INDIA’S FISCAL PERSPECTIVE – A NUANCED APPROACH
Focus:
- Traditional rigid fiscal targets are losing credibility worldwide.
- Finance Secretary emphasizes a more nuanced and realistic approach to debt sustainability.
About the Fiscal Outlook:
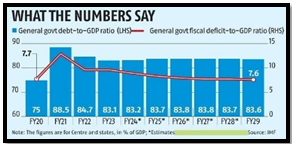
- India’s high growth trajectory enables a gradual decline in debt-to-GDP ratio.
- Inflationary risks persist, requiring a delicate balance between growth and managing price rise concerns.
- The pre-pandemic goal of reducing Central government debt to 40% of GDP needs recalibration.
- Advocates a gradual decline in debt-to-GDP ratio, considering India’s favorable growth-rate interest-rate differential.
| Key Term
Debt-to-GDP ratio:
· The Debt-to-GDP ratio measures a country’s total debt relative to its gross domestic product (GDP). · It indicates the proportion of a nation’s economic output that is owed as debt. · A higher ratio suggests a heavier debt burden and may signal economic vulnerability if unsustainable. · According to the FRBM Act, the Debt-to-GDP ratio is targeted at approximately 60%; o 40% allocated for the Central Government and o 20% for the State Government. |

 Source: Business Standards
Source: Business Standards


