INDIA’S DEFENCE BUDGETING AND THE POINT OF DETERRENCE
Syllabus
- GS3 : Achievements of Indians in Science & Technology; Indigenization of Technology and Developing New Technology.
Why in the News?
- The Indian government faces a crucial challenge in balancing electoral promises with the nation’s defence needs.
- Budget constraints and the evolving security landscape necessitate a careful examination of defence allocations to ensure preparedness without compromising on affordability.
Source: CNBC Tv 18
Challenges in Defence Budget Allocation
MMRCA Programme Dilemma
- The Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft (MMRCA) program, labeled the ‘mother of all procurements,’ faced challenges with the purchase of 36 Rafale jets, falling short of the required 126.
- The decade-long delay and limited acquisition strain the Indian Air Force (IAF), contributing to a dismal squadron strength of 32.
Depleting Squadron Strength
- IAF Chiefs express concerns over depleting squadron strength, currently standing at 32 and projected to reach 35 in the next decade.
- This shortfall compromises India’s air defense capabilities.
Army and Navy Deficiencies
- Similar deficiencies plague the Indian Army and Navy, exacerbating national security concerns.
- Reports highlight major shortcomings, raising alarms about the overall preparedness of the country’s defense forces.
Electoral Imperatives and Budget Impact
- As India enters election mode, there’s apprehension that defence allocations in Budget 2024-25 might face cuts due to electoral sops.
- Such reductions could undermine India’s deterrence posture, crucial for maintaining national security and preparedness.
Source: TOI
Assessing Defence Priorities
Affordable Defence vs. Affordable Effectiveness
- The perennial challenge of the “guns versus butter” dilemma raises the question of whether the pursuit of ‘affordable defence’ or ‘affordable effectiveness’ should drive defence budget allocations.
- The recent decision by the Indian Air Force (IAF) to acquire 97 more Tejas Mk1A fighters, deviating from the planned 114 multi-role fighter aircraft, exemplifies this dilemma.
Budget Determining Defence Potency
- The dilemma arises: Should budget constraints dictate defense strength?
- Echoing General V.P. Malik’s Kargil conflict remark (“We will fight with what we have”), or should the imperative need for security determine budget allocations?
Northern Border Threat and Electoral Challenges
Dual Preparedness for Northern Borders
- Despite a seemingly calm western neighbor, the threat on India’s northern borders remains real.
- Dismissing their current stance as less risky is unwise.
- India must be ready for any scenario.
- Assessing how India plans to handle potential conflicts is crucial, especially during the current electoral climate.
Sea Power Accretion for Regional Deterrence
- Recognizing the critical need for sea power to deter China, especially in the Malacca Strait and Indian Ocean, underscores the necessity for budgetary focus on naval modernization.
- Simultaneously, the Indian Army, given its size, requires considerable budgetary support for modernization efforts.
Changing Military Strategies
Shift from Short Sharp Conflicts to Extended War Scenarios
- Pre-Russia-Ukraine war, the Indian military’s planning and budgeting centered around a short, sharp conflict.
- However, recent global events, particularly the Ukraine conflict, have prompted a shift in military leadership’s perspective towards envisioning extended war scenarios, demanding a reevaluation of military strategies.
Logistics and Industrial Base Considerations
- Insights from the article ‘You go to war with the industrial base you have, not the industrial base you want’ emphasize the importance of assessing logistics and industrial capabilities.
- Amidst the Atmanirbhar Bharat drive, understanding the practicalities of military engagements becomes vital.
Source: Mygov.in
The indigenous drive, R&D
Importance of Technological Modernization
- The armed forces’ constant need for technological modernization is indisputable.
- The development of a robust local defence industry is a prolonged process, requiring a delicate equilibrium between imports and indigenous advancements to ensure optimal potency.
Atmanirbhar Bharat Realities
- Despite the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative, a pragmatic assessment is crucial concerning the practicalities of the armament supply chain in the near to mid-term.
- The emphasis should be on realistic evaluations, moving beyond public relations narratives.
Stagnant Defence Budget
Stagnation in Real Terms
- India’s defence Budget, when adjusted for inflation, has remained relatively stagnant.
- The percentage of defence expenditure (revenue and capital) in the central government’s overall expenditure has dwindled, decreasing from 16.4% in 2012-13 to 13.3% in 2022-23.
- The shortfall in capital acquisitions funding, as seen in the 2023-24 budget, raises concerns.
Deficit in Capital Allocations
- Ministry of Defence requested ₹1,76,346 crore for capital acquisitions in 2023-24 but was allotted only ₹1,62,600 crore, resulting in a substantial deficit of ₹13,746 crore.
- This deficit jeopardizes critical modernization efforts.
R&D Challenges
Low R&D Expenditure
- India’s research and development expenditure, as highlighted by the Global Innovation Index 2022, is merely 0.7% of its GDP, ranking 53rd globally.
- In contrast, China allocated $421 billion in 2022, amounting to 2.54% of its GDP.
Positive Steps with iDEX Scheme
- The government’s focus on indigenization, particularly through the Innovations For Defence Excellence (iDEX) scheme and service-specific projects like the Baba Mehar Singh competition for unmanned aerial vehicles, is commendable.
- Allocating 25% of the R&D budget to the private sector is a positive step.
Long Gestation Period for Indigenization
Structural Changes and Negative Lists
- The restructuring of the Ordnance Factory Board and the formulation of negative lists for imports inspire confidence in the private sector for assured contracts.
- However, the drive towards indigenization still requires substantial time for fruition.
Sustaining Momentum
- The momentum toward indigenization must be sustained with a continuous policy approach and adequate defence budgeting.
- Making defence budgeting election-proof in a vibrant democracy necessitates bipartisan statesmanship to ensure a consistent and unwavering commitment to national security.
Assessing Adversarial Capacities
- It is crucial to gauge the capabilities of potential adversaries, avoiding overspending against a lesser threat.
- However, when faced with multiple militarily adept nations, like China and another formidable entity, India’s defense strategy should align with the evolving geopolitical scenario.
China’s Impact on Regional Dynamics
- China’s assertiveness has triggered significant responses, including Japan doubling its defense budget, increased arming of Taiwan, and a reshaping of regional alliances.
- The historic S.-South Korea-Japan summit further underscores the intensified focus on regional security.
National Security over Electoral Imperatives
- Amidst evolving geopolitical challenges, it is imperative to prioritize national security imperatives over electoral considerations.
- In the face of evolving threats, maintaining a robust defence budget is not just essential but a professional imperative.
| Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft (MMRCA) program
· A significant initiative by the Indian Air Force (IAF), was launched in 2007. Objectives of MMRCA program 1. Aircraft Replacement · The primary objective of the program is to replace aging MiG-21 and MiG-27 aircraft, which, despite their historical significance, have become technologically outdated, necessitating a modernized fleet. 2. Enhancing Air Superiority · The MMRCA program aims to enhance air superiority by equipping the IAF with fighter jets capable of deep penetration strikes, aerial refueling, and effective electronic warfare. 3. Technological Advancements · A key goal is to boost technological advancements within the IAF.
|
Source
https://www.thehindu.com/topic/rafale-deal/
https://carnegieendowment.org/files/dogfight.pdf
Mains Practice Question
Critically analyze the impact of electoral imperatives on India’s defence budget and national security goals. Discuss the challenges posed by the allocation of funds based on political considerations and suggest measures for maintaining effective deterrence capabilities

 Source: CNBC Tv 18
Source: CNBC Tv 18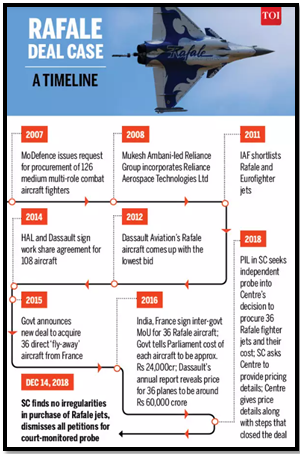 Source: TOI
Source: TOI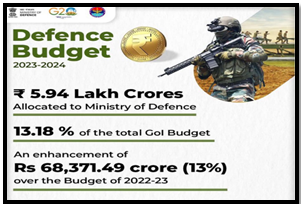 Source: Mygov.in
Source: Mygov.in

