, excluding those most in need of secure retirement planning solutions.
Simplicity and Security with InDIAS
- Ease of Understanding: Designed for straightforward access, these government-issued instruments link savings directly to retirement income goals.
- Inflation and Standard-of-Living Adjustments: InDIAS addresses key concerns by offering inflation-protected payouts, ensuring real income remains constant throughout retirement.
- Predictable and Tailored Solutions: Offers a retirement income solution that is both predictable and customizable to individual financial needs.
Leveraging Digitalization for Inclusive Access
- Digital Ecosystem Integration: Capitalizes on India’s advanced digital payment infrastructure, including UPI, to facilitate easy access and transactions.
- Democratizing Investment: Enables small-scale investments, making it possible for individuals from all economic backgrounds to participate.
- Enhancing Financial Inclusion: Bridges the divide between the informal sector and formal financial systems, promoting broader financial participation.
Comparative Advantage Over Traditional Pension Schemes
- Simplification of Retirement Planning: Eliminates the need for complex calculations, offering a straightforward path to retirement security.
- Defined-Benefit Plan Assurance: Provides a government-guaranteed income in retirement, devoid of market and economic risks.
- Economic Stability Contribution: Supports a diversified and stable government debt structure, benefiting the broader economy.
- Encourages Long-Term Savings: By offering a secure and predictable retirement plan, it motivates individuals to engage in long-term savings behavior.
- Promotion of Sustainable Investing: InDIAS encourages investments that are sustainable over the long term, aligning with national economic goals.
- Risk Mitigation for Retirees: Offers a safeguard against the financial uncertainty that plagues traditional pension schemes, ensuring a stable retirement phase.
Impact and Adoption: Insights from Brazil’s RendA+ Experience
- First-Time Investor Attraction: Brazil’s RendA+ has successfully engaged a new demographic of investors, showcasing the potential for InDIAS to do the same in India.
- Enhanced Savings Behavior: The introduction of RendA+ led to improved savings habits among Brazilians, indicating a similar positive outcome could be expected with InDIAS adoption.
- Promotion of Financial Inclusion: The success of RendA+ in Brazil highlights how InDIAS could significantly enhance financial inclusion in India by reaching underserved populations.
- Expansion of Investor Base: By attracting first-time and small-scale investors, InDIAS has the potential to broaden India’s investor base, similar to the impact observed with RendA+ in Brazil.
- Infrastructure Financing: The adoption of InDIAS, inspired by RendA+’s model, could secure long-term funds for critical infrastructure projects in India, leveraging the increased demand for government securities.
- Model Viability Confirmation: The achievements of RendA+ confirm the viability of inflation-protected, deferred-income securities in fostering a culture of investment and savings, setting a precedent for InDIAS in India.
InDIAS presents a groundbreaking opportunity for India to revolutionize its approach to retirement security. By offering a low-cost, accessible, and predictable path to retirement income, it addresses the needs of the most vulnerable while supporting national economic goals. The government’s swift action can reduce the cost of securing a dignified retirement for all citizens, paving the way for a more inclusive and prosperous future.
Comparison between the Old and New Pension Systems
Old System: · Under the old system, government employees at both the central and state levels received a pension fixed at 50% of their last drawn basic pay. New System: · The new pension system was implemented for government employees joining services from January 1, 2004. · It introduced an assured or ‘defined’ benefit to the retiree, making it a ‘Defined Benefit Scheme.’ · For example, if a government employee’s basic monthly salary at retirement was Rs 10,000, they would be assured a pension of Rs 5,000. · Monthly pension payouts increased with hikes in dearness allowance (DA) announced by the government for serving employees. Dearness Allowance (DA): · DA is calculated as a percentage of the basic salary. · It serves as an adjustment offered by the government to employees and pensioners to offset the rising cost of living. · DA hikes are typically announced biannually, usually in January and July. |
Source
The Hindu
Mains Question
Assess the potential of Inflation-Linked, Deferred-Income, Annuity-Like Securities (InDIAS) in addressing the challenges of pension planning in India. Discuss the advantages and possible impacts on financial inclusion and the economy.

 Source- HDFC
Source- HDFC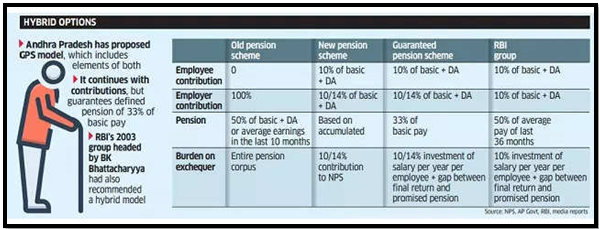 Source:- Economics Times
Source:- Economics Times

