INDIA’S HUNGER DECLINES, HEALTHY DIETS STILL UNAFFORDABLE
Why in the news?
India’s hunger declines, but a UN report highlights high costs of healthy diets and rising obesity due to junk food consumption.
 source:medium
source:medium
Government Efforts and Health Impact:
- World’s largest free food program: 5 kg cereals to 810 million people monthly.
- School meal programs vary by state (e.g., eggs daily in Tamil Nadu, none in Uttar Pradesh).
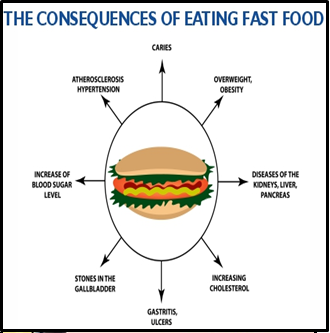
- Unhealthy diets cause over half of India’s disease burden (National Institute of Nutrition).
- Processed food is a major expense for families.
About Obesity:
- Definition: Excess body fat impairing health; chronic condition.
Causes:
- Imbalance of energy intake and expenditure.
- Genetic, cultural, and societal factors.
- Reduced physical activity, insomnia, endocrine disorders, certain medications.
- High carbohydrate and sugar intake, decreased energy metabolism.
- Measurement: BMI over 25 (overweight), over 30 (obese).
- Health Risks: Cardiovascular disease, diabetes, stroke, gallstones, fatty liver, sleep apnea, cancers.
- Treatment: Requires multipronged, lifelong strategies.
- Impact: Second leading preventable death cause after smoking.
Body Mass Index (BMI) Explained
- BMI = weight (kg) / height (m²)
- Example: BMI of 25 means 25 kg/m²
- Ideal BMI range for adults: 18.5 to 24.9
- High BMI indicates high body fatness
- Screens for weight-related health issues, not body fat or health diagnosis
Associated Article:
https://universalinstitutions.com/global-hunger-index-highlights-indias-malnutrition-challenge/ |
source:medium