INDIAN RAILWAYS AND SAFETY CHALLENGES
Syllabus:
GS 3:
- Disaster and Disaster Management
- Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways
Why in the News?
- The recent collision between a GFCJ container train and Kanchanjunga Express has spotlighted ongoing safety challenges within Indian Railways.
- This incident underscores the critical need for robust safety measures and effective management practices to prevent accidents and ensure passenger safety across the railway network.
Source: Edukemy
The Tragic Incident
- The GFCJ container train collision with the Kanchanjunga Express resulted in 11 deaths and around 40 injuries.
- Criticism arose regarding safety measures despite improvements in track maintenance and unmanned level crossing closures.
- Modern systems offer potential for zero-fatality records, a goal Indian Railways should actively pursue.
- Government’s substantial investment of nearly 25% of total capex to railways makes safety funding feasible.
- A statutory inquiry by the Commissioner of Railway Safety (CRS) is underway to determine accident cause and responsibility.
Information Management and Communication
- The premature declaration by the Railway Board Chairperson about the accident’s cause raised concerns.
- Slow rollout of the indigenous signalling system, Kavach, was attributed to limited industrial capacity.
- Delayed execution of safety projects like Kavach suggests a lack of focus on critical safety initiatives.
- Recommendations from previous CRS reports highlight the need for faster implementation of safety systems like Kavach.
- Ambiguity in protocol for station masters and crews during Automatic signal failure undermines safety procedures.
Staffing and Vacancies
- Indian Railways faces overstaffing issues but critical safety positions like loco crew and station masters are understaffed.
- Nearly 20,000 vacancies for loco pilots/assistant loco pilots indicate operational gaps despite recent recruitment efforts.
- Vacancy management impacts operational stress and safety, potentially contributing to accidents.
- Enquiry into whether the recent accident was isolated or part of systemic issues in affected sections is crucial.
- Utilization of AI-enabled applications for safety post-mortems and actionable alerts remains underutilized.
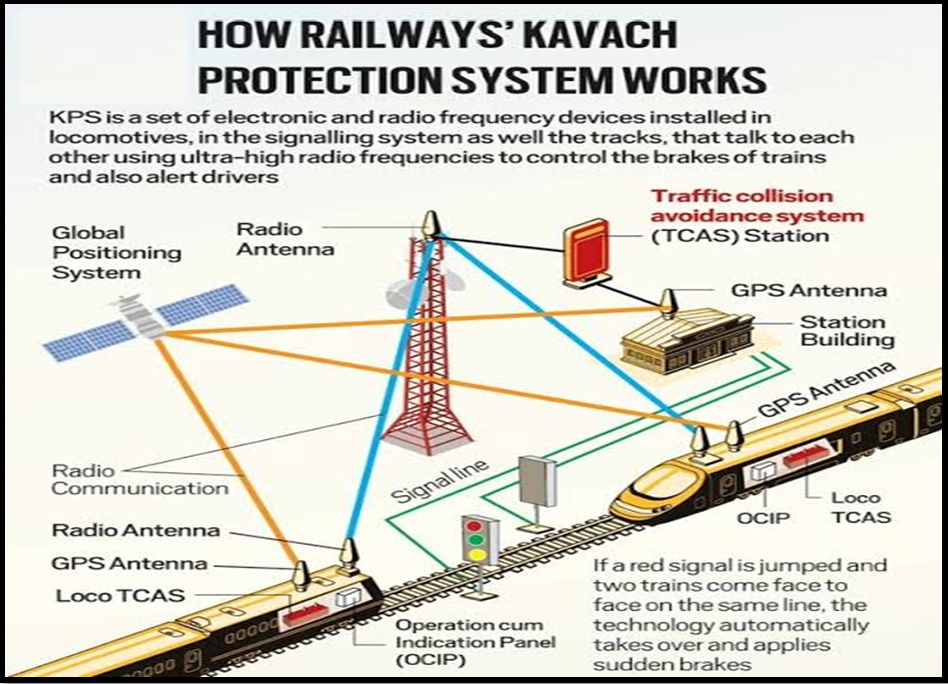
| About Kavach System
Indigenous Development: The Kavach System is an Automatic Train Protection (ATP) system developed indigenously by the Research Design and Standards Organisation (RDSO) under Indian Railways (IR), in collaboration with Medha Servo Drives Pvt Ltd, HBL Power Systems Ltd, and Kernex Microsystems. Functional Components:
Testing Phase:
Applications:
Kavach assists locomotive pilots in preventing Signal Passing At Danger (SPAD) and controlling train speeds to avoid overspeeding.
The system automatically halts trains if it detects another train within a specified distance on the same track, enhancing safety and preventing collisions.
It continuously relays signals to the locomotive, aiding pilots during low visibility conditions like dense fog.
Kavach intervenes by automatically applying brakes if the pilot fails to do so, ensuring prompt response in critical situations such as inclement weather. |
Challenges:
- Safety Infrastructure: Improving safety infrastructure remains paramount, including upgrading tracks, signals, and level crossings to prevent accidents.
- Modernization Delays: Delays in adopting modern technologies like the Kavach signalling system hinder progress towards safer operations.
- Staffing Shortages: Significant vacancies in critical roles such as loco pilots and station masters strain operational capacity and compromise safety.
- Communication Gaps: Inadequate communication protocols during emergencies and signal failures contribute to operational risks.
- Resource Allocation: Despite substantial funding, ensuring efficient resource allocation for safety enhancements remains a challenge.
- Management Oversight: Issues of managerial oversight and accountability need addressing to prevent recurrent safety lapses.
- Technological Integration: Integrating AI and digital solutions for real-time monitoring and decision-making requires robust implementation frameworks.
Path Forward
- The CRS enquiry report should address managerial issues to guide Indian Railways towards accident-free operations.
- Enhanced digital data management and AI applications can significantly improve safety monitoring and response.
- Clear directives from the enquiry are essential for charting a safer future for Indian Railways.
- Priority installation of safety systems like Kavach in high-risk areas should be accelerated.
- Commitment to comprehensive safety measures is imperative to restore public trust in Indian Railways.
- Training and Skill Development: Investing in comprehensive training programs for railway staff to enhance operational efficiency and safety awareness.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Launching campaigns to educate passengers about safety protocols and encourage adherence to rules while traveling.
- International Collaboration: Partnering with global railway networks to exchange best practices and implement advanced safety technologies effectively.
Conclusion
Addressing the challenges faced by Indian Railways demands a multi-faceted approach, including infrastructure upgrades, technological advancements, streamlined management, and enhanced safety protocols. By prioritizing these areas and fostering collaboration, Indian Railways can strengthen its operations and uphold its commitment to passenger safety.
Source:Indian Express
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the major challenges facing Indian Railways in ensuring passenger safety and operational efficiency. What measures should be taken to address these challenges effectively?
Associated Article:
https://universalinstitutions.com/railway-safety-and-accountability-in-india/